| [1] 朴俊红,庞莲萍,刘忠厚.等.中国人口状况及原发性骨质疏松症诊断标准和发生率[J].中国骨质疏松杂志.2002,8(1):1-7.[2] 文天林,孙天胜,王玲.骨质疏松症的流行病学?病因和分类[J].人民军医,2010(9):662-663.[3] Javed F, Ahmed HB, Crespi R, et al. Role of primary stability for successful osseointegration of dental implants: Factors of influence and evaluation. Interv Med Appl Sci. 2013;5(4):162-167. [4] Rasmusson L, Meredith N, Kahnberg KE, et al. Stability assessments and histology of titanium implants placed simultaneously with autogenous onlay bone in the rabbit tibia. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1998;27(3):229-235.[5] Friberg B, Sennerby L, Linden B, et al. Stability measurements of one-stage Brånemark implants during healing in mandibles. A clinical resonance frequency analysis study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999;28(4):266-272.[6] 周正,周坚,邹石莹,等.种植牙龈沟液中碱性磷酸酶水平与预后的关系[J].中国医学科学院学报,2003,23(1):58-59.[7] Lekholm U, Zarb GA. Patient selection and preparation// Branemark PI, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T. Tissue Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence Publ Co., 1985: 199-209.[8] 刘忠厚,杨定焯,朱汉民,等.中国人骨质疏松症建议诊断标准(第二稿)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2000,6(1):1-3.[9] Novakovic N, Todorovic T, Rakic M, et al. Salivary antioxidants as periodontal biomarkers in evaluation of tissue status and treatment outcome. J Periodontal Res. 2014;49(1):129-136. [10] 柴琳,詹渊博,宋雪静,等.牙周基础治疗对慢性牙周炎患者非刺激性全唾液?龈沟液及血清中基质金属蛋白酶-9水平的影响[J].国际免疫学杂志,2014,37(6):531-535.[11] Kribbs PJ, Smith DE, Chesnut CH 3rd. Oral findings in osteoporosis. Part II: Relationship between residual ridge and alveolar bone resorption and generalized skeletal osteopenia. J Prosthet Dent. 1983;50(5):719-724.[12] Schwarz MS, Rothman SL, Rhodes ML, et al. Computed tomography: Part I. Preoperative assessment of the mandible for endosseous implant surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1987;2(3):137-141.[13] Schwarz MS, Rothman SL, Rhodes ML, et al. Computed tomography: Part II. Preoperative assessment of the maxilla for endosseous implant surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1987;2(3):143-148.[14] Stratemann SA, Huang JC, Maki K, et al. Comparison of cone beam computed tomography imaging with physical measures. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37(2):80-93.[15] Kim GT, Kim SH, Choi YS, et al. Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of orthodontic miniplate anchoring screws in the posterior maxilla. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;136(5):628.e1-10; discussion 628-629.[16] Merheb J, Van Assche N, Coucke W, et al. Relationship between cortical bone thickness or computerized tomography-derived bone density values and implant stability. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(6):612-617.[17] Takaishi Y, Arita S, Honda M, et al. Assessment of alveolar bone mineral density as a predictor of lumbar fracture probability. Adv Ther. 2013;30(5):487-502.[18] Erdo?an O, Shafer DM, Taxel P, et al. A review of the association between osteoporosis and alveolar ridge augmentation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;104(6):738.e1-13.[19] Sakakura CE, Giro G, Gonçalves D, et al. Radiographic assessment of bone density around integrated titanium implants after ovariectomy in rats. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(2):134-138.[20] Marquezan M, Osório A, Sant'Anna E, et al. Does bone mineral density influence the primary stability of dental implants? A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012; 23(7):767-774.[21] 王瑶,耿威,谭包生,等.亲水性大颗粒喷砂酸蚀表面种植体骨愈合期的共振频率分析及早期负荷临床探讨[J].口腔医学研究,2012, 28(7):694-698.[22] Tsolaki IN, Madianos PN, Vrotsos JA. Outcomes of dental implants in osteoporotic patients. A literature review. J Prosthodont. 2009;18(4):309-323.[23] 韩劼,陈智滨,李玮,等.早期愈合阶段牙种植体周沟液骨代谢相关因子的检测和种植体稳定性共振频率分析[J].北京大学学报(医学版),2015(1):37-41.[24] Sanikop S, Patil S, Agrawal P. Gingival crevicular fluid alkaline phosphatase as a potential diagnostic marker of periodontal disease. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2012;16(4):513-518.[25] George K, Zafiropoulos GG, Murat Y, et al. Clinical and microbiological status of osseointegrated implants. J Periodontol. 1994;65(8):766-770.[26] 杨慧英,崔颖,松雪.复方氯己定含漱液对种植义齿后种植体周围龈沟液中骨桥蛋白和碱性磷酸酶水平的影响[J].感染?炎症?修复,2014(3):166-168.[27] Turkyilmaz I, McGlumphy EA. Influence of bone density on implant stability parameters and implant success: a retrospective clinical study. BMC Oral Health. 2008;8:32.[28] Aksoy U, Eratalay K, Tözüm TF. The possible association among bone density values, resonance frequency measurements, tactile sense, and histomorphometric evaluations of dental implant osteotomy sites: a preliminary study. Implant Dent. 2009;18(4):316-325. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨质疏松:是一种因骨量减少、骨骼微细结构发生破坏,导致骨骼脆弱而易发生骨折的骨骼系统疾病。骨质疏松的发生与诸多因素相关,其中雌激素水平变化、营养、遗传、生活方式等最为密切。骨质疏松可分为原发性和继发性两类。原发性骨质疏松系指不伴引起本病的其他疾患;继发性骨质疏松则是由于各种全身性或内分泌代谢性疾病引起的骨组织量减少,颌骨可成为骨质疏松的主要发生部位,引起颌骨骨量降低,从而影响种植。
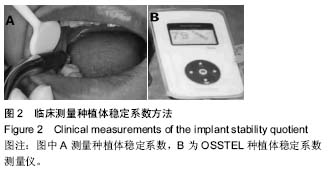
种植义齿:是在口腔缺牙区的牙槽骨内植入种植体(人工牙根),待种植体成活后,再在其上端制作修复体完成种植义齿的修复。它能显著地提高患者的咀嚼功能,且具有良好的美学效果,利用锥形束CT检查种植区骨质骨量,动度测量仪检测种植体稳定性,以及后期的随访观察都可以为种植义齿的远期修复提供临床依据。
文题释义:
骨质疏松:是一种因骨量减少、骨骼微细结构发生破坏,导致骨骼脆弱而易发生骨折的骨骼系统疾病。骨质疏松的发生与诸多因素相关,其中雌激素水平变化、营养、遗传、生活方式等最为密切。骨质疏松可分为原发性和继发性两类。原发性骨质疏松系指不伴引起本病的其他疾患;继发性骨质疏松则是由于各种全身性或内分泌代谢性疾病引起的骨组织量减少,颌骨可成为骨质疏松的主要发生部位,引起颌骨骨量降低,从而影响种植。
种植义齿:是在口腔缺牙区的牙槽骨内植入种植体(人工牙根),待种植体成活后,再在其上端制作修复体完成种植义齿的修复。它能显著地提高患者的咀嚼功能,且具有良好的美学效果,利用锥形束CT检查种植区骨质骨量,动度测量仪检测种植体稳定性,以及后期的随访观察都可以为种植义齿的远期修复提供临床依据。
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
骨质疏松:是一种因骨量减少、骨骼微细结构发生破坏,导致骨骼脆弱而易发生骨折的骨骼系统疾病。骨质疏松的发生与诸多因素相关,其中雌激素水平变化、营养、遗传、生活方式等最为密切。骨质疏松可分为原发性和继发性两类。原发性骨质疏松系指不伴引起本病的其他疾患;继发性骨质疏松则是由于各种全身性或内分泌代谢性疾病引起的骨组织量减少,颌骨可成为骨质疏松的主要发生部位,引起颌骨骨量降低,从而影响种植。
种植义齿:是在口腔缺牙区的牙槽骨内植入种植体(人工牙根),待种植体成活后,再在其上端制作修复体完成种植义齿的修复。它能显著地提高患者的咀嚼功能,且具有良好的美学效果,利用锥形束CT检查种植区骨质骨量,动度测量仪检测种植体稳定性,以及后期的随访观察都可以为种植义齿的远期修复提供临床依据。
文题释义:
骨质疏松:是一种因骨量减少、骨骼微细结构发生破坏,导致骨骼脆弱而易发生骨折的骨骼系统疾病。骨质疏松的发生与诸多因素相关,其中雌激素水平变化、营养、遗传、生活方式等最为密切。骨质疏松可分为原发性和继发性两类。原发性骨质疏松系指不伴引起本病的其他疾患;继发性骨质疏松则是由于各种全身性或内分泌代谢性疾病引起的骨组织量减少,颌骨可成为骨质疏松的主要发生部位,引起颌骨骨量降低,从而影响种植。
种植义齿:是在口腔缺牙区的牙槽骨内植入种植体(人工牙根),待种植体成活后,再在其上端制作修复体完成种植义齿的修复。它能显著地提高患者的咀嚼功能,且具有良好的美学效果,利用锥形束CT检查种植区骨质骨量,动度测量仪检测种植体稳定性,以及后期的随访观察都可以为种植义齿的远期修复提供临床依据。