| [1] Caplazi P, Baca M, Barck K, et al. Mouse Models of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Vet Pathol. 2015;52(5):819-826.[2] Zhang WT, DU XK, Huo TL, et al. Combination of (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging is an optimal way to evaluate rheumatoid arthritisin rats dynamically. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013;126(19): 3732-3738.[3] 郭强,曹晓瑞,张大伟,等.二甲双胍对Ⅱ型胶原诱导类风湿性关节炎大鼠模型的抗炎及关节保护作用的研究[J].国际外科学杂志, 2014, 41(4):261-264.[4] Bartok B, Firestein GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255.[5] Bevaart L, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Tak PP. Evaluation of therapeutic targets in animal models of arthritis: how does it relate to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(8): 2192-2205.[6] Bendele A. Animal models of rheumatoid arthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2001;1(4):377-385. [7] Gauldie SD, McQueen DS, Clarke CJ, et al. A robust model of adjuvant-induced chronic unilateral arthritis in two mouse strains. J Neurosci Methods. 2004;139(2): 281-291.[8] Cai X, Zhou H, Wong YF, et al. Suppressive effects of QFGJS, a preparation from an anti-arthritic herbal formula, on rat experimental adjuvant-induced arthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;337(2):586-594.[9] 谢映梅.中药NDRF对佐剂性关节炎家兔血清炎性因子的影响及病理观察[D].遵义:遵义医学院, 2013.[10] Abd El-Rahman RS, Suddek GM, Gameil NM, et al. Protective potential of MMR vaccine against complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammation in rats. Inflammopharmacology. 2011;19(6):343-348.[11] Torres-Guzman AM, Morado-Urbina CE, Alvarado-Vazquez PA, et al. Chronic oral or intraarticular administration of docosahexaenoic acid reduces nociception and knee edema and improves functional outcomes in a mouse model of Complete Freund's Adjuvant-induced knee arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R64.[12] Gylys-Morin VM, Graham TB, Blebea JS, et al. Knee in early juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: MR imaging findings. Radiology. 2001;220(3):696-706.[13] 熊壮,余永强,吕益忠,等.佐剂性关节炎早期病变的X线位相对比成像研究[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2004, 8(8):471-475.[14] Hill CL, Schultz CG, Wu R, et al. Measurement of hand bone mineral density in early rheumatoid arthritis using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. Int J Rheum Dis. 2010;13(3):230-234.[15] Dey S, Jahan A, Yadav TP, et al. Measurement of bone mineral density by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Indian J Pediatr. 2014;81(2): 126-132.[16] Hashida R, Kobayashi S, Shirota H, et al. Stimulation of prostaglandin synthesis in cultured rat synovial cells by a factor derived from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Prostaglandins. 1984;27(5):697-709.[17] 贾红伟,赵宁,李艳,等.宣发膜原方对胶原免疫性关节炎大鼠关节滑膜细胞超微结构的影响[J]. 中医杂志, 2006, 47(4): 301-302.[18] 王俊伟,陈利锋,王丽平,等.一种实验兔膝关节滑膜组织提取新方法[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2016, 26(6):94.[19] Fidlerová H, Sovová V, Krekule I, et al. Immunofluorescence detection of the vimentin epitope in chromatin structures of cell nuclei and chromosomes. Hereditas. 1992;117(3):265-273.[20] Berg KD, Tamas RM, Riemann A, et al. Caveolae in fibroblast-like synoviocytes: static structures associated with vimentin-based intermediate filaments. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;131(1):103-114.[21] 熊建文,肖化,张镇西. MTT法和CCK-8法检测细胞活性之测试条件比较[J].激光生物学报, 2007, 16(5):559-562.[22] 马静,路琛,左丽,等. CCK-8法检测重组人白细胞介素-2的活性[J].贵阳医学院学报,2011,36(5):503-504,507.[23] Xing R, Jin Y, Sun L, et al. Interleukin-21 induces migration and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016;184(2): 147-158.[24] Zong M, Lu T, Fan S, et al. Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:100.[25] Abeles AM, Pillinger MH. The role of the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis: cartilage destruction and the regulation of matrix metalloproteinases. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2006;64(1-2):20-24.[26] Noss EH, Brenner MB. The role and therapeutic implications of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammation and cartilage erosion in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2008;223:252-270.[27] Kaneko K, Miyabe Y, Takayasu A, et al. Chemerin activates fibroblast-like synoviocytes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R158.[28] Liu FL, Wu CC, Chang DM. TACE-dependent amphiregulin release is induced by IL-1β and promotes cell invasion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2014;53(2):260-269.[29] 雍刘军.膝关节滑膜相关结构的解剖与影像学观测及临床应用研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学, 2011.[30] Ohata J, Zvaifler NJ, Nishio M, et al. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes of mesenchymal origin express functional B cell-activating factor of the TNF family in response to proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol. 2005;174(2): 864-870.[31] 李婷,戴冽,杨斌,等.改良组织块法培养细针活检滑膜组织成纤维样滑膜细胞[J].中山大学学报: 医学科学版, 2010,31(4): 567-571.[32] 李培培,解国雄,宋珊珊,等.大鼠佐剂性关节炎模型表现特征及评价指标[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2012, 28(5):453-457.[33] Fernandes ES, Russell FA, Alawi KM, et al. Environmental cold exposure increases blood flow and affects pain sensitivity in the knee joints of CFA-induced arthritic mice in a TRPA1-dependent manner. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:7.[34] Bonezzi FT, Sasso O, Pontis S, et al. An Important Role for N-Acylethanolamine Acid Amidase in the Complete Freund's Adjuvant Rat Model of Arthritis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016;356(3):656-663.[35] 平泽朋.膝关节滑膜淋巴孔及关节腔积液淋巴重吸收研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学, 2015.[36] 张晓明,陈飞虎,黄学应,等.佐剂性关节炎大鼠成纤维样滑膜细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].解剖学杂志, 2007, 30(6):770-773. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。
文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。.jpg) 文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。
文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。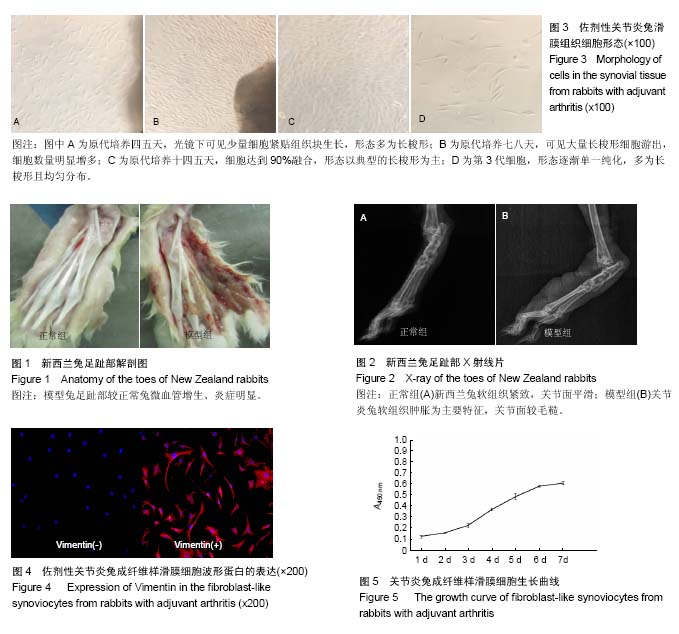
.jpg) 文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。
文题释义:
佐剂性关节炎:是由T细胞介导的慢性、系统性免疫性炎症。关节破坏分为软组织肿胀、骨侵蚀和关节间隙改变3个方面,其临床表现的主要评价指标为关节肿胀数、足爪肿胀度、踝关节病理、足爪X射线摄片等。X射线法诊断观察炎症早期主要表现为关节软组织肿胀,致炎后14-16 d骨质破坏最为显著,软组织肿胀达到高峰,出现关节间隙增宽。
成纤维样滑膜细胞:是介导类风湿关节炎炎症发生的主要细胞,其特征性标记物有波形蛋白、尿二苷磷酸葡萄糖脱氢酶、促衰变因子、血管细胞黏附分子1等。体外原代培养成纤维样滑膜细胞的方法主要有3 种:酶消化法、组织块贴壁法和滑液分离培养法。