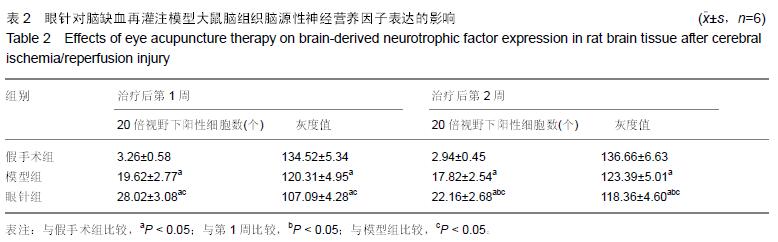
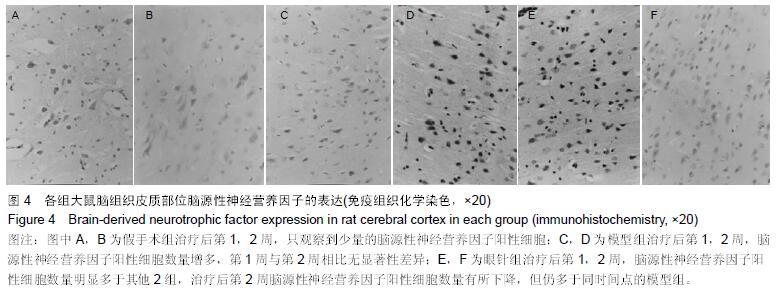
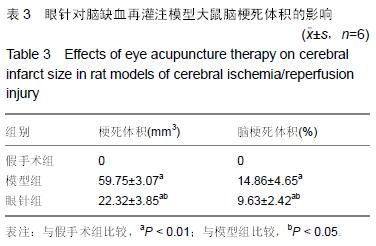
| [1] Che J, Piao LH, Tian WZ. Professor Tian Wei-zhu's clinical experiences in acupuncture treatment of stroke. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2007;27(8):609-611. [2] Huang J, McCaskey MA, Yang S, et al. Effects of acupuncture and computer-assisted cognitive training for post-stroke attention deficits: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2015;16(1):546. [3] Zhang S, Zhang LH, Wang YJ, et al. Effects of synchronous treatment of bilateral scalp acupuncture and rehabilitation training on activities of daily life in patients with cerebral infarction at acute phase. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2014;34(9):837-840. [4] Bai ZH, Zhang ZX, Li CR, et al. Eye acupuncture treatment for stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:871327. [5] Zhou HF, Wang J, Cao TJ, et al. Effects of eye acupuncture on SEPCT-determined cerebral blood flow in patients with cerebral infarction. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2011;31(5):391-394. [6] Lu H, Liu X, Zhang N, et al. Neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and noggin-modified bone mesenchymal stem cells in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016; 25(2):410-418. [7] Cheng CY, Lin JG, Su SY, et al. Electroacupuncture- like stimulation at Baihui and Dazhui acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects through activation of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-mediated MEK1/2/ERK1/2/p90RSK/bad signaling pathway in mild transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:92. [8] Kong SY, Li QF, Yang J, et al. The effect of butylphthalide on expression of NGF and BDNF in ischemia stroke tissue of rat cerebrum. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007;38(3):400-403, 407. [9] 王刚,范顺武,李强,等.神经生长因子梯度缓释系统促进周围神经再生的临床疗效观察[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2013, 36(6):558-562. [10] 赵淑杰,朱雨岚.脑源性神经营养因子对帕金森病大鼠多巴胺能神经元的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2015, 18(13):40-41. [11] Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91. [12] 田维柱.中华眼针[M].沈阳:辽宁科技出版社,1998:78-85. [13] 王鹏琴,王健,周鸿飞.眼针对急性脑梗死患者神经功能缺损及血浆纤维蛋白原水平的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2006,21(2):118-120. [14] 姜华锋.眼针运动疗法并用治疗中风恢复期30例[J].实用中医内科杂志,2009,23(5):95-96. [15] 荆思琪,王鹏琴.彭氏眼针治疗头痛疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2015,34(11):1038-1039. [16] 常红专,卢建立,阴盛奎.眼针治疗急性腰扭伤56例报告[J].河南实用神经疾病杂志,2001,4(5):81. [17] 胡玉莲,林强,厉岩.眼针治疗原发性痛经疗效观察[J].上海针灸杂志,2011,30(6):370-371. [18] 何宇,何川,孙年怡,等.作业治疗结合眼针对脑卒中患者日常生活活动能力和上肢运动功能的疗效观察[J].中国康复医学杂志,2015,30(9):949-950. [19] 张雪松.眼针治疗脑中风26例疗效观察[J].实用中医内科杂志,2010,24(2):100-101. [20] Cheng S, Ma M, Ma Y, et al.Combination therapy with intranasal NGF and electroacupuncture enhanced cell proliferation and survival in rats after stroke. Neurol Res. 2009;31(7):753-758. [21] Andsberg G, Kokaia Z, Björklund A,et al.Amelioration of ischaemia-induced neuronal death in the rat striatum by NGF-secreting neural stem cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10(6):2026-2036. [22] 禄韶英,王燕.神经生长因子对脑缺血大鼠学习与记忆的影响[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2012,11(4): 339-342. [23] Li HF, Wang YR, Huo HP, et al.Neuroprotective effects of ultrasound-guided nerve growth factor injections after sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10 (11): 1846-1855. [24] 刘鹏,王瑾,苗常青,等.大鼠局灶性脑缺血后神经营养因子表达的自然变化[J].卒中与神经疾病,2015,22(4): 211-214. [25] Solev IN, Balabanyan VY, Volchek IA, et al. Involvement of BDNF and NGF in the mechanism of neuroprotective effect of human recombinant erythropoietin nanoforms. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2013; 155(2):242-244. [26] Kokaia Z, Zhao Q, Kokaia M, et al. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion with and without brain damage.Exp Neurol. 1995;136(1):73-88. [27] Choi Y, Kang SG, Kam KY. Changes in the BDNF-immunopositive cell population of neocortical layers I and II/III after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2015;16(5):76-82. [28] Harada S, Fujita-Hamabe W, Tokuyama S. Ameliorating effect of hypothalamic brain-derived neurotrophic factor against impaired glucose metabolism after cerebral ischemic stress in mice. J Pharmacol Sci. 2012;118(1):109-116. [29] Guan J, Tong W, Ding W, et al. Neuronal regeneration and protection by collagen-binding BDNF in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Biomaterials. 2012;33(5):1386-1395. [30] Wang Q, Mao-Draayer Y.Interferon beta (IFN-β) treatment exerts potential neuroprotective effects through neurotrophic factors and novel neurotensin/ neurotensin high affinity receptor 1 pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(12): 1932-1933. [31] Zhang YR, Zhang H, Zhang GC, et al.Combining acellular nerve allografts with brain-derived neurotrophic factor transfected bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells restores sciatic nerve injury better than either intervention alone. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9 (20): 1814-1819. [32] 马贤德,王守岩,张威.眼针对脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠脑组织BDNF、p75NTR表达影响及其脑保护作用机制[J].北京中医药大学学报,2014,37(1):48-52. [33] 王欢,郭峰,单德红,等.眼针对脑缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠海马区BDNF及TrkB表达的影响[J].吉林中医药, 2011, 31(5): 475-477. [34] 王哲,王守岩,王德山,等.眼针对急性脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠海马组织BDNF表达影响[J].针灸临床杂志, 2011, 27(7):57-60. |
.jpg)
.jpg)