| [1] Hathaway LJ, Griffin GE, Sansonetti PJ, et al. Human monocytes kill Shigella flexneri but then die by apoptosis associated with suppression of proinflammatory cytokine production. Infect Immun. 2002;70(7):3833-3842.
[2] Zychlinsky A, Thirumalai K, Arondel J, et al. In vivo apoptosis in Shigella flexneri infections. Infect Immun. 1996;64(12):5357-5365.
[3] Sansonetti PJ, Tran Van Nhieu G, Egile C.Rupture of the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier and Mucosal Invasion by Shigella flexneri. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28(3):466-475.
[4] Ashkenazi S, Levy I, Kazaronovski V, et al. Growing antimicrobial resistance of Shigella isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51(2):427-429.
[5] Sansonetti PJ. Microbes and microbial toxins: paradigms for microbial-mucosal interactions III. Shigellosis: from symptoms to molecular pathogenesis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280(3):G319-323.
[6] Kotloff KL, Winickoff JP, Ivanoff B, et al.Global burden of Shigella infections: implications for vaccine development and implementation of control strategies. Bull World Health Organ. 1999;77(8):651-666.
[7] Von SL, Kim DR, Ali M, et al.A multicentre study of Shigella diarrhoea in six Asian countries: disease burden, clinical manifestations, and microbiology.Plos Medicine.2006;3(9): e353.
[8] BingGu, XingKe, ShiyangPan, et al. Prevalence and trends of aminoglycoside resistance in Shigella worldwide, 1999-2010. J Biomed Res. 2013 ;27(2):103-115.
[9] Yang SF, Xue WJ, Lu WH, et al. High Prevalence of Antibiotic Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Integrons among Shigella Isolates in Eastern China. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1549-1551.
[10] Qiu S, Wang Y, Xu X, et al. Multidrug-Resistant Atypical Variants of Shigella flexneri in China. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013;19(7):1147-1150.
[11] Barry EM, Pasetti MF, Sztein MB, et al. Progress and pitfalls in Shigella vaccine research. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013 ;10(4):245-55 255.
[12] Bodhidatta L, Pitisuttithum P, Chamnanchanant S, et al. Establishment of a Shigella sonnei, human challenge model in Thailand ☆. Vaccine.2012; 30(49):7040-7045.
[13] Heine SJ,Diaz-Mcnair J,Martinez-Becerra FJ,et al. Evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of orally delivered Shigella type III secretion system proteins IpaB and IpaD. Vaccine.2013;31(28):2919-2929.
[14] Braude R, Newport MJ, Porter JWG. Outer Membrane Protein A (OmpA) of Shigella flexneri 2a Induces B Cell Activation And Protective Immune Response in Mouse Model. Faseb Journal.2015;29(3):827-842.
[15] Camacho AI, Irache JM, Souza JD, et al. Nanoparticle- based vaccine for mucosal protection against Shigella flexneri, in mice. Vaccine.2013; 31(32):3288-3294.
[16] Fernandez MI, Thuizat A, Pedron T, et al. A newborn mouse model for the study of intestinal pathogenesis of shigellosis. Cellular Microbiology.2003; 5(7):481-491.
[17] Shim DH, Chang SY, Park SM, et al. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy offered by a ribosomal-based vaccine from Shigella flexneri, 2a. Vaccine. 2007; 25(25):4828-4836.
[18] Voino-Yasenetsky MV, Voino-Yasenetskaya MK. Experimental pneumonia caused by bacteria of the Shigella group. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung. 1962; 11:439-454.
[19] Barman S, Koley H, Ramamurthy T, et al.Protective immunity by oral immunization with heat-killed Shigella strains in a guinea pig colitis model. Microbiol Immunol. 2013;57(11):762-771.
[20] Chowdhury FM, Rahman MZ, Khan SI, et al.An Environmental Escherichia albertii, Strain, DM104, Induces Protective Immunity to Shigella dysenteriae, in Guinea Pig Eye Model.Current Microbiology.2014; 68(5):642-647.
[21] Shim DH, Suzuki T, Chang SY, et al.New animal model of shigellosis in the Guinea pig: its usefulness for protective efficacy studies. J Immunol. 2007 15;178(4):2476-2482.
[22] Rabbani GH,Albert MJ,Rahman H,et al. Development of an improved animal model of shigellosis in the adult rabbit by colonic infection with Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1995;63(11):4350-4357.
[23] Schnupf P, Sansonetti PJ. Quantitative RT-PCR profiling of the rabbit immune response: assessment of acute Shigella flexneri infection. Plos One. 2012;7(6): e36446-e36446.
[24] Shipley ST, Panda A, Khan AQ, et al.A challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae 1 in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis).Comparative Medicine. 2010;60(1):54-61.
[25] Islam D, Ruamsap N, Khantapura P, et al. Evaluation of an intragastric challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae, 1 in rhesus monkeys ( Macaca mulatta ) for the pre-clinical assessment of Shigella, vaccine formulations. Apmis Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Et Immunologica Scandinavica, 2014;122(6):463-475.
[26] Mostowy S, Boucontet L, Mazon Moya M J, et al. The zebrafish as a new model for the in vivo study of Shigella flexneri interaction with phagocytes and bacterial autophagy.Plos Pathogens.2013;9(9):191-197.
[27] 邓超,曹均强,梁鸿寅,等.早期腹腔置管引流对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎相关肠黏膜损伤的作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2016,41(2):119-122.
[28] 刘松,金梅香,谭兴文.西洋参茎叶皂苷保护大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的作用[J].中成药, 2016,38(2):418-421.
[29] 郭敏,李延青,于秀娟,等.大鼠急性肠道感染后肠功能紊乱动物模型的建立[J].山东大学学报:医学版, 2006, 44(6): 586-589.
[30] Savchenko ZI, Iushchuk ND, Tsyb AF, et al. [Immunostimulating activity of eubiotic bioflor in intestinal dysbacteriosis of various origin]. Klin Med (Mosk). 2000;78(3):50-53.
[31] 吴利先,王国富,高峰.两歧双歧杆菌抗福氏痢疾杆菌感染的机制研究[J]. 大理学院学报:综合版, 2010, 9(6):16-18.
[32] Mitra S, Barman S, Nag D, et al.Outer membrane vesicles of Shigella boydii, type 4 induce passive immunity in neonatal mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2012;66(2):240-250.
[33] Lawson JD, Mainwaring SJ. Detection of pseudodiarrhoea by simple clinical assessment of intestinal transit rate. BMJ. 1990;300(6722):439-440.
[34] Bai J, Hao J, Zhang X,et al. Netrin-1 attenuates the progression of renal dysfunction by blocking endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the 5/6 nephrectomy rat model. BMC Nephrol. 2016;17(1):47.
[35] Chang SY, Lee SN, Yang JY, et al.Autophagy Controls an Intrinsic Host Defense to Bacteria by Promoting Epithelial Cell Survival: A Murine Model. Plos One. 2013;8(11):e81095.
[36] Islam D,Ruamsap N,Khantapura P,et al.Evaluation of an intragastric challenge model for Shigella dysenteriae, 1 in rhesus monkeys ( Macaca mulatta ) for the pre-clinical assessment of Shigella, vaccine formulations. APMIS. 2014;122(6):463-475.
[37] Kim YJ, Yeo SG, Park JH, et al.Shigella vaccine development: prospective animal models and current status.Curr Pharm Biotechnol.2013;14(10):903-912.
[38] 孙艳玲, 张炳华. 两歧双歧杆菌对鼠伤寒感染小鼠模型的生物治疗作用[J]. 新疆医科大学学报, 2006, 29(6): 483-484.
[39] Pimentel M,Chatterjee S,Chang C,et al.A New Rat Model Links Two Contemporary Theories in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2008;53(4):982-989.
[40] Ross S, Controni G, Khan W. Resistance of shigellae to ampicillin and other antibiotics. Its clinical and epidemiological implications. JAMA. 1972;221(1):45-47. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。
文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。.jpg) 文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。
文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。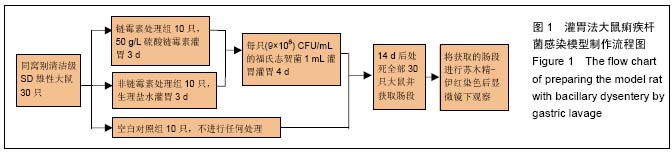
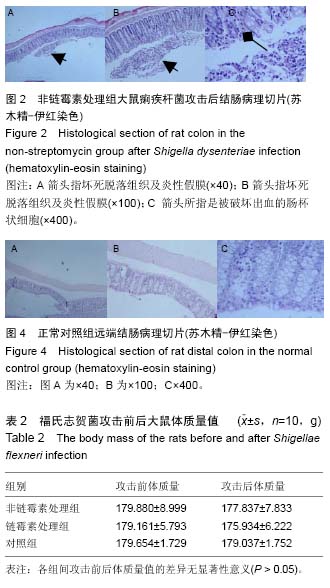
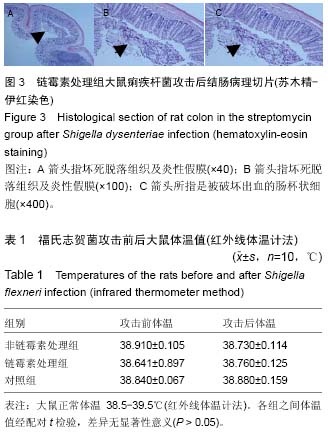
.jpg) 文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。
文题释义:
福氏志贺菌:福氏志贺菌(S.flexneri)属于人类细菌性痢疾病原菌,志贺菌属(Shigella),俗称痢疾杆菌的一种。1989年由Shiga首先分离并以他命名。志贺菌属根据菌体O抗原分为四群40余血清型及亚型,即A、B、C、D四群。B群即福氏志贺菌,有13个血清型,各型之间有交叉反应。
病理学:是研究人体疾病发生的原因、发生机制、发展规律以及疾病过程中机体的形态结构、功能代谢变化和病变转归的一门基础医学科学。正因如此,病理学一直被视为是基础医学与临床医学之间的“桥梁学科”,充分表明了它在医学中不可替代的重要作用,这是由病理学的性质和任务所决定的。