中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (18): 2628-2633.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.18.007
• 周围神经损伤动物模型 Animal models of peripheral nerve injury • 上一篇 下一篇
脑及脊髓冲击震动损伤模型生化指标的变化
朱亚鹏1,郭延岭2,常 祺2
- 1解放军第四军医大学第一附属医院骨科医院,骨科研究所,陕西省西安市 710032;2解放军150中心医院,河南省洛阳市 471000
Changes of biochemical indexes in the brain and spinal cord after shock and vibration damage
Zhu Ya-peng1, Guo Yan-ling2, Chang Qi2
- 1Institute of Orthopedics, Orthopedic Hospital, First Affiliated Hospital, the Fourth Military Medical University, Xi’an 710032, Shaanxi Province, China; 2PLA 150 Central Hospital, Luoyang 471000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
.jpg)
文题释义:
冲击伤:是冲击波超压和负压引起的损伤,主要造成含气器官如肺脏、听器、胃肠道的损害,超强压还可以造成内脏破裂和肋骨骨折等,但一般较少造成体表损伤。单纯冲击伤致伤时,体表多完好无损,但常有不同程度的内脏损伤,表现为外轻内重的特点。
生化指标:全套主要包括肝功能(总蛋白、白蛋白、球蛋白、白球比,总胆红素、直接、间接胆红素,转氨酶);血脂(总胆固醇,三酰甘油,高、低密度脂蛋白,载脂蛋白);空腹血糖;肾功能(肌酐、尿素氮);尿酸;乳酸脱氢酶;肌酸肌酶等。
背景:高能震动易于损伤机体非空腔器官且损伤效应显著,但目前针对高能震动致伤过程的研究较少。
目的:了解高能震动致伤后动物机体生理生化及病理改变。
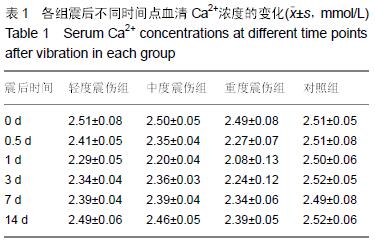
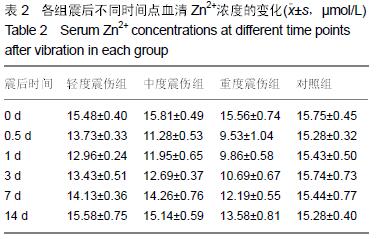
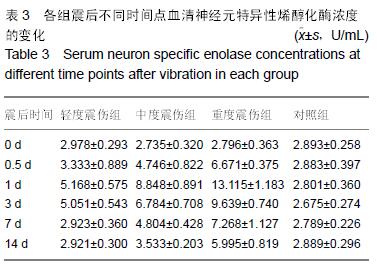
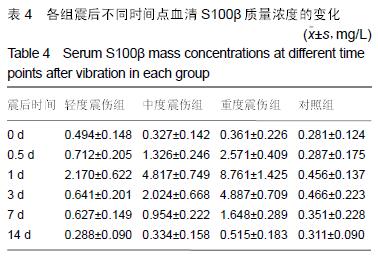
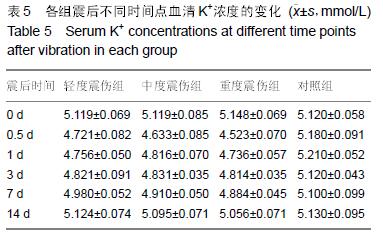
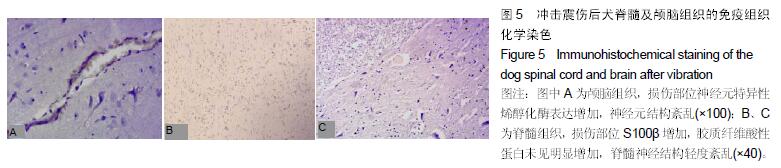
方法:将32只中华田园犬随机分为4组,轻度震伤组、中度震伤组及重度震伤组分别实施700,1 000,2 100 m/s²的冲击震动,对照组为正常对照。于震后14 d内检测血清血清K+、Ca2+、Zn2+、S100β、神经元特异性烯醇化酶浓度,并进行脊髓及颅脑组织免疫组织化学染色观察。
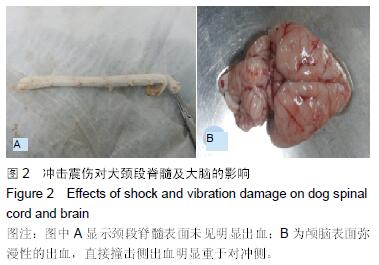
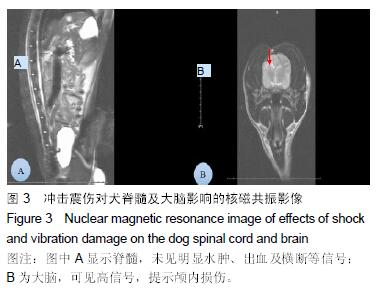
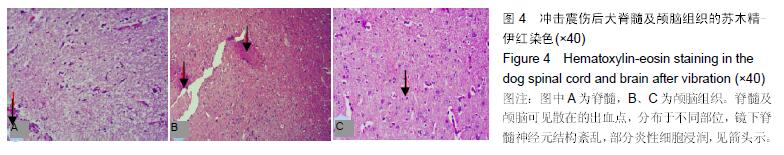
结果与结论:震伤3组血清K+、Ca2+、Zn2+浓度呈现规律性变化,震后即时无明显变化,K+浓度于震后0.5 d降到最低,Ca2+浓度至震后1 d降到最低,Zn2+浓度于震后0.5 d或1d降到最低,此后均逐渐增加,至14 d时恢复正常水平;震伤3组血清神经元特异性烯醇化酶、S100β均于震后0.5 d开始增加,于震后1 d达到最高值,此后均逐渐降低,至14 d时恢复至正常或偏高水平。震伤3组脊髓及颅脑均出现接触部位及对冲部位的出血点,震后即时处死时出血程度较14 d时明显,脊髓及颅脑损伤部位S100β、胶质纤维酸性蛋白、神经元特异性烯醇化酶增多。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-4550-8911(常祺)
.jpg)
.jpg)