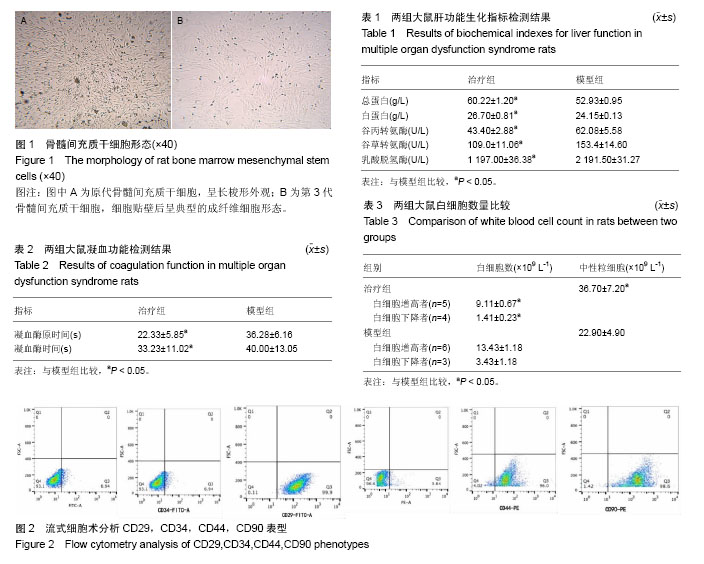
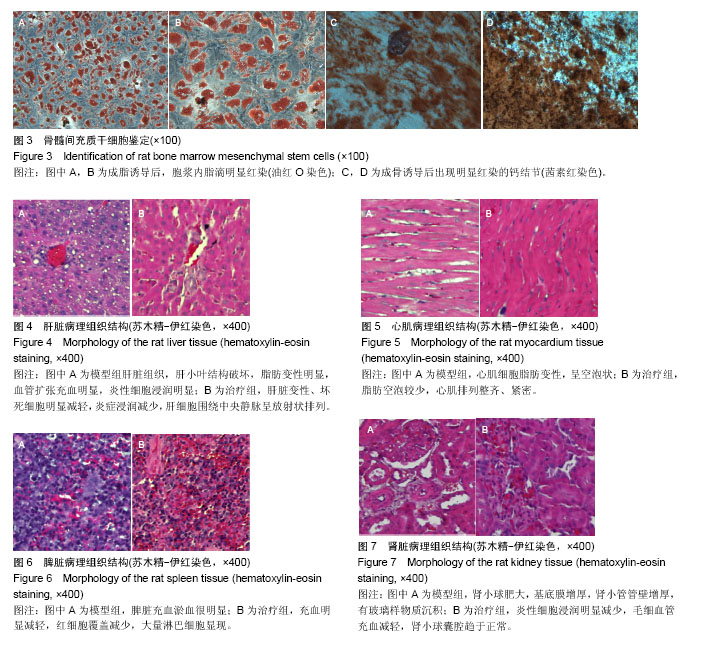
| [1] 胡森,盛志勇,周宝桐.MODS动物模型研究进展[J].中国危重病急救医学,1999,11(8):504-507.[2] Short B, Wagey R. Isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;946: 335-347.[3] 王今达,王宝恩.多脏器功能失常综合征(MODS)病情分期诊断及严重程度评分标准[J].中国危重病急救医学,1995,7(6):346-347.[4] Delorme B, Charbord P. Culture and characterization of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Methods Mol Med. 2007;140:67-81.[5] 平易,刘骏峰,谢琼红,等.内毒素介导的多脏器功能障碍综合征动物模型的研究[J].中国临床医学, 2009, 16(2):287-290.[6] Zhu Q, Qian X, Wang S, et al. A comparison of elderly and adult multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in the rat model. Exp Gerontol. 2006;41(8):771-777.[7] Wang YL, Shen HH, Cheng PY, et al. 17-DMAG, an HSP90 Inhibitor, Ameliorates Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome via Induction of HSP70 in Endotoxemic Rats. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):e0155583. [8] Baue AE, Durham R, Faist E. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS), multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS), multiple organ failure (MOF): are we winning the battle. Shock. 1998;10(2):79-89.[9] Marshall JC. Inflammation, coagulopathy, and the pathogenesis of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7 Suppl):S99-106.[10] 布秀娟.肝损伤动物模型制作研究进展[J].中国医药导报, 2014, 11(12):166-168.[11] Battiwalla M, Hematti P. Mesenchymal stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cytotherapy. 2009; 11(5):503-515.[12] Kanazawa H, Fujimoto Y, Teratani T, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in a rat model. PLoS One. 2011; 6(4):e19195.[13] Kim WH, Hong F, Radaeva S, et al. STAT1 plays an essential role in LPS/D-galactosamine-induced liver apoptosis and injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;285(4): G761-768.[14] Chimenti I, Smith RR, Li TS, et al. Relative roles of direct regeneration versus paracrine effects of human cardiosphere-derived cells transplanted into infarcted mice. Circ Res. 2010;106(5):971-980.[15] Cao J, Li X, Chang N, et al. Dual-modular molecular imaging to trace transplanted bone mesenchymal stromal cells in an acute myocardial infarction model. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(10): 1365-1373.[16] 边晓慧,赵桂锋,孙立,等.骨髓间充质干细胞延缓大鼠残肾模型肾纤维化的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2014,43(2):131-135.[17] Panteli ES, Fligou F, Aretha D, et al. Role of Serotonin in MODS: Deficiency of Serotonin Protects Against Zymosan-Induced Multiple Organ Failure in Mice. Shock. 2015;44(4):383.[18] Villanueva S, Ewertz E, Carrión F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell injection ameliorates chronic renal failure in a rat model. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;121(11):489-499.[19] Lee SR, Lee SH, Moon JY, et al. Repeated administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved the protective effects on a remnant kidney model. Ren Fail. 2010; 32(7):840-848.[20] Wakabayashi K, Nagai A, Sheikh AM, et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stem cells promotes functional improvement and increased expression of neurotrophic factors in a rat focal cerebral ischemia model. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(5):1017-1025.[21] 庞荣清,陈忠明,徐永清,等.一种多器官功能障碍综合征模型的建立[J].中华实验外科杂志,2001,18(6):506-507.[22] Stappenbeck TS, Miyoshi H. The role of stromal stem cells in tissue regeneration and wound repair. Science. 2009;324 (5935):1666-1669.[23] Najar M, Rouas R, Raicevic G, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells promote or suppress the proliferation of T lymphocytes from cord blood and peripheral blood: the importance of low cell ratio and role of interleukin-6. Cytotherapy. 2009;11(5): 570-583.[24] Djouad F, Charbonnier LM, Bouffi C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8): 2025-2032.[25] Saldanha-Araujo F, Haddad R, Farias KC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells promote the sustained expression of CD69 on activated T lymphocytes: roles of canonical and non-canonical NF-κB signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16(6): 1232-1244.[26] Andruszkow H, Fischer J, Sasse M, et al. Interleukin-6 as inflammatory marker referring to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in severely injured children. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2014;22:16. |
.jpg)
.jpg)