| [1] Pappou IP,Papadopoulos EC,Swanson AN,et al. Osteoporotic Vertebral Fractures and Collapse With Intravertebral Vacuum Sign (Kümmel’s Disease). Orthopedics. 2008;31(1):61-66.
[2] Kümmell H. Die rarefizierende ostitis der Wirbelkorper. Deuts che Med.1895;21(1): 180-181.
[3] Wu AM,Chi YL,Ni WF.Vertebral Compression Fracture with Intravertebral Vacuum Cleft Sign: Pathogenesis, Image, and Surgical Intervention.Asian Spine J. 2013; 7(2):148-155.
[4] Li KC,Li AF,Hsieh CH, et al. Another option to treat Kümmell's disease with cord compression. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9):1479-1487.
[5] Li H,Liang CZ,Chen QX.Kümmell's disease, an uncommon and complicated spinal disorder: a review.J Int Med Res.2012;40(2):406-414.
[6] Yang H,Pan J,Wang G.A review of osteoporotic vertebral fracture nonunion management. Spine. 2014; 39(26):B4-6.
[7] Heo DH,Chin DK,Yoon YS,et al.Recollapse of previous vertebral compression fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Osteoporos Int.2009;20(3):473-480.
[8] Park SJ,Kim HS,Lee SK,et al.Bone Cement- Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation: An Effective Treatment for Kummell's Disease? J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(1):54-59.
[9] 黎一兵,闫宏伟.经椎弓根椎体内骨水泥强化结合后路短节段内固定治疗Kummell病43例[J].陕西医学杂志, 2015, 44(3):317-320.
[10] Matzaroglou C,Georgiou CS,Panagopoulos A,et al. Kümmell's Disease: Clarifying the Mechanisms and Patients' Inclusion Criteria.Open Orthop J. 2014;15(8):288-297.
[11] Chow JH,Chan CC.Validation of the Chinese version of the Oswestry Disability Index. Work. 2005;25:307-314.
[12] Huang Y,Peng M,He S,et al.Clinical Efficacy of Percutaneous Kyphoplasty at Hyperextension Position for Treatment of Osteoporotic Kümell's Disease.J Spinal Disord Tech.2015.[Epub ahead of print].
[13] Matzaroglou C,Georgiou CS,Assimakopoulos K,et al.Kümmell's disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment and the role of nuclear medicine. Rationale according to our experience.Hell J Nucl Med. 2011;14(3):291-299.
[14] 杨圣,芦建民,赵德伟,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥结合椎体成形重建非感染性缺血坏死的椎体[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2001,14(51):9683-9686.
[15] Lee SH,Kim ES,Eoh W.Cement augmented anterior reconstruction with short posterior instrumentation: a less invasive surgical option for Kummell's disease with cord compressionJ Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(4): 509-514.
[16] Chen L,Dong R,Gu Y,et al.Comparison between Balloon Kyphoplasty and Short Segmental Fixation Combined with Vertebroplasty in the Treatment of Kümmell's Disease.Pain Physician.2015;18(4):373-381.
[17] 任海龙,王吉兴,陈建庭,等. 单侧与双侧穿刺经皮椎体成形术治疗Kummell's病的临床对比[J].南方医科大学学报, 2014,34(9):1370-1374.
[18] Kanayama M, Ishida T, Hashimoto T. Role of major spine surgery using Kaneda Anterior instrumentation for osteoporoticvertebral collapse.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010;23(1): 53-56.
[19] McConnell CT Jr,Wippold FJ 2nd,Ray CE Jr,et al.ACR appropriateness criteria management of vertebral compress fratures.J Am Coll Radiol. 2014;11(8):757-763
[20] Wang H,Sribastav SS,Ye F,et al.Comparison of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and Balloon Kyphoplasty for the Treatment of Single Level Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Meta-analysis of the Literature.Pain Physician.2015;18(3):209-222.
[21] Kim KH,Kuh SU,Chin DK,et al.Kyphoplasty versus vertebroplasty: restoration of vertebral body height and correction of kyphotic deformity with special attention to the shape of the fractured vertebrae.J Spinal Disord Tech.2012;25(6):338-344.
[22] Kim YC,Kim YH,Ha KY.Pathomechanism of intravertebral clefts in osteoporotic compression fractures of the spine.Spine J.2014;14(4):659-666.
[23] Ren H,Wang J,Chen J,et al.Clinical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular percutaneous vertebroplasty for Kummell's disease.J South Med Univ. 2014;34(9):1370-1374.
[24] Kong LD,Wang P,Wang LF,et al.Comparison of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty in the treatment of osteoporoticvertebral compression fractures with intravertebral clefts.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24( Suppl 1):S201-208.
[25] Yang H,Gan M,Zou J,et al.Kyphoplasty for the treatment of Kümmell's disease. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(7):479.
[26] Wiggins MC,Sehizadeh M,Pilgram TK,et al. Importance of intravertebral fracture cleft in vertebroplasty outcome.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;188(3):634-640. |
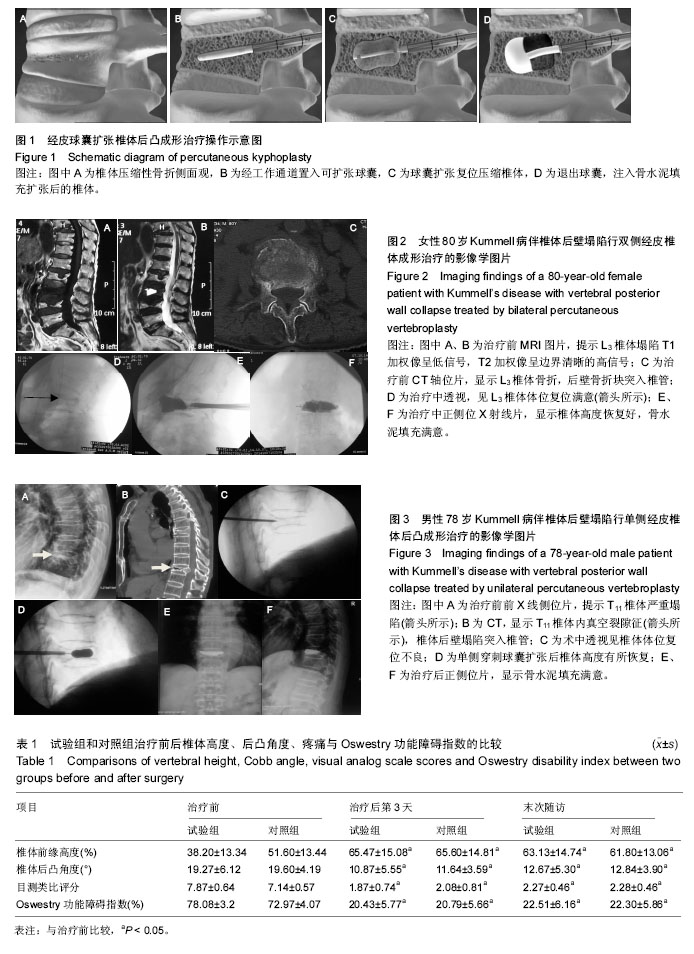
.jpg)
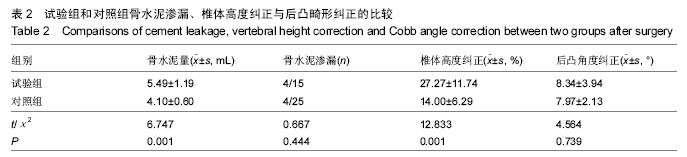
.jpg)