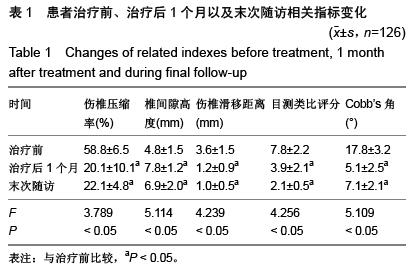
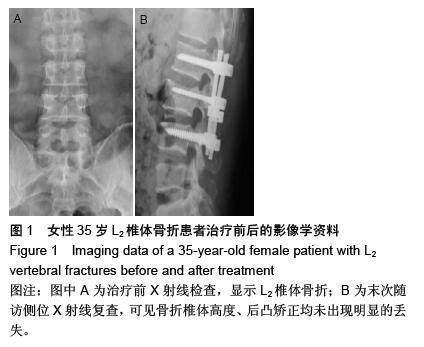
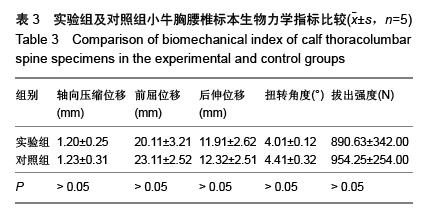
| [1] 李想,洪毅,唐和虎,等.短节段椎弓根钉内固定结合经伤椎椎体强化治疗胸腰椎骨折临床疗效的Meta分析[J].中国康复理论与实践,2012,18(5):440-443.[2] 于长水,杨卫良.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉置入内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(48):9065-9068.[3] 王洪伟,周跃,李长青,等.经伤椎与跨伤椎万向钉置钉固定脊柱骨折的生物力学对比研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2010,26(12): 1105-1108.[4] 徐桂军,马信龙,张弢,等.脊柱胸腰段骨折后路经伤椎单节段固定与常规短节段固定的力学性能比较[J].医用生物力学,2014, 29(2):126-130.[5] Yang H, Shi JH, Ebraheim M, et al. Outcome of thoracolumbar burst fractures treated with indirect reduction and fixation without fusion. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(7): 1193- 1193.[6] 李家谋,张昆亚,韩伟峰,等.短节段椎弓根螺钉置入内固定椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学检测[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39):7284-7287.[7] 成浩,徐建广,周蔚,等.后路椎弓根螺钉系统固定并颗粒型磷酸钙人工骨经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨治疗青壮年胸腰椎骨折30例随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(4):621-625.[8] 黄剑峰,宁锦龙,易椿均,等.微创经伤椎椎弓根植骨附加伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2011,5(22):6642-6647.[9] 徐学方,吴冰,单方军,等.胸腰椎爆裂性骨折经伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗52例疗效分析[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2014,38(8): 991-994.[10] 尹占民.经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨结合短节段钉棒系统内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折37例分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(4):369-371.[11] 李小斌,程俊文,周志康,等.微创经伤椎椎弓根植骨附加伤椎椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效观察[J].中国基层医药, 2015,(6):899-901.[12] 项良碧,祖启明,曹艳,等.植入椎弓根螺钉内固定胸腰椎骨折患者术后的矫正度丢失:植入体特征与临床技术的关系[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(5):953-956.[13] 李禾,邢更彦,杨传铎,等.脊柱内固定系统生物力学研究与临床应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(8):923-927.[14] 陈君生,高建伟,李华德,等.经伤椎钉棒系统节段固定治疗多节段胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(1):53-54.[15] Lee JK, Jang JW, Kim TW, et al. Percutaneous short-segment pedicle screw placement without fusion in the treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures: Is it effective? Comparative study with open short-segment pedicle screw fixation with posterolateral fusion. Acta Neurochirurgica. 2013;155(12): 2305-2312.[16] 林阳,潘剑成,张宗明,等.经伤椎椎体内植骨联合后路椎弓根系统内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折临床疗效研究[J].河北医学,2015,21(6): 1000-1003. [17] 潘兵,张志敬,宋舟锋,等.胸腰椎骨折伤椎短椎弓根钉固定的生物力学研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4):368-372.[18] 胡广询,易伟宏,魏富鑫,等.胸腰椎骨折后路单节段椎弓根钉固定与结合骨水泥强化固定的生物力学比较[J].中华创伤杂志, 2009, 25(1):36-40.[19] 俞宇,田晓华.经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨加椎弓根螺钉固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折的远期随访[J].安徽医学,2014,(10):1402-1403.[20] 李浩,徐建广,连小峰,等.经伤椎椎弓根磷酸钙人工骨植入及置钉治疗老年胸腰椎骨折[J].国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(2): 114-115,119.[21] 潘勇,初同伟,郝勇,等.经伤椎与不经伤椎椎弓根螺钉复位固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床对比研究[J].中华创伤杂志,2009,25(8): 694-697.[22] 黄明光,殷海东,赵洪斌,等.伤椎置钉短节段固定结合经伤椎椎弓根椎体内植骨治疗胸腰段爆裂性骨折的探讨[J].实用医学杂志, 2013,29(8):1325-1327.[23] 王洪伟,李长青,周跃,等.微创与传统开放附加伤椎经椎弓根螺钉内固定手术治疗胸腰椎骨折的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010,20(2):112-116.[24] Wu ZX, Gao MX, Sang HX, et al. Surgical treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures with open vertebral cement augmentation of expandable pedicle screw fixation: A biomechanical study and a 2-year follow-up of 20 patients. J Surg Res. 2012;173(1):91-98.[25] 周卓鹏,范建文,植伟宏,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉置入内固定修复胸腰椎骨折:3年随访效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(22): 3519-3524.[26] 曾忠友,黄伟,张建乔,等.椎弓根螺钉系统同时经伤椎置钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2009,19(8):609-613.[27] 鲁世保,孔超,海涌,等.单节段与双节段经伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗轻中度不稳定胸腰椎骨折的疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(6): 615-620.[28] 王金刚,干阜生,杨玉起,等.后路钉棒经伤椎固定与跨伤椎固定治疗爆裂型胸腰椎骨折的效果比较[J].创伤外科杂志,2015,17(2): 174-174,176.[29] 王许可,李长青,王洪伟,等.联合单向及万向椎弓根螺钉经伤椎经皮内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(5): 431-437. [30] Serin E, Karakurt L, Yilmaz E, et al.Effects of two-levels, four-levels, and four-levels plus offset-hook posterior fixation techniques on protecting the surgical correction of unstable thoracolumbar vertebral fractures: a clinical study. Eur J Orthop Surg. 2004;14(1):1-6.[31] 刘中坡,武玉江,侯市宾,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉固定三椎体治疗胸腰椎骨折疗效观察[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(36):4150-4151.[32] 易早元.经伤椎椎弓根植骨结合膨胀型椎弓根钉固定治疗老年性胸腰椎骨折[J].实用临床医药杂志,2014,18(19):124-126.[33] 陈贞庚,郑晓晖,涂致远,等.经伤椎椎弓根螺钉固定技术在79例胸腰椎骨折中的应用初步经验[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(14):1450-1452.[34] 蒙更耀,李启中,杜国聪,等.节段与双节段经伤椎椎弓根钉固定治疗轻中度不稳定胸腰椎骨折疗效观察[J].海南医学,2015,26(12): 1829-1831.[35] 魏富鑫,钟锐,崔尚斌,等.经伤椎置钉单椎间复位固定治疗创伤性胸腰椎骨折的远期疗效[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(9): 760-764.[36] 曾忠友,张建乔,金才益,等.经伤椎置钉椎弓根螺钉系统固定治疗胸腰椎骨折2年以上随访结果[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(2): 128-132.[37] 周飞,周文玉,于跃芹,等.经伤椎一侧椎弓根通道椎体内植骨并对侧椎弓根置钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2008,23(4):271-273.[38] 黄河,李保华,陈旭东,等.经伤椎椎弓根植骨结合后路钉棒内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床观察[J].四川医学,2014,35(8): 1016-1017.[39] 张玉新,马信龙,徐桂军,等.后路经伤椎单节段固定胸腰椎骨折力学性能的三维有限元分析[J].中华创伤杂志,2013,29(6): 507-510.[40] 刘上楼,徐军,倪卓民,等.经胸腰段伤椎单节段椎弓根螺钉固定后的生物力学特性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(39): 6908-6913. |
.jpg)