中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 8015-8020.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.025
• 相关因子与动物模型 related factors in animal models • 上一篇 下一篇
角膜炎模型大鼠白细胞介素10及环氧酶2的表达
陆 霞1,潘旭斌1,谢玉涛2,季秋娣3
- 无锡市第四人民医院,1眼科,2手术室,3皮肤科,江苏省无锡市 214062
Expression of interleukin-10 and cyclooxygenase 2 in keratitis rat models
Lu Xia1, Pan Xu-bin1, Xie Yu-tao2, Ji Qiu-di3
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, 2Operating Room, 3Department of Dermatology, the Fourth People’s Hospital of Wuxi, Wuxi 214062, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
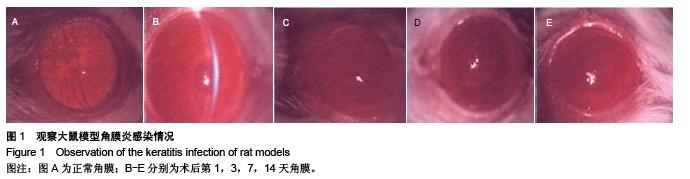
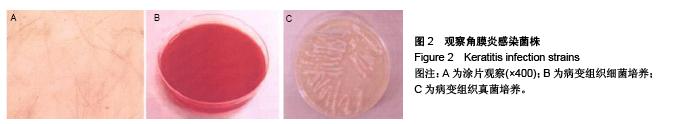
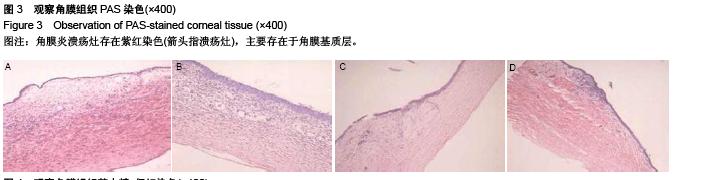
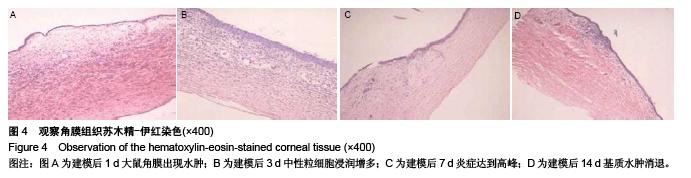
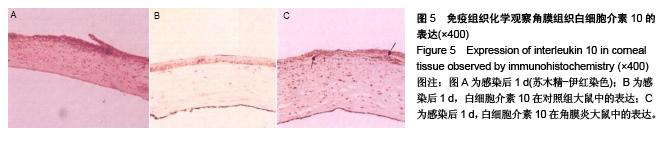
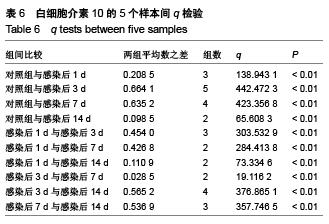
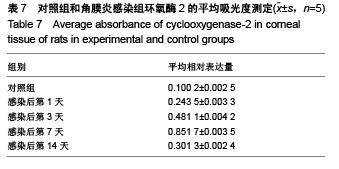
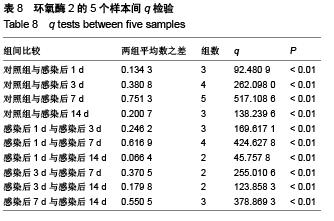
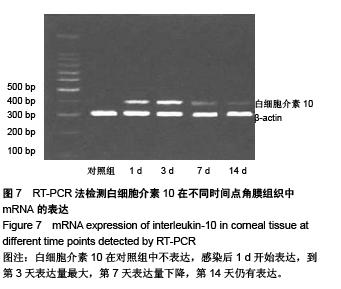
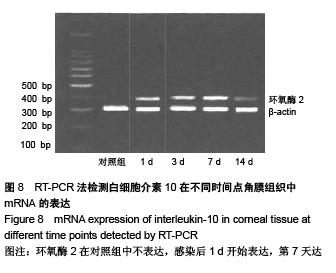
背景:研究白细胞介素10、环氧酶2与模型大鼠角膜炎发生发展的关系,对角膜炎的治疗有重大意义。 目的:检测白细胞介素10及环氧酶2在大鼠模型角膜炎中的表达情况,分析白细胞介素10、环氧酶2与模型大鼠角膜炎发生发展的关系。 方法:随机选取26只健康大鼠,不限雌雄,大鼠左眼选为实验组,采用角膜表面镜片术法建立角膜炎感染模型;右眼作为正常对照组。建模后第1,3,7及14天摘取角膜组织,观察大鼠左右眼角膜组织病理学变化,并采用免疫组织化学及反转录聚合酶链式反应(RT-PCR)法,检测白细胞介素10及环氧酶2在不同程度角膜炎的角膜组织中的表达情况。 结果与结论:①组织病理学观察显示角膜炎病灶有严重组织坏死及中性粒细胞浸润,PAS染色结果显示菌丝主要存在于角膜基质层。②白细胞介素10在对照组大鼠角膜中基本不表达,感染角膜炎后,白细胞介素10的表达先上升后下降,各时间点有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。③环氧酶2在对照组大鼠角膜中基本不表达,感染角膜炎后,环氧酶2的表达逐渐升高,第14天降低,各时间点有显著性差异(P < 0.01)。PAS染色及病变组织培养实验证明建立大鼠模型角膜炎成功。结果显示白细胞介素10在角膜炎病变后期有表达,推测其可能参与角膜炎后期的组织损伤修复;环氧酶2的表达位于角膜炎组织,是角膜炎病变的敏感炎症因子。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)