| [1] 方剑,沈幸,曾婷,等.复方麝香对小儿先天性心脏病体外循环术后认知功能障碍的影响[J].广东医学,2011,32(11):1484-1486.[2] 洪艳丽,蒋凤荣.人工麝香对过氧化氢造模的HUVEC保护作用机制研究[J].时珍国医国药,2011,22(2):402-404.[3] 穆融融,李海涛.人工麝香对体外培养的心肌细胞的保护作用[J].中药药理与临床,2011,27(3):56-58.[4] 段石顽,王欣,王斌,等.麝香?冰片?薯蓣皂苷及栀子苷对大鼠脑缺血再灌注急性期炎性损伤的保护作用[J].中药药理与临床,2012, 28(3):43-46.[5] 王洋,王建,班炳坤.麝香与冰片及其配伍对脑缺血缺氧小鼠模型的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2011,27(2):96-98.[6] 王丹丹,王建,彭颖,等.四味芳香开窍药的挥发性成分对缺血缺氧PC12细胞及细胞内Ca2+的影响[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2012,33(3):370-373.[7] 马丽锋,郝六平,李丽娟,等.麝香酮的药理与合成研究进展[J].河北化工,2010,33(2);11-14.[8] 邹亮,林俊芝,王战国,等.麝香酮在大鼠肠灌注液中GC-MS/MS测定方法及其大鼠肠吸收动力学特征[J].中国中药杂志,2012, 37(16): 2456-2460.[9] 谢兴文,侯费祎,李宁,等.不同浓度麝香酮对外源性骨髓间充质干细胞在体内迁移的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2012,32(7): 980-985.[10] 金合,李晋玉,俞兴,等.骨碎补总黄酮对颅骨缺损修复大鼠血清碱性磷酸酶、钙、磷的影响[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(9):757-760.[11] 侯费祎,谢兴文,席芳琴,等.Hoechst33342标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其在大鼠体内的迁移[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012, 18(7):618-622.[12] 孙蓉,张作平,黄伟,等.麝香酮对完全性脑缺血大鼠的保护作用[J].中药新药与临床药理,2009,20(3):197-200.[13] Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhyan RK, Gerasimov UV. Bone marrow osteogenic stem cells: in vitro cultivation and transplantation in diffusion chambers. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1987; 20(3):263-272.[14] 张俊山,田发明,张柳.骨髓间充质干细胞及其向神经元细胞分化的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2012,28(17):2974-2976.[15] Zhou HX,Liu ZG,Liu XJ,et al.Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation combined with hyperbaric oxygen treatment for repair of traumatic brain injury.Neural Regen Res.2016;11(1): 107-113.[16] 刘嘉祺,林峰,李孟全.骨髓间充质干细胞的培养及生物学特性[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2011,32(3):10-12.[17] 黄杨,尹文,刘健,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对急性百草枯中毒肺损伤的保护作用[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(5):751-754.[18] 郭希民,王常勇,王永红,等.人骨髓间充质干细胞分离培养及向软骨细胞定向分化的实验研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2003,38(1): 63-66.[19] 张亮,丁寅,邵金陵,等.骨髓间充质干细胞联合纤维蛋白胶修复大鼠牙槽骨缺损的研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2011,29(2): 125-128.[20] 罗庆,张晨,宋关斌.骨髓间充质干细胞旁分泌作用在组织损伤修复中的研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(5): 999-1002.[21] 孙蓉,张作平,黄伟,等.麝香酮对谷氨酸所致PC12细胞损伤的保护及作用机制研究[J].中国中药杂志,2009,34(13):1701-1704.[22] 孙蓉,张作平,黄伟,等.麝香酮对完全性脑缺血大鼠的保护作用[J].中药新药与临床药理,2009,20(3):197-200.[23] 吕丽莉,张作平,黄伟,等.麝香酮对局灶性脑缺血大鼠模型的保护作用及对BBB转运功能的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2009,25(2): 31-35.[24] 洪艳丽,蒋凤荣.麝香酮对氧化应激损伤人血管内皮细胞凋亡的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2011,26(9):2178-2180.[25] 侯费祎,谢兴文,席芳琴,等.麝香酮含药血清对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖?分化的影响[J].西安交通大学学报,2013,34(1): 110-114.[26] Friedenstein AJ. Precursor cells of mechanocytes. Int Rev Cytol. 1976;47:327-359.[27] 郭军,林国生,鲍翠玉,等.干细胞因子对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国医师杂志,2004,6(12):1601-1604.[28] 路娟英,高杰,麻丹丹,等.干细胞因子促进人乳牙牙髓干细胞增殖与向成骨方向分化[J].南方医科大学学报,2011,31(3):531-534.[29] 郭军,林国生,贾光宏,等.干细胞因子对骨髓间充质干细胞的促增殖?分化作用[J].中华心血管病杂志,2004,32(s1):857.[30] 王芳,李松英.干细胞因子对牙周膜细胞增殖分化能力的影响[J].浙江医学,2008,30(4):316-318.[31] 鲍翠玉,郭军,马业新,等.干细胞因子与粒细胞集落刺激因子预处理对大鼠骨髓间质干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2007,23(7):1363-1367.[32] Cho KA, Park M, Kim YH, et al. Th17 cell-mediated immune responses promote mast cell proliferation by triggering stem cell factor in keratinocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. in press. [33] Zhuo HL, Bai LP, Liu D, et al. Effects of retinol on expressions of epidermal growth factor, stem cell factor, colony-stimulating factor 1 and leukemia inhibitory factor in human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016;37(2):221-225.[34] Nam SY, Kim HY, Kim HM, et al. Βeta-eudesmol reduces stem cell factor-induced mast cell migration. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;48:1-7. [35] Leist M, Sünder CA, Drube S, et al. Membrane-bound stem cell factor is the major but not only driver of fibroblast-induced murine skin mast cell differentiation. Exp Dermatol. 2017; 26(3):255-262. [36] Fayazi M, Salehnia M, Ziaei S. The effect of stem cell factor on proliferation of human endometrial CD146(+) cells. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 2016;14(7):437-442. [37] Hao L, Hailun Z, Qi W, et al. Changes in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells osteogenesis by the regulation of Lnk/stem cell factor-cKit signaling. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015;33(6):633-637. [38] Wang L, Wang J, Li Z, et al. Silencing stem cell factor attenuates stemness and inhibits migration of cancer stem cells derived from Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(6):7213-7227. [39] Mahadik BP, Pedron Haba S, Skertich LJ, et al. The use of covalently immobilized stem cell factor to selectively affect hematopoietic stem cell activity within a gelatin hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2015;67:297-307. |
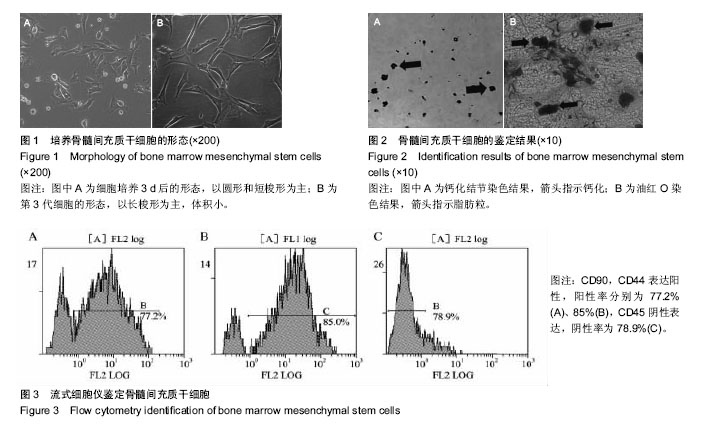
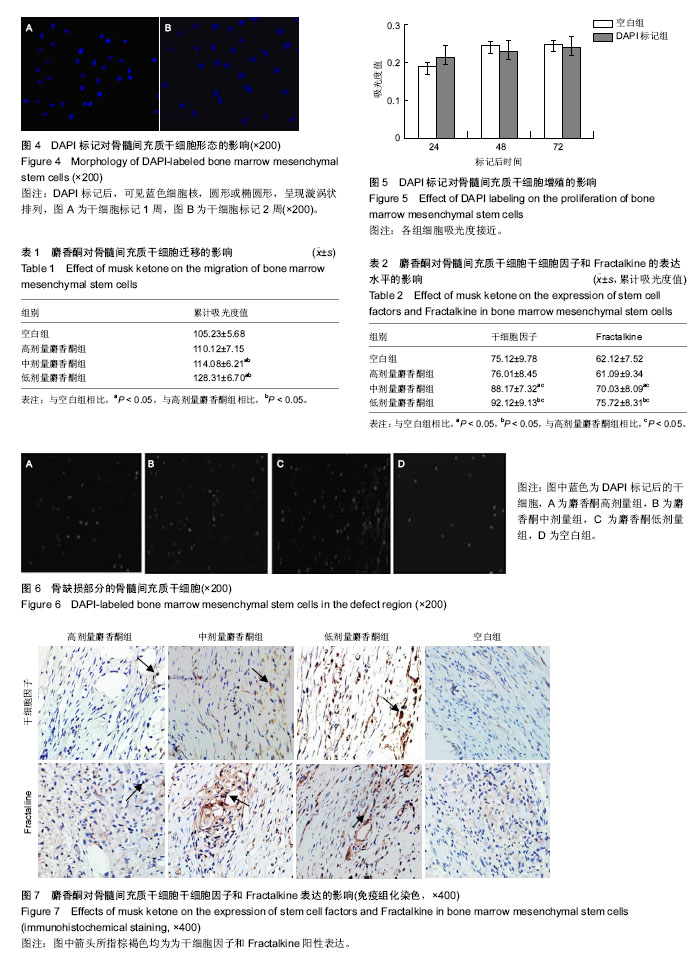
.jpg)
.jpg)