| [1]袁广银,章晓波,牛佳林,等.新型可降解生物医用镁合金JDBM的研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报, 2011,21(10): 2476-2488.
[2]陈宝爱,罗七一.可降解支架材料热学?机械性能及与受体的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(29):5475-5478.
[3]Stack RS, Califf RM, Phillips HR, et al. Interventional cardiac catheterization at Duke Medical Center. Am J Cardiol. 1988;62(10 Pt 2):3F-24F.
[4]郭清奎.用于制备完全生物可降解心血管支架的高分子聚合物材料的生物相容性降解性能和生物力学性能研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2012.
[5]冯海全,孙丽丽,韩青松,等.狭窄血管内支架变形行为及力学性能模拟研究?[J].功能材料, 2015(22):22085-22089, 22094.
[6]章晓波,毛琳,张佳,等.Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr可降解镁合金心血管支架的制备及性能研究[C]//第二届生物材料与组织工程产品质量控制国际研讨会论文集.2011:142-148.
[7]葛淑萍.WE可降解镁基血管支架材料的制备及其生物学性能的研究[D].重庆:重庆大学,2012.
[8]范仲雄,智丽丽,郭富强,等.镁合金在植入医疗器械中的应用进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志, 2015,38(4): 242-246.
[9]郭莉莎,何永辉,王娟,等.生物可降解Mg-2Zn-0.2Mn合金的体外生物相容性[J].材料科学与工程学报, 2013,31(5): 703.
[10]张璐,宁成云,滕伟,等.不同改性处理钛表面对血小板黏附行为影响的比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2015,50(9): 565-569.
[11]彭程.生物可降解聚合物材料的物理性能与组织相容性降解性能研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2014.
[12]易雷,周倩,蒋小莹,等.镁合金可降解血管支架发展历史与研究现状[J].医学与哲学,2015(6):60-62,91.
[13]Antonsen L, Maeng M, Thayssen P, et al. Intimal hyperplasia and vascular remodeling after everolimus-eluting and sirolimus-eluting stent implantation in diabetic patients: the randomized Diabetes and Drug-Eluting Stent (DiabeDES) IV Intravascular Ultrasound trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;83(6):864-872.
[14]武欣,谷涌泉,段红永,等.可降解组织工程血管支架成功用于犬股动脉移植[C]//2011东莞第二届国际小型猪学术论坛暨大型实验动物生物医药研究应用研讨会论文集, 2011: 406-410.
[15]于婷,曲守方,黄杰,等.医疗器械体外细胞毒性试验相关标准的比较及有关内容的商榷[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2015, (6):858-860.
[16]赵丹阳,顿锁,田慧卿,等.生物可降解聚合物血管支架膨胀性能有限元分析[J].大连理工大学学报, 2014,54(1): 54-59.
[17]郭清奎.生物可降解材料聚乳酸/聚羟基乙酸复合壳聚糖在人工冠状动脉血管支架制备中的应用[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志,2012,19(3):314-317.
[18]皇甫强,袁思波,韩建业,等.生物可降解血管支架研究进展[J].中国材料进展,2015,34(5):396-400.
[19]毛琳,Kwak Minsuk,沈雳,等.可降解镁合金血管支架炎症反应及支架内再狭窄研究[C]//第十四届全国青年材料科学技术研讨会论文集.2013:310.
[20]郭清奎,吕志前.可完全生物降解材料聚乳酸-聚羟基乙酸复合壳聚糖在人工心血管支架制备中的应用[J].北京生物医学工程,2011,30(6):652-655.
[21]程旭艳.AZ91D镁合金固态热扩渗锌及其耐腐蚀性能研究[D].西安:长安大学,2014.
[22]Bartkowiak-Jowsa M, B?dziński R, Koz?owska Anna, et al. Mechanical, rheological, fatigue, and degradation behavior of PLLA, PGLA and PDGLA as materials for vascular implants. Meccanica. 2013;48(3):721-731.
[23]Hlawaty H, Jacob MP, Louedec L, et al. Leukotriene receptor antagonism and the prevention of extracellular matrix degradation during atherosclerosis and in-stent stenosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009;29(4):518-524.
[24]季川祥.血管支架用Mg-Zn-Y-Nd(-Zr)合金组织及性能研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2014.
[25]Major A, Guidoin R, Soulez G, et al. Implant degradation and poor healing after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms: an analysis of explanted stent-grafts. J Endovasc Ther. 2006;13(4): 457-467.
[26]Colombo A, Guha S, Mackle JN, et al. Cyclic strain amplitude dictates the growth response of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro: role in in-stent restenosis and inhibition with a sirolimus drug-eluting stent. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2013;12(4):671-683.
[27]Grabow N, Bünger CM, Kischkel S, et al. Development of a sirolimus-eluting poly (L-lactide)/poly (4-hydroxybutyrate) absorbable stent for peripheral vascular intervention. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2013; 58(5): 429-437.
[28]Zahedmanesh H, Lally C. Determination of the influence of stent strut thickness using the finite element method: implications for vascular injury and in-stent restenosis. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009;47(4): 385-393.
[29]Strickler F, Richard R, McFadden S, et al. In vivo and in vitro characterization of poly(styrene-b-isobutylene- b-styrene) copolymer stent coatings for biostability, vascular compatibility and mechanical integrity. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;92(2):773-782.
[30]Kang KW, Ko YG, Shin DH, et al. Impact of positive peri-stent vascular remodeling after sirolimus-eluting and paclitaxel-eluting stent implantation on 5-year clinical outcomes: intravascular ultrasound analysis from the Poststent Optimal Stent Expansion Trial multicenter randomized trial. Circ J. 2012;76(5): 1102-1108.
[31]Liu T, Zeng Z, Liu Y, et al. Surface modification with dopamine and heparin/poly-L-lysine nanoparticles provides a favorable release behavior for the healing of vascular stent lesions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(11):8729-8743.
[32]Piorkowski M, Freitas B, Schmidt A, et al. The use of the GORE® TIGRIS® Vascular Stent with dual component design in the superficial femoral and popliteal arteries at 6 months. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2013;54(4):447-453.
[33]Han DW, Jung DY, Park JC, et al. Underlying mechanism for suppression of vascular smooth muscle cells by green tea polyphenol EGCG released from biodegradable polymers for stent application. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(2):424-433.
[34]王文革,邹兴政,王宏,等.一种新型医用高氮无镍不锈钢的生物相容性研究[J].功能材料,2013,44(16):2362-2366.
[35]Shirota T, Yasui H, Shimokawa H, et al. Fabrication of endothelial progenitor cell (EPC)-seeded intravascular stent devices and in vitro endothelialization on hybrid vascular tissue. Biomaterials. 2003;24(13):2295-2302.
[36]章晓波,毛琳,袁广银,等.心血管支架用Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr生物可降解镁合金的性能研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(6):1300-1305. |
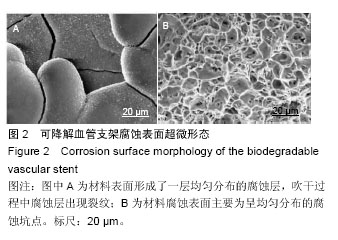
.jpg)

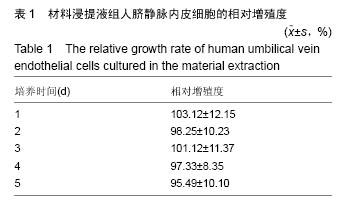
.jpg)
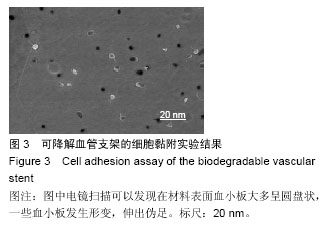
.jpg)