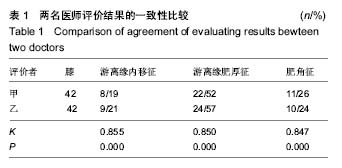
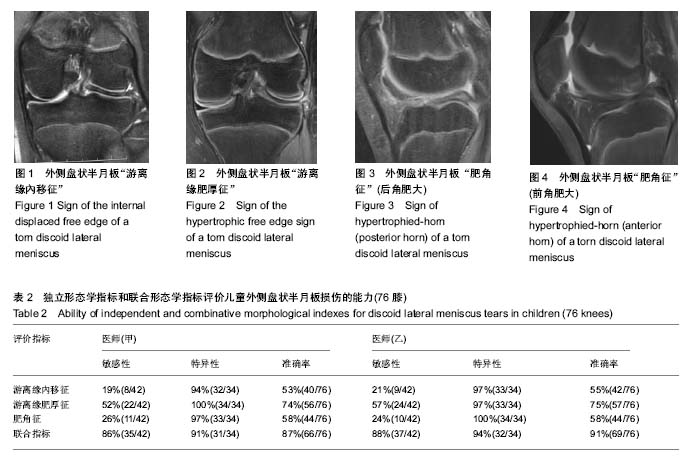
| [1] Chedal-Bornu B, Morin V, Saragaglia D. Meniscoplasty for lateral discoid meniscus tears: Long-term results of 14 cases. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2015; 101(6): 699-702.[2] Carter CW, Hoellwarth J, Weiss JM. Clinical outcomes as a function of meniscal stability in the discoid meniscus: A preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop. 2012; 32(1):9-14. [3] Ahn JH, Kim KI, Wang JH, et al. Long-term results of arthroscopic reshaping for symptomatic discoid lateral meniscus in children. Arthroscopy. 2015; 31(5): 867-873. [4] Lee CH, Song IS, Jang SW, et al. Results of arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for lateral discoid meniscus tears associated with new technique. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25(1):30-35. [5] Jochymek J, Peterková T. Long-Term outcomes of surgical management of symptomatic fibular discoid meniscus in childhood. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2015; 82(5): 353-357. [6] Wasser L, Knörr J, Accadbled F, et al. Arthroscopic treatment of discoid meniscus in children: Clinical and MRI results. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2011; 97(3): 297-303.[7] Chang CY, Huang TF, Ma HL, et al. Imaging evaluation of meniscal injury of the knee joint: a comparative MR imaging and arthroscopic study. Clin Imaging. 2004;28(5): 372-376.[8] Kocher MS, DiCanzio J, Zurakowski D, et al. Diagnostic performance of clinical examination and selective magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of intraarticular knee disorders in children and adolescents. Am J Sports Med. 2001; 29(3):292-296. [9] Yaqoob J, Alam MS, Khalid N. Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging in assessment of meniscal and ACL tear: Correlation with arthroscopy. Pak J Med Sci. 2015; 31(2): 263-268. [10] Lee CH, Song IS, Jang SW, et al. Results of arthroscopic partial meniscectomy for lateral discoid meniscus tears associated with new technique. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2013; 25(1):30-35.[11] Yoo WJ, Choi IH, Chung CY, et al. Discoid lateral meniscus In children: Limited knee extension and meniscal in Stability in the posterior segment. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008; 28:544-548.[12] Lee MH, Choi SH, Woo SY. Quantitative analysis of the difference between an intact complete discoid lateral meniscus and a torn complete discoid meniscus on MR imaging: a feasibility study for a new classification. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(12): 1193-1197.[13] 王淑丽,王林森,王植. 膝关节盘状半月板类型及损伤的MRI分析[J].临床放射学杂志,2004, 23 (1):66-69.[14] 陈瑞, 赵青,汪宝军,等.膝关节盘状半月板MRI表现[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2016, 30(5):495-497.[15] 王安震,丁长青,刘德海,等.盘状半月板的MRI表现[J].中国临床研究,2016, 29(4):554-557.[16] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 成人症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤患者前交叉韧带形态及信号变化的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2013,32(10):857-862.[17] 孙晓新,周伟,梁春雨, 等. 症状性与非症状性儿童外侧盘状半月板MRI形态学差异的研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015, 23(11): 996-999. [18] 孙晓新, 周伟, 左淑萍, 等. 成人外侧盘状半月板损伤的有效影像学指标:MRI影像学评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(24): 3535-3540.[19] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 儿童症状性外侧盘状半月板患者前交叉韧带形态及信号变化的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(7):607-612. [20] 孙晓新, 周伟, 左淑萍, 等. 成人完全型外侧盘状半月板损伤的形态学特征及MRI评价[J].中国运动医学杂志,2016,35(9): 799-803.[21] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 儿童症状性外侧盘状半月板患者前交叉韧带形态及信号变化的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(7):607-612. [22] Yoo WJ, Lee K, Moon HJ, et al.Meniscal morphologic changes on magnetic resonance imaging are associated with symptomatic discoid lateral meniscal tear in children. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(3):330-336.[23] Ahn JH, Lee YS, Ha HC, et al. A novel magnetic resonance imaging classification of discoid lateral meniscus based on peripheral attachment. Am J Sports Med. 2009;37(8): 1564-1569.[24] 田眷艳,郑卓肇.MRI评价肩关节冈上肌腱部分撕裂[J].中国医学影像技术,2010,26(10):1946-1949.[25] 刘秀香,郑卓肇,程钢,等.MR诊断膝关节内、外侧半月板后根部撕裂的价值[J]. 中华放射学杂志,2014,48(11):919-922.[26] Fields LK, Caldwell PE. Arthroscopic saucerization and repair of discoid lateral meniscal tear. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(2): 185-188.[27] Harato K, Niki Y, Nagashima M, et al. Arthroscopic visualization of abnormal movement of discoid lateral meniscus with snapping phenomenon. Arthrosc Tech. 2015; 4(3): 235-238.[28] Jung JY, Choi SH, Ahn JH, et al. MRI findings with arthroscopic correlation for tear of discoid lateral meniscus: comparison between children and adults. Acta Radiol. 2013; 54(4):442-447. [29] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等.儿童症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤对前交叉韧带形态及信号影响的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2015,9(1):21-24.[30] 孙晓新,余家阔,张柳,等. 成人症状性外侧盘状半月板损伤对前交叉韧带形态及信号影响的MRI影像学研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2013,2(12):685-690.[31] Atay OA, Pekmezci M, Dorol MN, et al.Discoid meniscus: An ultrastructural study with transmission electron microscopy. Am J Sports Med.2007; 35(3): 475-478.[32] Papadopoulos A, Kirkos JM, Kapetanos GS. Histomorphologic study of discoid meniscus. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(3):262-268.[33] Rao SK, Rao PS. Clinical, radiologic and arthroscopic assessment and treatment of bilateral discoid lateral meniscus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2007; 15:597-601.[34] Araki Y, Ashikaga R, Fujii K, et al. MR imaging of meniscal tears with discoid lateral meniscus. Eur J Radiol. 1998;27(2): 153-160.[35] Ryu KN, Kim IS, Kim EJ, et al. MR imaging of tears of discoid lateral menisci. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 71(4):963-967. |
.jpg)
.jpg)