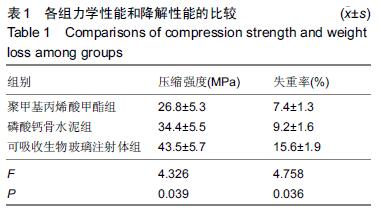
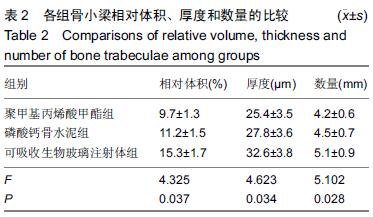
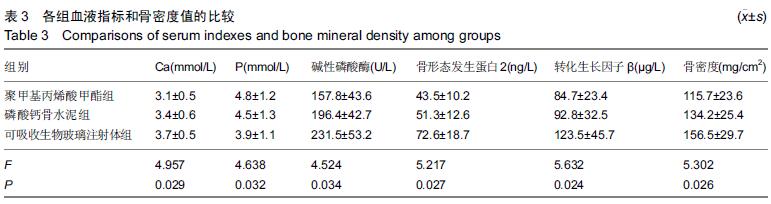
| [1] Zhang YP,Xia RY,Zhang B,et al.Gender Differences on Osteoporosis Health Beliefs and Related Behaviors in Non-academic Community Chinese.J Community Health. 2014;39(3):545-551. [2] Bonura F.Prevention,screening,and management of osteoporosis:an overview of the current strategies. Postgrad Med.2009;121(4):5-17. [3] 吴建斌.不同填充材料及脂肪源干细胞移植对骨质疏松大鼠的影响[D].南方医科大学,2013. [4] Marciniak C,Gabet J,Lee J,et al.Osteoporosis in adults with cerebral palsy: feasibility of DXA screening and risk factors for low bone density.Osteoporos Int. 2015; 17(1):1-3. [5] 中国老年学学会骨质疏松委员会骨质疏松诊断标准学科组.中国人原发性骨质疏松症诊断标准(试行)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,1999,5(7):1-3. [6] 胡军,张华,牟青.骨质疏松症的流行病学趋势与防治进展[J].临床荟萃,2011,26(8):729-731. [7] 杨卫红,周建烈.补充钙和维生素D预防骨质疏松性骨折疗效述评[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(11):797-803. [8] 刘明,潘薇,陈德才.甲状旁腺激素治疗骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2012,5(2):151-156. [9] 杨丰建,林伟龙,朱炯,等.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(1):50-54. [10] Xu HHK, Zhao L,Detamore MS,et al.Umbilical cord stem cell seeding on fast-resorbable calcium phosphate bone cement.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16: 2743-2753. [11] Puska M,Moritz N,Aho AJ,et al.Morphological and mechanical characterization of composite bone cement containing polymethylmethacrylate matrix functionalized with trimethoxysilyl and bioactive glass.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2015;59:11-20. [12] Friedmann DP,Kurian A,Fitzpatrick RE. Delayed granulomatous reactions to facial cosmetic injections ofpolymethylmethacrylate microspheres and liquid injectable silicone: A case series.J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2016;6(1):1-13. [13] 叶冬平,周子强,梁伟国.一种可注射自固化含锶复合胶原磷酸钙骨水泥的结构和性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(38):7411. [14] Ginebra MP,Canal C,Espanol M,et al.Calcium phosphate cements as drug delivery materials.Adv Drug Del Rev.2012;64(1):1090-1110. [15] Hoppe A,Guldal NS,Boccaccini AR.A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials. 2011; 32(11):2757-2774. [16] Gerhardt LC,Widdows KL,Erol MM,et al.The pro-angiogenic properties of multi-functional bioactive glass composite scaffolds.Biomaterial. 2011;32(17): 4096-4108. [17] Hautamaki M,Meretoja VV,Mattila RH,et al.Osteoblast response to polymethyl methacrylate bioactive glass composite.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21:1685-1692. [18] 于龙. 可注射生物玻璃-磷酸钙骨水泥复合生物材料的实验研究[D].第四军医大学,2013. [19] 李素萍.骨质疏松动物模型的研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(20):3767-3770. [20] 虞惊涛,马信龙,马剑雄.骨质疏松动物模型评价方法[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2014,7(1):66-70. [21] 张智海,刘忠厚,李娜,等.中国人骨质疏松症诊断标准专家共识(第三稿•2014版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(9): 1007-1010. [22] Huan ZG,Chang J.Calcium-phosphate-silicate composite bone cement:self-setting properties and in vitro bioactivity.J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2009;20(1): 833-841. [23] Lanao RPF,Leeuwenburgh SCG,Wolke JGC,et al.In vitro degradation rate of apatite calcium phosphate cement with incorporated PLGA microspheres.Acta Biomater.2011; 7(1): 3459-3468. [24] 卢锦东,谢平金.骨质疏松大鼠造模法研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2015,17(5):248-251. [25] 郭鱼波,马如风,王丽丽,等.骨质疏松动物模型及其评价方法的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(9): 1149-1154. [26] Zhang YF,Han JX.Progress in research on animal model of osteoporosis.Prog Vet Med.2005;12(3):8-11. [27] Ryf C,Goldhahn S,Radziejowski M,et al.A new injectable brushite cement: first results in distal radius and proximal tibia fractures.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2009;35(6):389-396. [28] Rojbani H,Nyan M,Ohka K,et al.Evaluation of the osteoconductivity of α-tricalcium phosphate, β-tricalcium phosphate, and hydroxyapatite combined with or without simvastatin in rat calvarial defect.J Biomed Mater Res Part A.2011;98(3):488-498. [29] 樊博,王臻,吴畅,等.生物玻璃条索修复骨缺损的有效性研究[J].解放军医学杂志,2014,39(4):283-287. [30] 李阳,吴子祥,雷伟.生物玻璃生物学性能及其临床应用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2012,33(3):160-162. [31] 李阳, 雷伟,王征,等.生物玻璃和壳聚糖改性的多孔活性骨水泥体内实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(3):320-325. [32] Yuan H,Bruijn JD,Zhang X,et al.Bone induction by porous glass ceramic made from Bioglass(45S5).J Biomed Mater Res.2001;58(3):270-276. [33] Kirk JF,Ritter G,Waters C,et al.Osteoconductivity and osteoinductivity of NanoFUSE® DBM.Cell Tissue Bank.2012;14(1):33-44. [34] 李玉莉,陈晓峰,韩雪,等.微纳米生物玻璃的体外成骨性能研究[J].中国材料进展,2012,31(6):7-12. [35] 郑德宇,杨依勇,赵凯,等.生物玻璃活性陶瓷复合人骨形态发生蛋白2基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞修复颅骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(42):7807-7810. [36] 李扬,刘怡卓,郭亚平,等.介孔生物玻璃对人骨髓间充质干细胞早期黏附增殖行为的影响[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2013,10(4):8-14. [37] Ghodasra JH,Weatherford BM,Nickoli MS,et al.The effect of rhBMP-2 in a novel, non-instrumented extremity nonunion model.J Orthop Sci. 2015;28(12): 23-25. [38] 沈宇辉,邓廉夫,潘浩波,等.含锶可降解生物陶瓷及生物玻璃骨植入材料研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2011,32(2): 75-77. [39] 孙君超,肖荣驰.生物活性玻璃复合材料研究进展[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(3):27-30. |
.jpg)


.jpg)