| [1]肖骁,王锡阳,罗承科.脊柱结核的外科治疗进展[J].现代实用医学, 2016,28(6):703-704.[2]黄定安,徐宏光.胸腰段脊柱结核的外科治疗[J].中医药临床杂志, 2016(4):579-582.[3]姚黎明,赵茜,贾晨光,等.脊柱结核术后复治原因的临床分析研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2016,37(3):260-263.[4]蒋之,屈满英,万轲.耐药脊柱结核的临床分析及疗效研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2016,26(11):132-136.[5]金大地.化疗和外科干预并重,进一步提高脊柱结核治疗水平[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(2):65-67.[6]鲜文峰.不同术式治疗脊柱结核疗效评价及预后[J].中国现代药物应用,2016,10(11):55-56.[7]姜俐洋,王倩,李树香.脊柱结核治疗的研究进展[J].局解手术学杂志,2016,25(8):616-618.[8]黄定安,徐宏光.胸腰段脊柱结核的外科治疗[J].中医药临床杂志, 2016(4):579-582.[9]吕文宾.脊柱结核诊断与治疗的进展研究[J].医药卫生:文摘版, 2016(3):293.[10]蒋之,屈满英,万轲.耐药脊柱结核的临床分析及疗效研究[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2016,26(11):132-136.[11]郭卫东,黄国顺,高峰.脊柱结核的两种手术方式的疗效对比研究[J].中国药物与临床,2016,16(6):862-864.[12]李新建,薛毅珑,罗芸,等.海藻酸盐-多聚赖氨酸-海藻酸盐微胶囊膜的强度和生物相容度测定[J].解放军医学院学报,2001,22(2): 94-96.[13]张传杰,朱平,王怀芳.高强度海藻酸盐纤维的制备及其结构与性能研究[J].天津工业大学学报,2008,27(5):23-27.[14]李秀森,郭子宽,杨靖清.骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J].解放军医学杂志,2000,25(5):346-348.[15]方利君,付小兵,孙同柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞分化为血管内皮细胞的实验研究[J].中华烧伤杂志,2003,19(1):22-24.[16]孙磊,孟国林,窦榆生,等.不同浓度的海藻酸盐与异种骨构建组织工程载体研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2003,17(2):140-142.[17]毕擎,夏冰,万智勇,等.一种新的生物材料海藻酸盐修复长距离周围神经缺损的实验研究[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2003,12(7): 457-459.[18]李冬菊,李良,吴江.去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外成脂肪分化能力的研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2007,24(3): 641-645.[19]胡静波,周燕,蒋丹丹,等.体外扩增过程中人骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖与分化规律[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2006,22(1):7-10.[20]宋兴华.抗结核性骨组织工程复合体的构建及其治疗兔脊柱结核的实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2015(8):937.[21]庄勇,尚显文,张皓,等.钛合金内固定材料修复脊柱结核:生物相容性及力学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(30): 4509-4514.[22]张卓,孙宇航,耿广起,等.载三联抗痨药硫酸钙/聚氨基酸人工骨植入脊柱结核病灶内:植骨界面的组织学改变[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(47):7027-7033.[23]向研,施建党,王自立,等.载三联抗结核药硫酸钙/氨基酸聚合物人工骨体内缓释实验研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(6): 531-536.[24]丛晓明.载三联抗痨药HRZ硫酸钙/聚氨基酸复合人工材料在兔脊柱结核模型体内缓释性能的实验研究[J].银川:宁夏医科大学,2014.[25]He H, Qiao X, Wu S. Carbamylated erythropoietin attenuates cardiomyopathy via PI3K/Akt activation in rats with diabetic cardiomyopathy. Exp Ther Med. 2013;6(2):567-573. [26]Xu X, Cao Z, Cao B, et al. Carbamylated erythropoietin protects the myocardium from acute ischemia/reperfusion injury through a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Surgery. 2009;146(3):506-514. [27]Dashkevich A, Hagl C, Beyersdorf F, et al. VEGF Pathways in the Lymphatics of Healthy and Diseased Heart. Microcirculation. 2016;23(1):5-14. [28]Cubrani? A, Redzovic A, Dobrila-Dintinjana R, et al. Mystery Story about Erythropoietin (Epo) and Erythropoietin Receptor (EpoR) are Disguised? Hepatogastroenterology. 2015;62 (139):585-589.[29]陶亢,张峥,呼西旦•阿巴拜克力,等.兔脊柱结核模型建立的实验研究[J].新疆医科大学学报,2015(8):937-940.[30]Kim DJ, Yun YH, Moon SH, et al. Posterior instrumentation using compressive laminar hooks and anterior interbody arthrodesis for the treatment of tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(13):E275-279.[31]王法正,李毛召,阿不力克木•阿不都热西提,等.胸腰椎结核前路病灶清除单纯植骨或内固定疗效比较[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2008,31(3):303-304,307.[32]Farage L, Martins JW, Farage Filho M. Anterior instrumentation of spine in tuberculous spondylitis: Pott's disease: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002;60(1): 142-144.[33]Satoh Y, Kanou T, Takagi N, et al. A modified retroperitoneal approach to the kidney in patients with a highly deformed thorax: obtaining a wide operative field through subperiosteal resection of the 10th, 11th and 12th ribs. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 2005;96(5):576-580.[34]Boontheekul T, Kong HJ, Mooney DJ. Controlling alginate gel degradation utilizing partial oxidation and bimodal molecular weight distribution. Biomaterials. 2005;26(15):2455-2465.[35]Ha KY, Chung YG, Ryoo SJ. Adherence and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis on various spinal implants. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):38-43.[36]吴永超,郑启新,谢宗平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞表达神经营养因子及治疗脊髓损伤的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(2): 139-141.[37]王颖,冯世庆,赵鹏,等.大鼠脊髓损伤后不同时期移植人脐带间充质干细胞的修复效果观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(11): 918-925.[38]周军,杨惠林.骨髓间充质干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(10):795-798.[39]路康,杨匡,李海音,等.髓核细胞来源外泌体对骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的作用[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2016,26(10): 933-938.[40]周先虎,冯世庆,陈有,等.激活态雪旺细胞联合脐血间充质干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的实验研究[C].全国脊柱脊髓学术会议暨贵州省骨科年会,2012:29.[41]姜刚强.非接触式共培养条件下两种间充质干细胞对同源退变髓核细胞生物学影响的比较研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2014.[42]陶媛.间充质干细胞治疗强直性脊柱炎的临床研究[D].济南:山东大学,2015.[43]童晓,贠云飞,王志强.多孔钽复合间充质干细胞在脊柱融合术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012(6):653-656.[44]杨小荣,吴良绍,方煌.重组人骨形成蛋白2/骨髓间充质干细胞复合磷酸三钙应用于脊柱融合的实验研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012(6):1156-1159.[45]Gurav AN. Management of diabolical diabetes mellitus and periodontitis nexus: Are we doing enough? World J Diabetes. 2016;7(4):50-66. [46]Montserrat N, Nivet E, Sancho-Martinez I, et al. Reprogramming of human fibroblasts to pluripotency with lineage specifiers. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;13(3):341-350. [47]Cao Y, Xiong J, Mei S, et al. Aspirin promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-based calvarial bone regeneration in mini swine. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:210.[48]Sanchis-Gomar F, Garcia-Gimenez JL, Pareja-Galeano H, et al. Erythropoietin and the heart: physiological effects and the therapeutic perspective. Int J Cardiol. 2014;171(2):116-125. [49]Ogunshola OO, Bogdanova AY. Epo and non-hematopoietic cells: what do we know? Methods Mol Biol. 2013;982:13-41. |
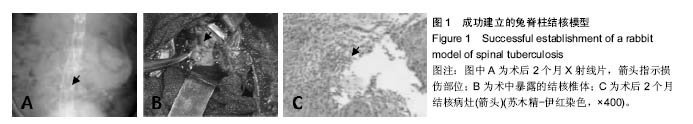
.jpg)
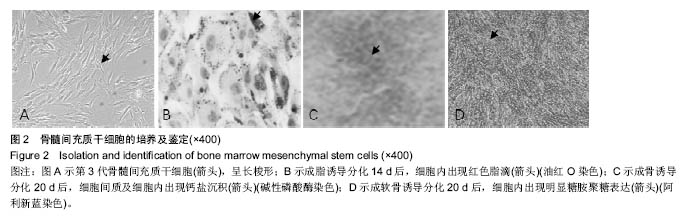
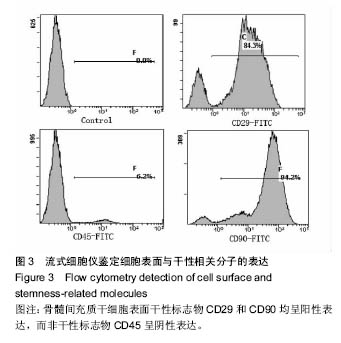
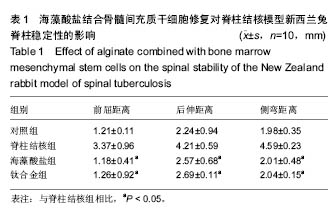
.jpg)