中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (4): 481-485.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.04.005
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
膝关节置换时股骨髓内定位对假体排列的影响
李乐翔,薛 峰,盛晓文,彭育沁
- 苏州大学附属常熟医院(常熟第一人民医院)骨科,江苏省常熟市 215500
Effect of femoral intramedullary guides on prosthesis arrangement in total knee arthroplasty
Li Le-xiang, Xue Feng, Sheng Xiao-wen, Peng Yu-qin
- Department of Orthopedics, Changshu Hospital, Affiliated to Soochow University (Changshu No.1 People’s Hospital), Changshu 215500, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
膝关节置换股骨髓内定位:膝关节置换是利用人工假体治疗膝关节疾病的新技术,需要医生熟知膝关节及股骨、胫骨解剖形态学知识。传统髓内定位系统以股骨解剖轴为参考,将髓内定位杆准确地插入股骨髓腔,精确的定位杆插入点可以得到精准的力线,下肢力线精准能够延长假体生存率。而由于个体膝关节、股骨解剖形态学的差异,如何精准地髓内定位仍然是需要解决的问题。
下肢力线:是象征正常人体下肢在负重位时的力学传导通路的一条假想直线,起始于股骨头旋转中心,止于内外踝中点。保持正常的下肢力线可以使应力分布均匀,对于假体的长期生存十分关键,常辅助利用骨髓内定位杆保持下肢力线正常,骨髓内定位杆进针点的位置对下肢力线造成偏差,研究其造成的偏差相关程度及影响因素对于延长假体生存率的认识举足轻重。
背景:膝关节置换时股骨髓内定位精确度要求高,操作复杂,选择更精确的定位方法及确定正确的进针点对于假体及关节功能都十分重要。
目的:膝关节置换时观察应用不同股骨髓内定位方法时进针点位置对假体排列的影响。
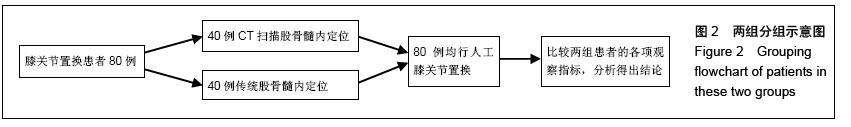
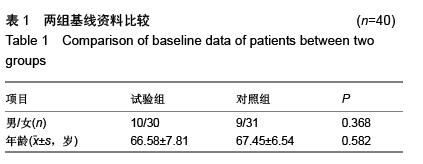
方法:选择2012年1月至2015年7月在常熟第一人民医院接受膝关节置换的80例患者,按照随机数字法分为试验组和对照组,每组40例。试验组利用CT扫描进行股骨髓内定位,借助影像学参数对股骨髓内定位进入点的理论位置进行标记。对照组采用传统膝关节置换技术对股骨髓内定位进入点进行标记。观察应用不同股骨髓内定位方法时进针点的位置,探讨膝关节置换时股骨髓内定位对假体排列的影响。
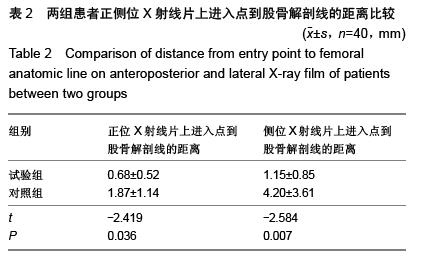
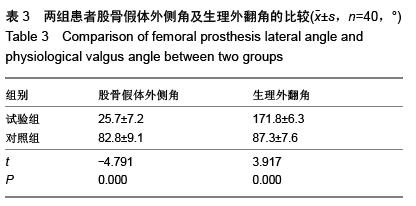
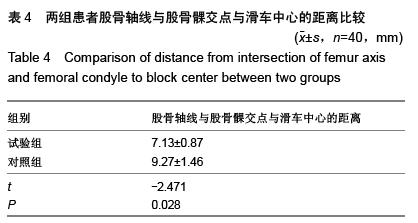
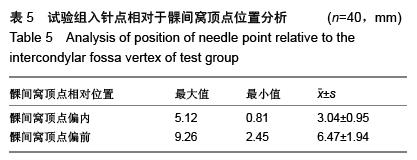
结果与结论:与对照组相比,试验组正侧位X射线片上进入点到股骨解剖线的距离更短,股骨假体外侧角及膝关节生理外翻角更接近理论值,股骨轴线与股骨髁交点与滑车中心的距离更短,差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。结果证实,三维CT扫描模拟定位与传统二维骨髓内定位相比进针点位置更为准确,多集中于髁间窝偏内2-5 mm,髁间窝偏前3-10 mm,三维CT扫描模拟定位是股骨髓内定位可靠的选择。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4072-871X(李乐翔)
.jpg)