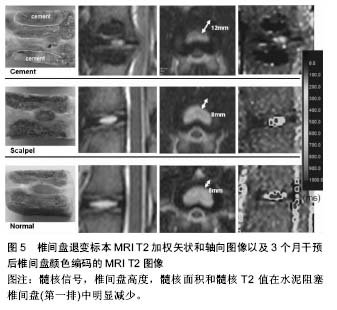
| [1] Sun F, Qu JN, Zhang YG. Animal models of disc degeneration and major genetic strategies. Pain Phys. 2013;16(3): E267-275.[2] 张昭,霍洪军,杨学军,等.兔椎间失稳软骨终板退变的实验研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2008,16(21):1650-1652.[3] Phillips FM,Reuben J,Wetzel FT.Intervertebral disc degeneration adjacent to a lumbar fusion.Bone Joint Surg[Br]. 2002;84-B:289-294.[4] Zhang K,Ding W.Beta1 integrin inhibits apoptosis induced by cyclic stretch in annulus fibrosus cells via ERK1/2 MAPK pathway. Apopotosis. 2016;21(1):13-24.[5] Lipson SJ,Muir H.1980 Volvo award in basic science Proteoglycans in experimental intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 1981;6:194-210.[6] Sun W, Zhang K, Zhao CQ, et al. Quantitative T2 mapping to characterize the process of intervertebral disc degeneration in a rabbit mode.BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders. 2013;14:357.[7] 崔运能,周荣平,麦奇光,等.肌间隙入路腰椎间盘退变模型的构建[J].南方医科大学学报 2012;32(3):404-408.[8] Obata S, Akeda K, Imanishi T, et al. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma-releasate on intervertebral disc degeneration in the rabbit anular puncture model: a preclinical study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14:R241.[9] Mwale F, Masuda K, Pichika R, et al. The efficacy of Link N as a mediator of repair in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration.Arthritis Res Ther.2011;13:R120.[10] Oehme D,Ghosh P.Reconstitution of degenerated ovine lumbar discs by STRO-3-positive allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells combined with pentosan polysulfate.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24(5):715-726.[11] Chen C,Jia Z, Han Z, et al.Quantitative T2 relaxation time and magnetic transfer ratio predict endplate biochemical content ofintervertebral disc degeneration in a canine model.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2015;16:157.[12] 黄河,李宁宁,胡朝晖,等.纤维环穿刺法与腰椎失稳法建立椎间盘退变模型[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(16):22-24[13] Guehring T, Unglaub F, Lorenz H, et al.Intradiscal pressure measurements in normal discs, compressed discs and compressed discs treated with axial posterior disc distraction: an experimental study on the rabbit lumbar spine model. Eur Spine J. 2006;15:597-604.[14] Guehring T, Nerlich A, Kroeber M, et al.Sensitivity of notochordal disc cells to mechanical loading: an experimental animal.study Eur Spine J. 2010;19:113-121.[15] Lindblom K.Intervertebral-disc degeneration considered as a pressure atrophy.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957;39(4):933-945.[16] Wertz K, Godburn K, MacLean JJ, et al. In vivo remodeling of intervertebral discs in response to short- and long-term dynamic compression. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(9):1235-1242.[17] Hamilton DJ, Seguin CA, Wang J, et al. Formation of a nucleus pulposus-cartilage endplate construct in vitro. Biomaterials. 2006;27:397-405.[18] Miyamoto S, Yonenobu K, Ono K. Experimental cervical spondylosis in the mouse.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991;16(10 Suppl):S495-500.[19] Shirazi-Adl A, Taheri M, Urban JP. Analysis of cell viability in intervertebral disc: Effect of endplate permeability on cell population. J Biomech. 2010;43(7):1330-1336.[20] Sobajima S,Kompel JF,Kim JS,et al.Aslowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI,X-ray,and histology.Spine.2005;30(1): 15-24.[21] Cinotti G, Della Rocca C, Romeo S, et al.Degenerative changes of porcine intervertebral disc induced by vertebral endplate injuries. Spine. 2005;30:174-180.[22] Holm S,Holm AK,Ekstrom L,et al. Experimental disc degeneration due to endplate injury. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(1):64-71.[23] 吕浩然,杨进顺,黄文铎,等.终板损伤建立兔腰椎间盘退变模型[J].广东医学,2008,29(1):44-45.[24] Sato K, Nagata K, Ariyoshi M, et al. Intradiscal pressure after intradiscal injection of hypertonic saline:an experimental study. Eur Spine J. 2000;9:213-217.[25] Hirsch C. Studies on the pathol-ogy of low back pain. Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959;41: 237-243.[26] Smith L.Enzyme dissolution of the nucleus pulposus in humans. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(206):4-9.[27] Lu DS,Luk KD,Lu WW,et al.Spinal flexibility increase after chymopapain injection is dose dependent:a possible alternative to anterior release in scoliosis.Spine. 2004;29(2): 123-128.[28] 颜登鲁,李健,高梁斌,等.白细胞介素-1β作用下椎间盘退变动物模型的建立[J].实用医学杂志,2006,22(20):2342-2345.[29] Omlor GW,Nerlich AG. A new porcine in vivo animal model of disc degeneration:response of annulus fibrosus cells, chondrocyte-like nucleus pulposus cells,and notochordal nucleuspulposus cells to partial nucleotomy.Spine. 2009; 34(25):2730-2739.[30] Guder E,Hill S,Kandziora F,et al. Partial nucleotomy of the ovine disc as an in vivo model for disc degeneration. Z Orthop Unfall. 2009;147(1):52-58.[31] Hoogendoorn RJ,Helder MN,Kroeze RJ,et al. Reproducible long-term disc degeneration in a large animal model.Spine. 2008;33(9):949-954.[32] Norcross JP,Lester GE,Weinhold P,et al.An in vivo model of degenerative disc disease. J Orthop Res. 2003;21(1):183-188.[33] Peeters M,Detiger SE,et al.BMP-2 and BMP-2/7 Heterodimers Conjugated to a Fibrin/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel in a Large Animal Model of Mild Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Biores Open Access.2015;4(1):398-406.[34] Boxberger JI,Auerbach JD,Sen S,et al.An in vivo model of reduced nucleus pulposus glycosaminoglycan content in the rat lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine. 2008;33(2):146-154.[35] Liu HF,Zhang H. A novel rabbit disc degeneration model induced by fibronectin fragment. Zhonghua Waike Zazhi. 2013;51(4):362-366.[36] Zhou H,Hou S,Shang W,et al.A new in vivo animal model to create intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI,radiography,CT/discogram,biochemistry,and hostology. Spine. 2007;32(8):864-872.[37] Oda H,Matsuzaki H,Tokuhashi Y,et al.Degeneration of intervertebral discs due to smoking:experimental assessment in a rat-smoking model.J Orthop Sci. 2004;9(2):135-141.[38] Nemoto Y,Matsuzaki H,Tokuhasi Y,et al.Histological changes in intervertebral discs after smoking and cessation: experimental study using a rat passive smoking model.J Orthop Sci. 2006;11(2):191-197.[39] Mao H, Geng D, Zhu X,et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration induced by intradiscal poly(methyl methacrylate) leakage after spine augmentation in an in vivo rabbit model. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(7):3059-3067.[40] Zhang YG, Sun ZM, Liu JT, et al. Features of intervertebraldisc degeneration in rat's aging process. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009;10(7):522-527.[41] Clouet J, Pot-Vaucel M, Grimandi G, et al. Characterization of the age-dependent intervertebral disc changes in rabbit by correlation between MRI, histology and gene expression.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:1471-1479.[42] Hamrick MW, Pennington C, Byron CD. Bone architecture and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine of mice lacking GDF- 8 (myostatin). J Orthop Res. 2003;21(6):1025-1032.[43] Wu WJ, Zhang XK, Zheng XF, et al. SHH-dependent knockout of HIF-1 alpha accelerates the degenerative process in mouse intervertebral disc. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.2013;26(3):601-609.[44] Bvod LM, Richardson WJ, Allen KD, et al. Eardy-onest degeneration of the intervertebral disc and vertebral end plate in mice deftcient in typeIX collagen. Arthritis Rheum. 2008; 58(1):164-171.[45] Gruber HE, Sage EH, Norton HJ, et al. Targeted deletion Of the SPARC gene accelerates disc degeneration in the aging mouse.J Histochen Cytochem. 2005;53(9):1131-1138.[46] Kang R, Li H, Ringgaard S, et al.Interference in the endplate nutritional pathway causes intervertebral disc degeneration in an immature porcine model. Int Orthop.2014;38(5):1011-1017.[47] Wed MJ, Lezuo P, Maissen O, et al. Decreased diffusion as a result of perfusion block in the ovine lumbar spine: a future model for disc degeneration.Proceedings of the 52th annual meeting of the orthopaedic research society.The Orthopaedic Research Society, Chicago, USA.2006,1234.[48] Wei F, Zhong R, Wang L, et al. Pingyangmycin-induced in vivo lumbar disc degeneration model of rhesus monkeys. Spine.2015;40(4):E199-210.[49] Zhang Y, Lenart BA, Lee JK, et al. Histological features of endplates of the mammalian spine: from mice to men. Spine. 2014;39(5):E312-317. |
.jpg)

.jpg)