| [1]Johnell O, Kanis J A. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(12): 1726-1733.[2]Kado DM, Duong T, Stone KL, et al. Incident vertebral fractures and mortality in older women: a prospective study. Osteoporos Int. 2003;14(7):589-594.[3]梁德,叶林强,江晓兵,等.骨水泥-椎体体积比及椎体骨壁裂口与椎体成形骨水泥渗漏的相关性分析[C].第十届中国南方骨质疏松论坛暨重庆市医学会骨质疏松年会,重庆,2014.[4]Gu CN, Brinjikji W, Evans AJ, et al. Outcomes of vertebroplasty compared with kyphoplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016;8(6):636-642.[5]Chen WJ, Kao YH, Yang SC, et al. Impact of cement leakage into disks on the development of adjacent vertebral compression fractures. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(1):35-39.[6]Habib N, Maniatis T, Ahmed S, et al. Cement pulmonary embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: an overview. Heart Lung. 2012;41(5):509-511.[7]Lee BJ, Lee SR, Yoo TY. Paraplegia as a complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylmethacrylate: a case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(19):E419-E422.[8]Wang H, Sribastav SS, Ye F, et al. Comparison of percutaneous vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of single level vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the literature. Pain Physician. 2015;18(3):209-222.[9]Papanastassiou ID, Filis A, Gerochristou MA, et al. Controversial issues in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:1-12.[10]Edidin AA, Ong KL, Lau E, et al. Cost-effectiveness analysis of treatments for vertebral compression fractures. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2012;10(4): 273-284.[11]Chen AT, Cohen DB, Skolasky RL. Impact of nonoperative treatment, vertebroplasty, and kyphoplasty on survival and morbidity after vertebral compression fracture in the medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(19):1729-1736.[12]何磊,钱宇,金以军.单球囊双侧交替扩张后凸成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤, 2014,27(12):1056-1061. [13]Liang D, Ye L, Jiang X, et al. Correlation analysis of cement leakage with volume ratio of intravertebral bone cement to vertebral body and vertebral body wall incompetence in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014; 28(11):1358-1363.[14]Noriega DC, Ramajo RH, Lite IS, et al. Safety and clinical performance of kyphoplasty and SpineJack ((R)) procedures in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a pilot, monocentric, investigator-initiated study. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(6): 2047-2055.[15]Wu Y, Wang F, Zhou J Q, et al. Analysis of clinical effects of percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty in treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(5):385-389.[16]Lee ST, Chen JF. Closed reduction vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 2004;100 (4 Suppl Spine):392-396.[17]Hulme PA, Krebs J, Ferguson SJ, et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine. 2006;31(17):1983-2001.[18]Klazen CA, Verhaar HJ, Lohle PN, et al. Clinical course of pain in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010; 21(9):1405-1409.[19]Han S, Wan S, Ning L, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty versus balloon kyphoplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a meta-analysis of randomised and non-randomised controlled trials. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(9):1349-1358.[20]Kumar K, Nguyen R, Bishop S. A comparative analysis of the results of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Neurosurgery. 2010;67(3 Suppl Operative):s171-s188.[21]Xiao H, Yang J, Feng X, et al. Comparing complications of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(S1):77-85.[22]Ma X, Xing D, Ma J, et al. Risk factors for new vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty: qualitative evidence synthesized from a systematic review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(12): E713-E722.[23]李东华,刘训伟,彭湘涛,等.骨填充网袋灌注骨水泥修复椎体压缩骨折:可降低骨水泥椎体外渗漏率[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(3):358-363.[24]刘训伟,魏岱旭,彭湘涛,等.经皮椎体后凸成形在治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折中恢复椎体高度局限性的观察及机制探讨[J].医学影像学杂志,2013,23(9):1457-1460.[25]Kim MJ, Lindsey DP, Hannibal M, et al. Vertebroplasty versus kyphoplasty: biomechanical behavior under repetitive loading conditions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(18):2079-2084.[26]刘训伟,孔小燕,钟建,等.骨填充网袋修复椎体压缩骨折的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014(16):2487-2492.[27]彭湘涛,刘训伟,金鹏,等.应用骨填充网袋治疗椎体压缩性骨折的临床研究[J].医学影像学杂志,2014,24(5):843-847.[28]Alfonso F, García-Guimarães M, Navarrete G, et al. Drug-eluting balloons in coronary interventions: The quiet revolution? Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016.[29]Lee HH, Hsu PC, Lee WH, et al. Longitudinal stent deformation caused by retraction of the looped main branch guidewire. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2016;32(5):616-618.[30]Mamas MA, George S, Ratib K, et al. 5-Fr sheathless transradial cardiac catheterization using conventional catheters and balloon assisted tracking; a new approach to downsizing. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2016.[31]Rasuli P, Connolly MJ. Response: Letter to the Editor and Response: Comparison of Cutting Balloon Angioplasty and Percutaneous Balloon Angioplasty of Arteriovenous Fistula Stenosis: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials. J Interv Cardiol. 2016;29(5):552.[32]Fernández-Rodríguez D, Regueiro A, Cevallos J, et al. Gender gap in medical care in ST segment elevation myocardial infarction networks: Findings from the Catalan network Codi Infart.Med Intensiva. 2016.[33]Seidler T, Hünlich M, Puls M, et al. Feasibility and outcomes of interventional treatment for vascular access site complications following transfemoral aortic valve implantation. Clin Res Cardiol. 2016.[34]Indolfi C, De Rosa S, Colombo A. Bioresorbable vascular scaffolds - basic concepts and clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016.[35]Kufner S, Xhepa E, Lutter C, et al. Optical coherence tomography in drug-eluting stent restenosis: a technique in need of a strategy. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2016.[36]Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Duncan TD, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the correction of spinal deformity in painful vertebral body compression fractures. Clin Imaging. 2002;26(1):1-5.[37]刘杰,王建.椎体后凸成形治疗骨质疏松胸椎椎体重度压缩性骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2008,22(4): 399-403. |
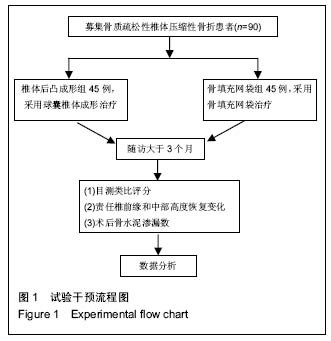
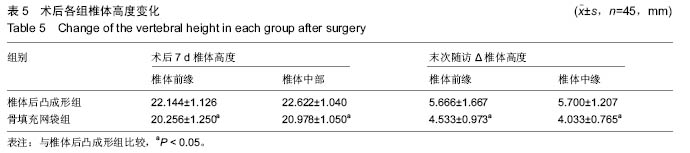
.jpg)
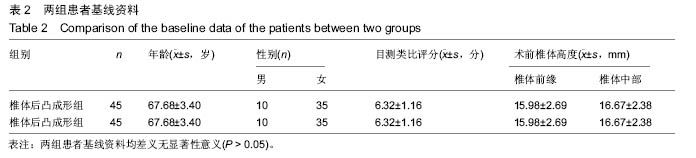
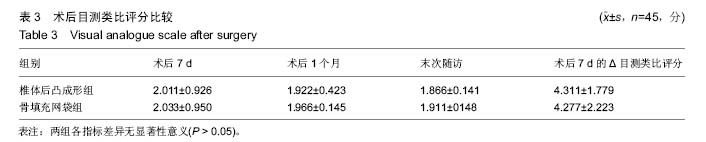
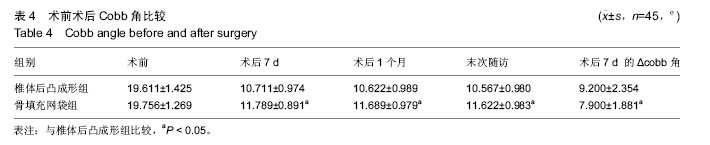
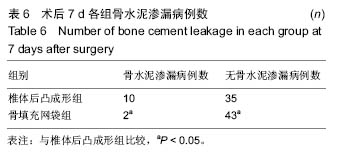
.jpg)
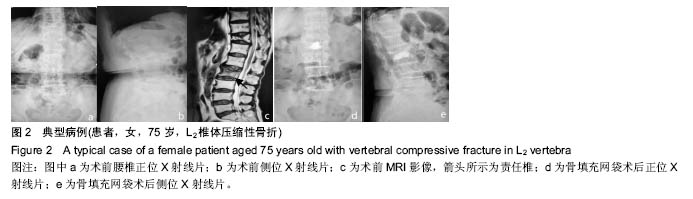
.jpg)