中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 1110-1114.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.07.023
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
骨性关节炎患者下肢力线改变与疼痛部位的关系:影像学评价
林汉文1,温俊茂1,黄超原1,周 驰2,唐宏宇2
- 1广州中医药大学,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院三骨科,广东省广州市 510405
Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation
Lin Han-wen1, Wen Jun-mao1, Huang Chao-yuan1, Zhou Chi2, Tang Hong-yu2
- 1Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2Third Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
下肢力线的概念:下肢力线(膝内翻角)[Lower limbs lines of force]:即股骨机械轴与胫骨机械轴的夹角,理想的角度为0°-5°,国人参考值为:男性(2.2±2.7)°,女性(2.2±2.5)°。股骨机械轴为股骨头圆心与股骨髁间窝顶点的连线,胫骨机械轴为胫骨髁间嵴中点与踝关节中心的连线,踝关节中心取内外踝的中点。从生物力学来说,下肢力线就是“双腿的重力线”。从解剖学来看,下肢力线就是“下肢各器官的结构学连接线”。通俗来讲,下肢力线就是“双腿的线条”。
下肢力线体表测量法:下肢力线的体表测量目前有3种方法:①自股骨头中心至踝关节中心拉一直线,髌骨中点位于此直线上;②自髂前上棘与踝关节拉一直线,该直线通过髌骨中心至髌骨外缘之间,髌骨中点位于其内侧;③自髂前上棘至第1、2趾间拉一直线,髌骨中点位于或接近此直线。
摘要
背景:下肢力学轴线角的改变与骨关节炎的发生发展存在着一定的关联性。
目的:分析下肢力线的改变与膝骨性关节炎患者疼痛部位的相关性。
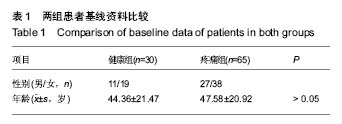
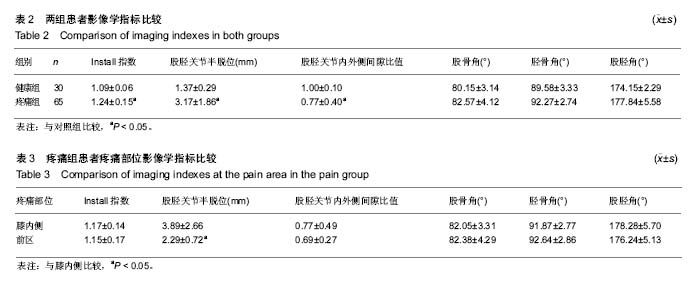
方法:选取膝骨性关节炎疼痛组患者65例和健康对照组患者30例,均行膝关节正侧位片的拍摄,在PACS影像学系统上分别采集Insall 指数(髌骨位置)、股胫关节半脱位程度、股胫内外侧关节间隙比值、股骨角、胫骨角、股胫角这6个影像学指标;将膝骨性关节炎患者疼痛部位分为临床常见的膝前区和膝内侧2个区域。
结果与结论:①膝骨性关节炎疼痛组与健康组患者在Insall 指数、股胫关节半脱位程度、股胫内外侧关节间隙比值的影像学指标比较,差异存在统计学意义;在股骨角、胫骨角和股胫角的比较,差异无显著性意义;②在膝骨性关节炎疼痛组患者的膝内侧和前区的部位比较上,股胫关节半脱位程度的差异有显著性意义;③结果说明,膝骨性关节炎伴膝关节疼痛患者多存在高位髌骨,股胫关节半脱位程度加重,股胫内外侧关节间隙变窄。其中膝前区疼痛患者的股胫关节半脱位程度较膝内侧更加严重。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)