中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (2): 227-231.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.02.012
• 细胞外基质材料 extracellular matrix materials • 上一篇 下一篇
猪脱细胞真皮与人表皮干细胞构建组织工程皮肤修复全层皮肤缺损
钱李科,钱明元
- 张家港市第一人民医院,江苏省张家港市 215600
Treatment outcomes of human epidermal stem cells/porcine acellular dermal tissue-engineered skin in the repair of full-thickness skin defects
Qian Li-ke, Qian Ming-yuan
- Zhangjiagang First People’s Hospital, Zhangjiagang 215600, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
猪脱细胞真皮结构:利用猪等身上的胶原蛋白制成,去除表皮及真皮内的细胞成分,保留正常的胶原纤维组织和基底膜等细胞外间质成分。这种无细胞真皮无免疫原性,完整保留了各种基底膜成分,且可提供近接近正常结构的真皮替代,有利于细胞的生长,是一种十分理想的支架材料。
组织工程皮肤:由表皮层和真皮层两部分组成,表皮层主要是利用人体干细胞培养出的皮肤组织。患者换肤后,人工皮肤会与自身皮肤融合并再生长。通过换肤,患者在避免自体取皮的同时,能修复皮肤创伤,重建功能。为此,在组织工程皮肤的构建过程中需要使用一定的种子细胞和真皮层支架材料。
背景:目前已有应用蚕丝蛋白、结缔细胞、生物高分子材料、合成高分子材料、纳米材料、传感器制成的生物人造皮,以及非生物人造皮,应用于临床试验都取得了良好效果,但它们与真正皮肤相比还有很大差距。
目的:观察表皮干细胞/猪脱细胞真皮组织工程皮肤修复大鼠全层皮肤缺损的效果。
方法:取20只SD大鼠,建立背部皮肤缺损模型,随机分为2组,实验组于皮肤缺损处植入人表皮干细胞-猪脱细胞真皮组织工程皮肤,对照组植入猪脱细胞真皮。植入后4周,进行大体、组织学和免疫组织化学观察。
结果与结论:①大体观察:实验组创面愈合良好,皮肤弹性佳;对照组移植区域呈现瘢痕愈合,触之质地偏硬;②组织学观察:两组在镜下均可见良好的表皮和真皮结构,表皮可明显区分为基底层、棘层和角化不全的角质层,与实验组相比,对照组可见较多纤维结缔组织;③免疫组织化学观察:实验组愈合创面抗人类白细胞抗原-Ⅰ型抗原呈现阳性,对照组愈合创面抗人类白细胞抗原-Ⅰ型抗原呈阴性;④结果表明:人表皮干细胞/猪脱细胞真皮组织工程皮肤修复动物全层皮肤缺损,可有效抑制瘢痕形成及挛缩。
中图分类号:
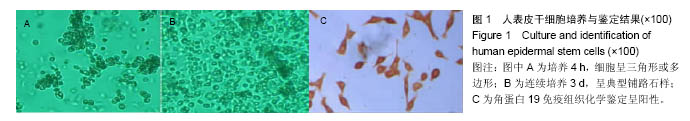
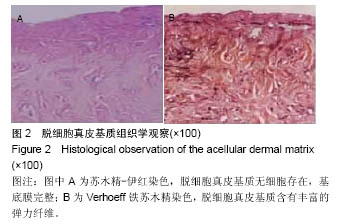
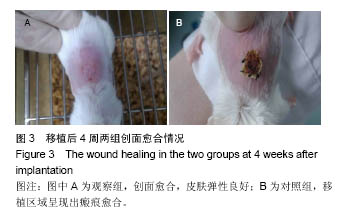

.jpg)