中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (17): 2451-2458.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.17.003
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
有限元分析全膝关节置换股骨假体置入定位参数及临床优化验证
徐高伟1,董 斌1,崔海勇1,马 强2
- 1安徽理工大学第一附属医院(淮南市第一人民医院),安徽省淮南市 232007;2安徽医科大学第一附属医院,安徽省合肥市 230601
Finite element analysis of femoral prosthesis implant in total knee arthroplasty: positioning parameters and clinical optimization
Xu Gao-wei1, Dong Bin1, Cui Hai-yong1, Ma Qiang2
- 1First Affiliated Hospital (the First People’s Hospital of Huainan), Anhui University of Science & Technology, Huainan 232007, Anhui Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
全膝关节置换三维有限元仿真模型:是指对股骨假体截骨定位参数进行正交实验,选择股骨假体的平移量、外旋度数、外翻度数3个参数作为正交实验的相关因素,创建全膝关节置换膝关节的有限元模型。
活动平台型膝关节假体:其聚乙烯衬垫与托盘不固定,之间能够自由滑动和旋转,可以减少聚乙烯磨损和假体松动的风险,现阶段临床应用比较多的是活动性膝关节假体,该假体能够扩大相应界面与聚乙烯衬垫的接触面积,减少接触应力。
背景:三维有限元仿真分析在生物力学中有着广泛应用,但在膝关节置换中的研究不多,对股骨假体的研究也比较少。
目的:有限元分析膝关节置换股骨假体置入的优化定位参数,并对Gemini-PS膝关节假体全膝关节置换进行临床验证。
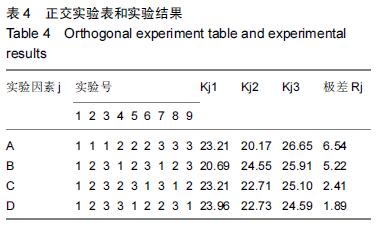
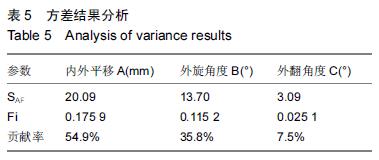
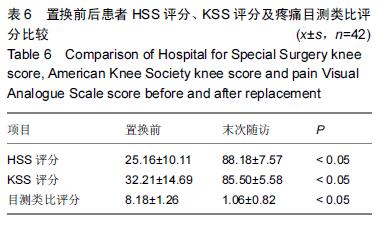
方法:①构建全膝关节置换膝关节有限元模型,对股骨假体截骨定位参数进行正交实验,选择股骨假体的平移量A、外旋度数B、外翻度数C 3个参数作为正交实验的相关因素,每个参数取3个值建立正交表,创建9个实验组合的全膝关节置换膝关节的有限元模型,对9个模型进行有限元分析,通过优化处理进行方差和极差分析。②纳入42例(47膝)中老年膝骨关节炎患者,采用Gemini-PS 膝关节假体进行全膝关节置换,采用美国特种外科医院膝关节评分及美国膝关节协会评分评价置换前后膝关节功能,以疼痛目测类比评分评估置换前后膝关节疼痛程度。
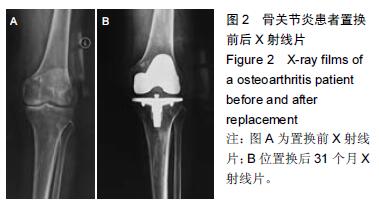
结果与结论:①聚乙烯衬底表面压应力峰值最小的为平移0 mm,外旋3°,外翻6°组合,压应力峰值为15.9 MPa;聚乙烯衬垫表面压应力的影响因素中,内外平移的影响大于外旋角度的影响大于外翻角度的影响;通过极差分析和方差分析发现股骨假体置入的最佳定位参数组合为平移0 mm,外旋3°,外翻6°;通过仿真计算证明正交实验是有效的;②42例患者均得到随访,随访时间12-36个月,1例发生术口下段皮下脂肪液化;置换后末次随访患膝美国特种外科医院膝关节评分及美国膝关节协会评分均较置换前显著提高(P < 0.05);置换后疼痛目测类比评分较置换前显著降低(P < 0.05)。X射线检查未发现骨溶解、假体脱位及松动等并发症,置换后膝关节功能恢复良好;③结果提示,股骨假体置入位置的微小变化都会引起聚乙烯衬垫表面压应力峰值的异常分布,全膝关节置换术中对股骨假体进行准确定位可以取得良好的置换效果。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3861-0467(徐高伟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-3861-0467(徐高伟)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
#br#