| [1] Cheung C.The future of bone healing.Clin Podiatr Med Surg North Am.2005;22(4): 631-641. [2] Ogden JA,Alvarez RG,Levitt R,et al.Shock wave therapy (orthotripsy) in musculoskeletal disorders.Clin Orthop.2001;387:22-40.[3] Carano RAD,Filvaroff EH.Angioganesis and bone repair.Drug Discovery Today. 2003;8(21):980-989. [4] Karladani AH,Granhed H,Edshage B,et al.Displaced tibial shaft fractures. A prospective randomized study of closed intramedullary nailing versus cast treatment in 53 patients.Acta Orthop Scand. 2000;71:160-167.[5] Albrektsson T,Sennerby L.Direct bone anchorage of oral implants: clinical and experimental considerations of the concept of osseointegration. Int J Prosthodont. 1990;3(1):30-41.[6] Grotberg J,Hamlekhan A,Butt A,et al.Thermally oxidized titania nanotubes enhance the corrosion resistance of Ti6Al4V.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;1(59):677-689.[7] Butt A,Hamlekhan A,Patel S,et al.A Novel Investigation of the Formation of Titanium Oxide Nanotubes on Thermally Formed Oxide of Ti-6Al-4V.J Oral Implantol. 2015;41(5):523-531.[8] Li G,Liu S,Chen G,et al.Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Phalangeal Fracture Treated with Dorsolateral Approach or Post-middle Approach Using AO Mini Titanium Plate.Indian J Surg.2015;77(Suppl 2):657-661.[9] Sakamoto M,Watanabe H,Higashi H,et al.Pseudotumor Caused by Titanium Particles From a Total Hip Prosthesis.Orthopedics.2015;28:1-4.[10] Balioglu MB,Albayrak A,Akman YE,et al.The effect of vertical expandable prosthetic titanium rib on growth in congenital scoliosis.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2015; 6(4):200-205.[11] Darouiche RO.Treatment of infections associated with surgical implants. New Engl J Med. 2004;350: 1422-1429.[12] Green SA,Ripley MS.Chronic osteomyelitis in pin tracks.J Bone Jt Surg 1984;66A:1092-1098.[13] Hargreaves DG,Drew SJ,Eckersley R.Kirschner wire pin tract infection rates: a randomized controlled trial between percutaneous and buried wires.J Hand Surg Brit Eur.2004;29(4):374-376.[14] Torres-Claramunt R,Gil-González S,Leal J,et al.A new score assessing the surgical wound of a TKA and its relation with pain, infection and functional outcome.Acta Orthop Belg.2015;81(4):713-719.[15] Kim YH,Kulkarni SS,Park JW,et al.Comparison of infection control rates and clinical outcomes in culture-positive and culture-negative infected total-knee arthroplasty.J Orthop.2015;12(Suppl 1): S37-43.[16] Green SA.Complications of external skeletal fixation. Clin Orthop Rel Res. 1983;180:109-116.[17] Kilgus DJ,Howe DJ,Strang A.Results of periprosthetic hip and knee infections caused by resistant bacteria.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2002;(404):116-124.[18] Aw MS,Simovic S,Addai-Mensah J,et al.Polymeric micelles in porous and nanotubular implants as a new system for extended delivery of poorly soluble drugs.J Mater Chem. 2011;21(20):7082-7089.[19] Brammer KS,Oh S Cobb CJ,et al.Improved bone-forming functionality on diameter-controlled TiO(2) nanotube surface.Acta Biomater. 2009;5(8): 3215-3123. [20] Gulati K,Aw MS,Losic D.Drug-eluting Ti wires with titania nanotube arrays for bone fixation and reduced bone infection.Nanoscale Res Lett.2011;31(6):571.[21] Gulati K,Ramakrishnan S,Aw MS,et al.Biocompatible polymer coating of titania nanotube arrays for improved drug elution and osteoblast adhesion.Acta Biomater. 2012;8(1):449-456. [22] Zhang H,Sun Y,Tian A,et al.Improved antibacterial activity and biocompatibility on vancomycin-loaded TiO2 nanotubes: in vivo and in vitro studies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:4379-4789. [23] 张杭州,孙羽,王琳,等.羟基磷灰石/TiO2纳米管复合物的生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,18(3):335-340.[24] Turner IG,Pilliar RM,Srichana T,et al.Sterility and Infection. In: Narayan R, ed. Biomedical Materials.New York,NY:Springer Science,2009:239-258.[25] Ribeiro M,Monteiro FJ,Ferraz MP.Infection of orthopedic implants with emphasis on bacterial adhesion process and techniques used in studying bacterial-material interactions.Biomatter. 2012;2(4): 176-194. [26] Costerton JW,Stewart PS,Greenberg EP.Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science.1999;284:1318-1322.[27] Ginebra MP,Traykova T,Planell JA.Calcium phosphate cements as bone drug delivery systems: a review.J Control Release.2006;113(2):102-110.[28] Masse A,Bruno A,Bosetti M,et al.Prevention of pintrack infection in external fixation with silver coated pins:clinical and microbiological results.J Biomed Mater Res.2000;53:600-604.[29] Mankin HJ,Hornicek FJ,Raskin KA.Infection in massive bone allografts.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (432):210-216.[30] Collins I,Wilson-MacDonald J,Chami G,et al.The diagnosis and management of infection following instrumented spinal fusion.Eur Spine J. 2008;17(3): 445-450.[31] Proctor RA,von Eiff C,Kahl BC,et al.Small colony variants: a pathogenic form of bacteria that facilitates persistent and recurrent infections.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2006;4(4):295-305.[32] Neut D, Kluin OS, Crielaard BJ,et al.A biodegradable antibiotic delivery system based on poly-(trimethylene carbonate) for the treatment of osteomyelitis.Acta Orthop. 2009; 80(5):514-519.[33] Zhang DY,Tian A,Xue X,et al.The Effect of Temozolomide/PLGA/ nano-hydroxyapatite Microspheres on Glioma U87 Cells Behavior.Int J Mol Sci.2012;13:1109-1125.[34] Moseke C,Hage F,Vorndran E,et al.TiO2 nanotube arrays deposited on Ti substrate by anodic oxidation and their potential as a long-term drug delivery system for antimicrobial agents.Appl Surf Sci. 2012;258: 5399-5404.[35] Song YY,Schmidt-Stein F,Bauer S,et al.Amphiphilic TiO2 nanotube arrays: an actively controllable drug delivery system.J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131(12): 4230-4232. [36] Gulati K,Aw MS,Findlay D,et al.Local drug delivery to the bone by drug-releasing implants: perspectives of nano-engineered titania nanotube arrays.Ther Deliv. 2012;3(7):857-873.[37] Peng L,Mendelsohn AD,Latempa TJ,et al.Long-term small molecule and protein elution from TiO2 nanotubes. Nano Lett.2009;9(5):1932-1936. |
.jpg)

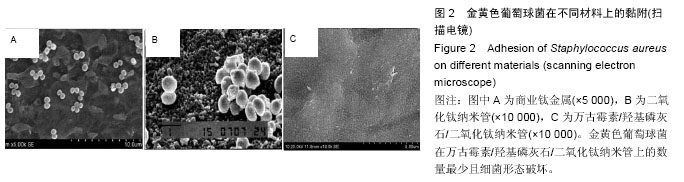
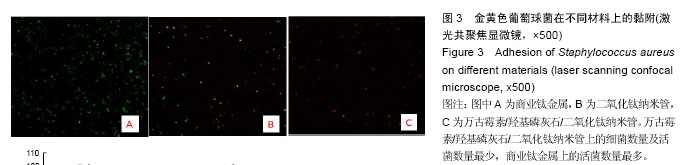
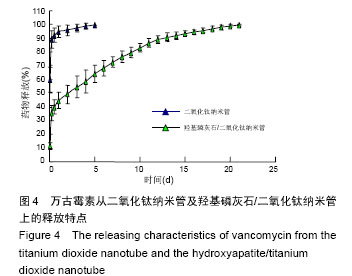
.jpg)
.jpg)