| [1] Santoni BG, Hynes RA, MeGilvray KC,et al.Cortical hone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws.Spine J. 2009;9(5):366-373.
[2] Glennie RA, Dea N,Kwon BK,et al.Early clinical results with cortically based pedicle screw trajectory for fusion of the degenerative lumbar spine. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(6):972-975.
[3] Calvert GC,Lawrence BD,Abtahi AM,et al.Cortical screws used to rescue failed lumbar pedicle screw construct:a biomeehanieal analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;22(21):1-7.
[4] Krag MH, Weaver DL,Beynnon BD,et al.Morphometry ofthe thoracic and lumbar spine related to transpedicularscrew placement for surgical spinal fixation.Spine. 1988;13(1):27-32.
[5] Mizuno K,Kuraishi K,Umeda Y,et al.Midline lumbar fusion with cortical bone trajectory screw. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(9):716-721.
[6] 吴东迎,袁峰,吴继彬,等.3D打印截骨导板在人工全膝关节置换中的应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,35(9):921-926.
[7] Owen BD, Christensen GE, Reinhardt JM, et al. Rapid prototype patient- specific drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg. 2007; 12(5): 303-308.
[8] Lu S, Xu YQ, Lu WW, et al. A novel patient-specific navigational template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Spine. 2009;34(26): E959-966.
[9] Schweizer A, Fürnstahl P, Nagy L. Three-dimensional correction of distal radius intra-articular malunions using patient-specificdrill guides. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(12): 2339-2347.
[10] Inzana JA, Olvera D, Fuller SM. 3D printing of composite calciumphosphate and collagen scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2014;35(13): 4026-4034.
[11] Ma T, Xu YQ, Cheng YB, et al. A nov computer-assisted drill guide template for thoracic pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;32(1):65-72.
[12] 陈玉兵,陆声,徐永清,等.快速成型个体化导航模板辅助胸椎椎弓根螺钉置入可行性研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(20):1557-1561.
[13] Davne SH, Myers DL.Complications of lumbar spinal fusion with transpedicular instrumentation. Spine. 1992; 17(6): S184-S189.
[14] Terman SW,Yee TJ, Lau D, et al. Minimally invasive versus open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: comparison of clinical outcomes among obese patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(6):644-652.
[15] Shea TM, Laun J,Gonzalez-Blohm SA,et al.Designs and techniques that improve the pullout strength of pedicle screws in osteoporotic vertebrae: current status. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 748393.
[16] Renner SM, Lim TH, Kim WJ, et al. Augmentation of pedicle screw fixation strength using an injectable Calcium phosphate cement as a function of injection timing and method. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(11): E212-E216.
[17] Matsukawa K, Yato Y, Kato T, et al. In vivo analysis of insertional torque during pedicle screwing using cortical bone trajectory technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(4): E240-E245.17:06 2016-12-2
[18] Inceoglu S,Montgomery WH Jr,St Clair S,et al.Pedicle screw insertion angle and pullout strength:comparison of 2 proposed strategies. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011; 14(5):670-676.
[19] Baluch DA, Patel AA, Lullo B, et al. Effect of physiologic loads oncortical and traditional pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(22): 1297-1302.
[20] Matsukawa K, Yato Y, Kate T, et al. In rive analysis of inserttonal torque dm'ing pedicle screwing using cortical bone trajectory technique. Spine. 2014;39(4): E240-245.
[21] Panjabi MM, Shin EK, Chen NC, et al. Internal morphology of human cervical pedicles. Spine. 2000; 25(10):1197-1205.
[22] 陈文杰,王洪立,姜建元,等.成人腰椎皮质骨钉道的解剖学研究[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2015,35(12):1213-1221.
[23] Hu Y, Gu YJ, Ye PH, et al. Posterior cervical spine arthrodesis incorporating C2 laminar screw fixation in the treatment of cervi cal spine injury. Oahop Surg. 2010;2(1):32-37.
[24] 胡勇,袁振山,谢辉,等.快速成型导向模板技术在枢椎椎板交叉螺钉置钉中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(6): 640-648.
[25] Rihn JA, Gandhi SD. Disc space preparation in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comparison of minimally invasive and open approaches. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(6):1800-1805.
[26] 郭时空,高浩然,李存孝,等.保留邻椎后方韧带复合体的改良后路椎间融合术临床疗效观察[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2014,22(11):990-995.
[27] Sato S,Yagi M,Machida M,et al.Reoperation rate and risk factots of elective spinal surgery for degenerative 8 pondylolisthesls:minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine J. 2015;15(7):1536-1544.
[28] Takata Y,Matsuura T,Higashino K,et al.Hybrid technique of cortical bone trajectory and pediele screwing for minimally invasive spine reconstruction surgery:A technical note.J Med Invest. 2014;61(3-4): 388-392.
[29] Goffin J,Van Brussel K,Martens K,et al. Three-dimensional computed tomography-based personalized drill guide for posterior cervical stabilization at C1-C2. Spine. 2001;26(12):1343-1347.
[30] 胡勇,袁振山,董伟鑫,等.数字化导向模板技术辅助置钉治疗寰枢椎不稳的临床应用[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014,30(8): 768-773. |
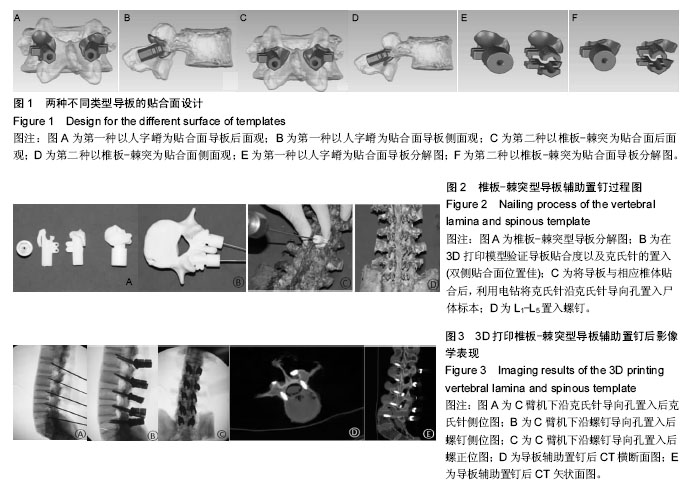
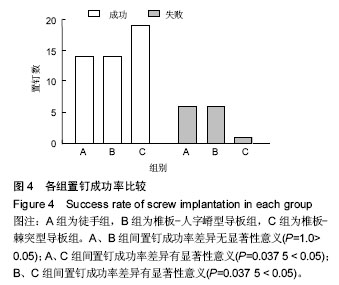
.jpg)
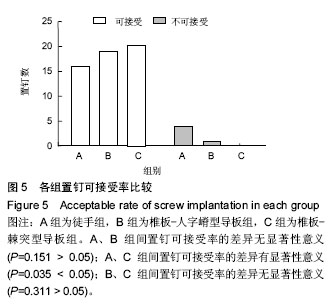
.jpg)