中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2133-2139.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.001
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
黄精多糖调控骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化
农梦妮1,曾高峰1,宗少晖2,杜 力3,李柯柯4,彭小明4,严芳娜4
- 广西医科大学,1公共卫生学院,4研究生学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;2广西医科大学第一附属医院脊柱骨病外科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;3广西医科大学,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021
Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide regulates osteoblastic differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
Nong Meng-ni1, Zeng Gao-feng1, Zong Shao-hui2, Du Li3, Li Ke-ke4, Peng Xiao-ming4, Yan Fang-na4
- 1College of Public Health of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4Graduate School of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
文题释义:
wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用, 相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路。
wnt信号通路分类:①典型Wnt/β-catenin信号通路:此通路激活核内靶基因的表达,与Wnt家族分泌蛋白、Frizzled家族跨膜受体蛋白Dishevelled(Dsh)、糖原合成激酶3(GSK3)、APC、Axin、β-连环蛋白及TCF/LEF家族转录调节因子等构成了经典通路;②平面极细胞通路:此通路参与JNK的激活及细胞骨架的重排;③Wnt/Ca+通路:激活磷脂酶C和蛋白激酶C;④胞内通路:调节纺锤体的方向和非对称细胞分裂。
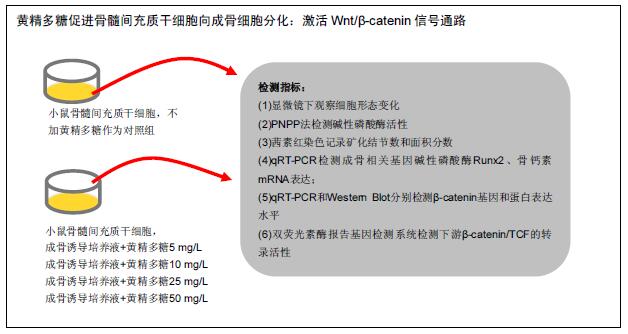
背景:骨髓间充质干细胞具有多向分化潜能。黄精多糖可能通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。
目的:探讨黄精多糖对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化过程中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响。
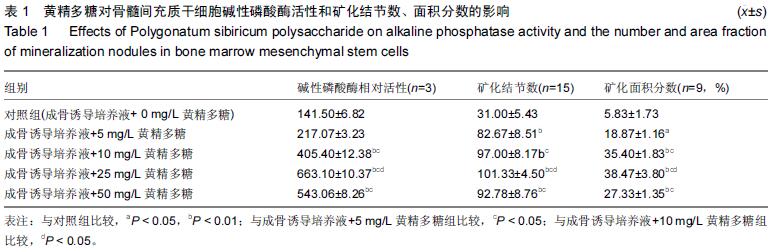
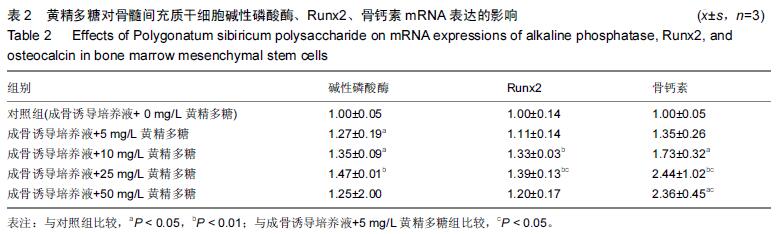
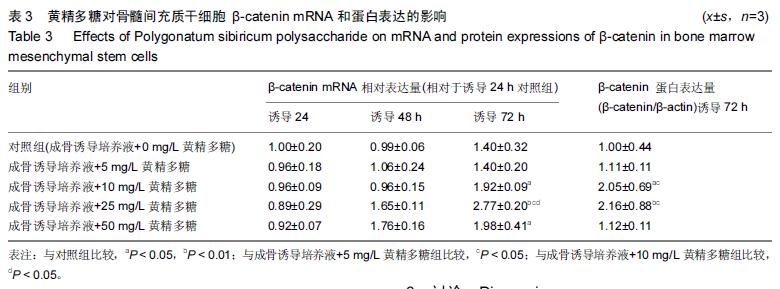
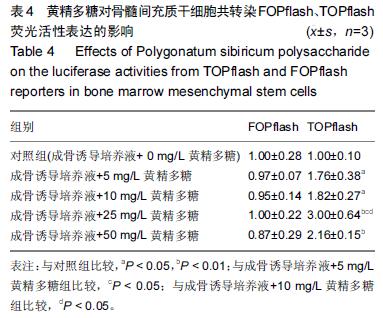
方法:培养小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,在传统成骨诱导培养基诱导下给予5,10,25,50 mg/L 黄精多糖进行干预,不加黄精多糖作为对照组,显微镜下观察细胞形态变化。PNPP法检测碱性磷酸酶活性;观察细胞发生矿化并进行茜素红染色,记录矿化结节数和面积分数;qRT-PCR检测成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶、Runx2、骨钙素mRNA表达;采用qRT-PCR和Western Blot分别检测β-catenin基因和蛋白表达水平;采用双荧光素酶报告基因检测系统检测下游β-catenin/TCF的转录活性。
结果与结论:①与对照组相比,不同质量浓度的黄精多糖以剂量依赖性的方式提高碱性磷酸酶活性(P < 0.05),显著增强细胞的矿化能力,明显提高碱性磷酸酶、Runx2、骨钙素基因的表达(P < 0.05);②诱导后β-catenin mRNA在第3天表达最高,黄精多糖在促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的过程中还能显著上调β-catenin的表达(P < 0.05),促使含有TCF结合位点的荧光素酶报告基因(TOPFlash)的高表达(P < 0.05);③说明黄精多糖通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0595-0043(曾高峰)