| [1]Brånemark PI. Osseointegration and its experimental background. J Prosthet Dent. 1983;50(3):399-410.[2]Hanawa T, Kon M, Doi H, et al. Amount of hydroxyl radical on calcium-ion-implanted titanium and point of zero charge of constituent oxide of the surface-modified layer. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 1998;9(2):89-92.[3]Hanawa T, Kamiura Y, Yamamoto S, et al. Early bone formation around calcium-ion-implanted titanium inserted into rat tibia. J Biomed Mater Res. 1997;36(1):131-136.[4]Rohanizadeh R, LeGeros RZ, Harsono M, et al. Adherent apatite coating on titanium substrate using chemical deposition. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;72(4):428-438.[5]Liang FH, Zhou L, Wang KG. Apatite formation on porous titanium by alkali and heat-treatment. Surf Coat Technol. 2003;165(2):133-139.[6]束蓉,李超伦,刘正,等.猪釉基质蛋白的提取及N末端氨基酸序列分析[J].口腔医学纵横,1999,15(2):67-68.[7]王晓洁,黄慧,杨斐,等.釉基质蛋白对碱热处理纯钛表面磷灰石生成的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2010,26(1):7-10.[8]王晓洁,黄慧,杨斐,等.釉基质蛋白对化学处理钛表面磷灰石生成的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2010,19(1):49-54.[9]Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1--review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont. 2004;17(5):536-543.[10]何福明,赵珊珊,刘丽,等.纯钛种植体表面多孔结构的制备与分析[J].上海口腔医学,2005,14(6):639-644.[11]Szmukler-Moncler S, Testori T, Bernard JP. Etched implants: a comparative surface analysis of four implant systems. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;69(1):46-57.[12]Grizon F, Aguado E, Huré G, et al. Enhanced bone integration of implants with increased surface roughness: a long term study in the sheep. J Dent. 2002;30(5-6):195-203.[13]Ong JL, Prince CW, Raikar GN, et al. Effect of surface topography of titanium on surface chemistry and cellular response. Implant Dent. 1996;5(2):83-88.[14]Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1--review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont. 2004;17(5):536-543.[15]Wen HB, Wolke JG, de Wijn JR, et al. Fast precipitation of calcium phosphate layers on titanium induced by simple chemical treatments. Biomaterials. 1997;18(22):1471-1478.[16]Wen HB, Moradian-Oldak J. Modification of calcium-phosphate coatings on titanium by recombinant amelogenin. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2003;64(3):483-490.[17]Du C, Schneider GB, Zaharias R, et al. Apatite/amelogenin coating on titanium promotes osteogenic gene expression. J Dent Res. 2005;84(11):1070-1074.[18]Zykova A, Safonov V, Yanovska A, et al. Formation of Solution-derived Hydroxyapatite Coatings on Titanium Alloy in the Presence of Magnetron-sputtered Alumina Bond Coats. Open Biomed Eng J. 2015;9:75-82. [19]Zhu X, Wang Y, Zhang H, et al. Study on the in vitro release behavior of bovine serum albumin from calcium phosphate coating on pure titanium surface. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;49(9):540-544. [20]Thammarakcharoen F, Suvannapruk W, Suwanprateeb J. Influence of process parameters on the content of biomimetic calcium phosphate coating on titanium: a Taguchi analysis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2014;14(10):7614-7620. [21]Cuijpers VM, Alghamdi HS, Van Dijk NW, et al. Osteogenesis around CaP-coated titanium implants visualized using 3D histology and micro-computed tomography. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3463-3473. [22]Li HC, Wang DG, Chen CZ, et al. Effect of CeO2 and Y2O3 on microstructure, bioactivity and degradability of laser cladding CaO-SiO2 coating on titanium alloy. Colloids Su rf B Biointerfaces. 2015;127:15-21. [23]Elyada A, Garti N, Füredi-Milhofer H. Polyelectrolyte multilayer-calcium phosphate composite coatings for metal implants. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(10):3511-3521. [24]McCafferty MM, Burke GA, Meenan BJ. Calcium phosphate thin films enhance the response of human mesenchymal stem cells to nanostructured titanium surfaces. J Tissue Eng. 2014;5:2041731414537513. [25]Liu Y, Zhang X, Liu Y, et al. Bi-functionalization of a calcium phosphate-coated titanium surface with slow-release simvastatin and metronidazole to provide antibacterial activities and pro-osteodifferentiation capabilities. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97741. [26]Yokota S, Nishiwaki N, Ueda K, et al. Evaluation of thin amorphous calcium phosphate coatings on titanium dental implants deposited using magnetron sputtering. Implant Dent. 2014;23(3):343-350.[27]Habelitz S, Denbesten PK, Marshall SJ, et al. Amelogenin control over apatite crystal growth is affected by the pH and degree of ionic saturation. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2005;8(4):232-238.[28]Iijima M, Moradian-Oldak J. Control of apatite crystal growth in a fluoride containing amelogenin-rich matrix. Biomaterials. 2005;26(13):1595-1603.[29]金红.医用钛合金及其表面改性技术的研究现状[J].稀有金属, 2003,7(6):794-798. [30]Liu KY, Chu PK, Ding CX. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2004;47(3-4):49-121. |
.jpg)
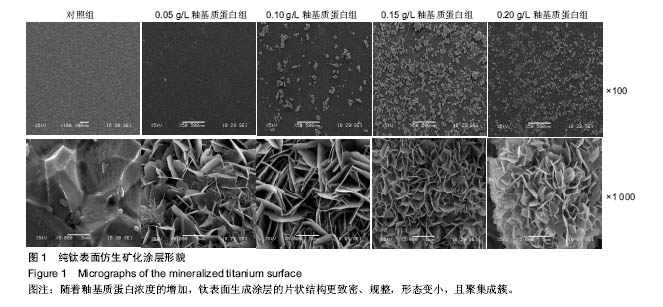
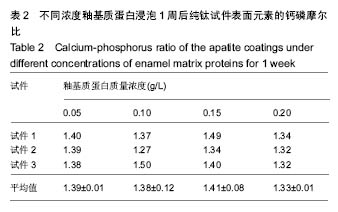
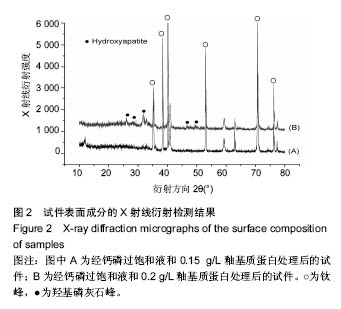
.jpg)
.jpg)