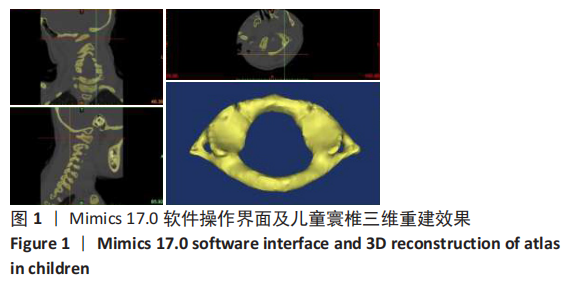
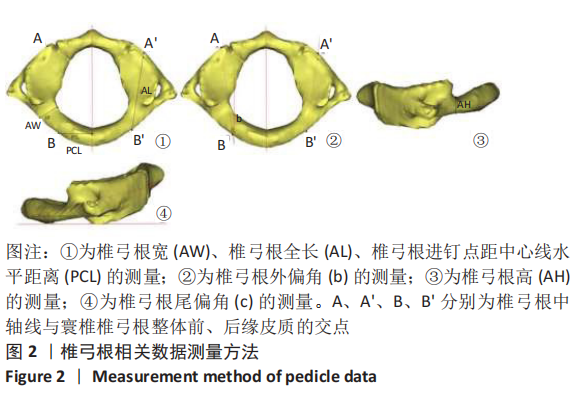
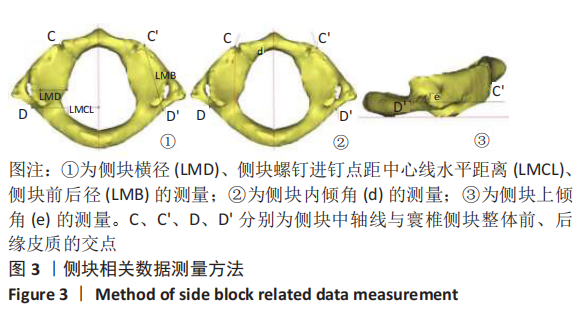
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (36): 5804-5809.doi: 10.12307/2021.346
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
学龄前期儿童行寰椎椎弓根或侧块螺钉内固定的可行性
熊 峰1,李 琨2,周书宇3,王 鹏4,党业兴4,李志军2,张少杰2
- 内蒙古医科大学,1鄂尔多斯临床医学院,2人体解剖学教研室,3中医学院,4第一临床医学院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000
Feasibility of atlantoaxial pedicle screw or lateral mass screw fixation in preschool children
Xiong Feng1, Li Kun2, Zhou Shuyu3, Wang Peng4, Dang Yexing4, Li Zhijun2, Zhang Shaojie2
- 1Ordos Clinical College, 2Department of Human Anatomy, 3College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 4First Clinical College, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
寰椎:即第一颈椎,位于脊柱顶端与枕骨相连处,是头颈部重要枢纽和力学桥梁,外观呈环形,无椎体,由前后弓和两侧块构成,可灵活地满足头颈部多维运动并提供力学支撑,其内走行脊髓,其周走行椎血管、神经根等重要软组织结构。螺钉内固定:内固定螺钉依靠其螺纹和骨质密切结合,深入骨皮质,较好地达到保持复位与内固定的作用,适用于撕裂骨折,特别是累及关节面的骨折,其骨折碎片小,肌肉的牵拉力量大,外固定难以保持复位。螺钉内固定术具有切口小、对软组织的损伤小、异物感少等优点。
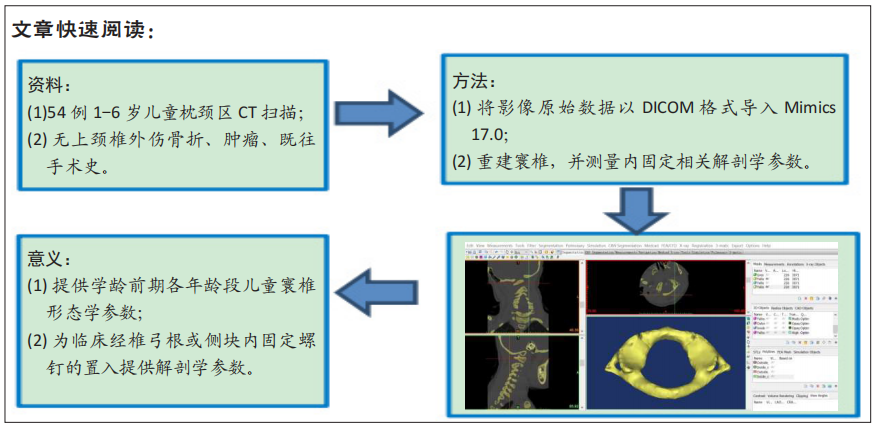
背景:在治疗枕颈区寰椎骨折患者时需行椎弓根或侧块内固定术,此手术多用于成人骨折。迄今国内外尚无学龄前期儿童在寰椎的共性化内固定置钉发育解剖数据。
目的:观测学龄前期儿童寰椎形态结构,探索1-6岁儿童寰椎椎弓根或侧块置入3.50 mm螺钉进行内固定的可行性。
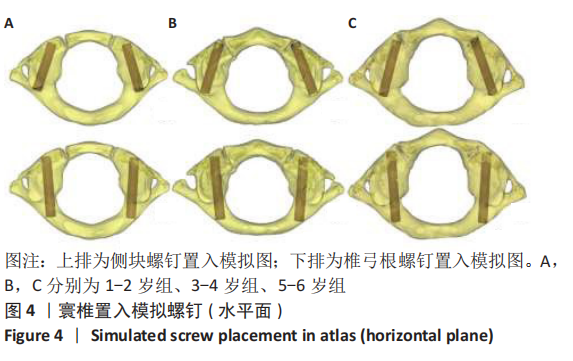
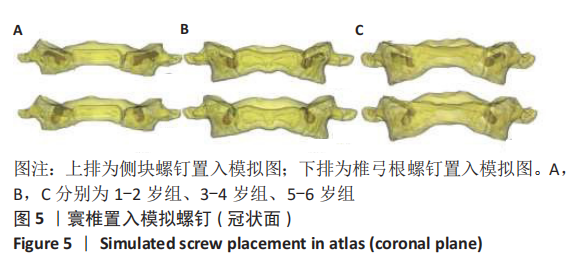
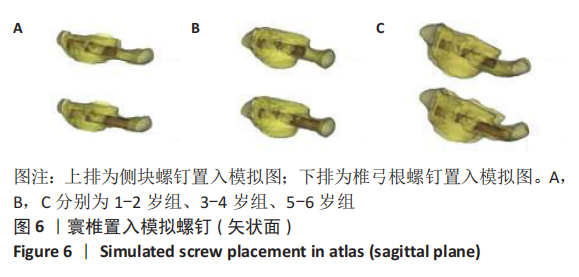
方法:在内蒙古医科大学附属医院、内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院和赤峰市医院收集54例1-6岁儿童头颈部螺旋CT扫描的影像资料,每2岁一组分为3组(1-2岁组、3-4岁组、5-6岁组)。将DICOM数据导入Mimics 17.0行三维重建,运用测量工具在影像资料和重建模型中测量寰椎各参数指标,并行统计学分析。
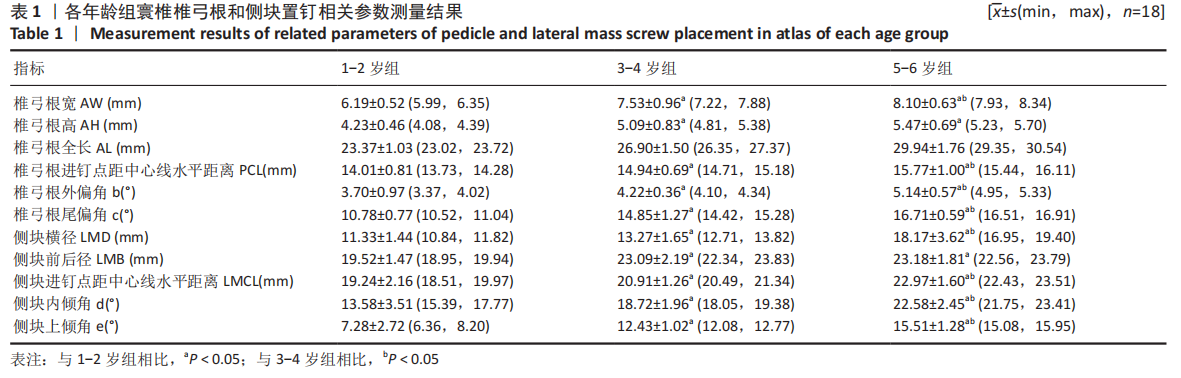
结果与结论:①各年龄段组儿童的寰椎各参数左右侧间比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②寰椎各指标随年龄增长呈上升趋势,其中椎弓根宽、椎弓根进钉点距中心线水平距离、椎弓根外偏角、尾偏角、侧块横径、侧块进钉点距中心线水平距离、侧块内倾角、上倾角在3组间比较有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③椎弓根置钉的主要限制因素是椎弓根宽(AW)和椎弓根高(AH),测量结果显示椎弓根宽>椎弓根高,1-2岁组、3-4岁组、5-6岁组的椎弓根高分别为(4.23±0.46),(5.09±0.46),(5.47±0.69) mm,侧块钉无明显限制;④提示:1-6岁儿童寰椎椎弓根或侧块均具有置入3.50 mm螺钉的可行性,但不同年龄儿童的置钉角度、位置、进钉长度应有所差异,临床操作需进行影像扫描及个体化制定手术方案。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2407-7670 (熊峰)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: