中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2184-2189.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.008
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
甘草黄酮对运动大鼠骨骼肌Perilipin mRNA及蛋白表达的影响
王成科1,莫伟彬2,3,潘昌红2,张 蒙2,黄 东2
- 1广西民族师范学院体育系,广西壮族自治区崇左市 532200;2广西师范大学体育学院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004;3药用资源化学与药物分子工程教育部重点实验室,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541004
Effects of Glycyrrhiza flavonoids on expression of perilipin mRNA and protein in skeletal muscle of rats after exhaustive exercise
Wang Cheng-ke1, Mo Wei-bin2, 3, Pan Chang-hong2, Zhang Meng2, Huang Dong2
- 1Department of Sports, Guangxi Normal University for Nationalities, Chongzuo 532200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Sport School of Guangxi Normal University, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3State Key Laboratory Cultivation Base for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources, Ministry of Science and Technology of China, Guilin 541004, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
甘草黄酮:黄酮类化合物,对肌肉组织具有抗自由基能力、保护肌肉的损伤、抗炎、减轻脂质过氧化的反应和调控脂肪组织方面的作用。
围脂滴蛋白:是一类细胞结构,同属于PAT蛋白家族,根据基因的编码不同,分为peri A、peri B和peri C等3种亚型,具有调控机体各脂肪组织的储存、释放和参与机体代谢的功能,其表达主要存在于腓肠肌、比目鱼肌、趾长伸肌、小肠、肝和心肌等组织中。
背景:甘草黄酮对肌肉组织具有抗自由基能力、保护肌肉的损伤、抗炎、减轻脂质过氧化的反应和调控脂肪组织方面的作用。
目的:通过研究甘草黄酮干预作用下运动性大鼠骨骼肌围脂滴蛋白mRNA及蛋白表达的作用及可能机制,观察甘草黄酮对调控不同的脂肪组织的储存、释放和参与机体能量代谢的能力。
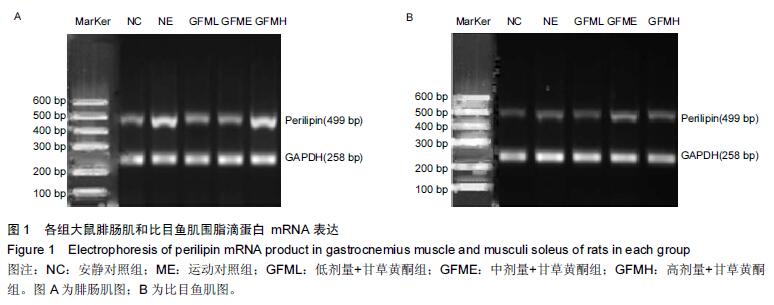
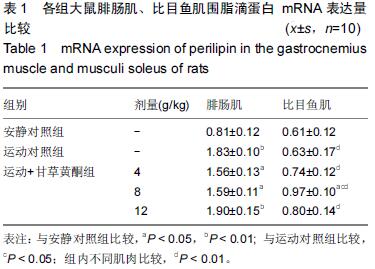
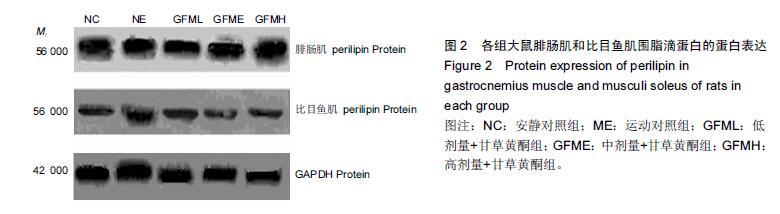
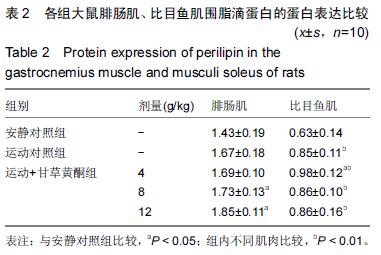
方法:SD雄性大鼠50只,每组10只,随机分为安静对照组、运动对照组、运动+甘草黄酮低、中、高剂量组。各组灌胃不同剂量甘草黄酮,对照组灌胃等量生理盐水,6周力竭运动训练后,处死大鼠。根据试剂盒的方法测定骨骼肌(腓肠肌和比目鱼肌)围脂滴蛋白 mRNA及蛋白表达水平。
结果与结论:运动对照组腓肠肌围脂滴蛋白mRNA表达水平高于安静对照组(P < 0.01);在甘草黄酮各组腓肠肌围脂滴蛋白 mRNA表达水平高于安静对照组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);运动+甘草黄酮中、高剂量组围脂滴蛋白蛋白表达高于安静对照组(P < 0.05)。运动+甘草黄酮中剂量组比目鱼肌围脂滴蛋白 mRNA表达水平高于安静对照和运动对照组(P < 0.05);同组比较时,运动对照组和在甘草黄酮各组比目鱼肌围脂滴蛋白 mRNA及蛋白表达均低于腓肠肌(P < 0.01)。结果提示甘草黄酮可能有利于改善骨骼肌纤维的有氧代谢能力和调控脂肪的酯解通路。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程 ORCID: 0000-0001-5864-8457(王成科)
.jpg)