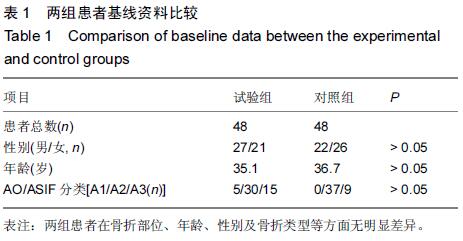
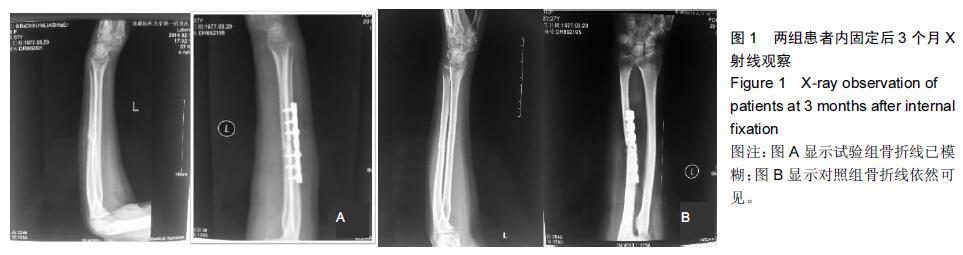
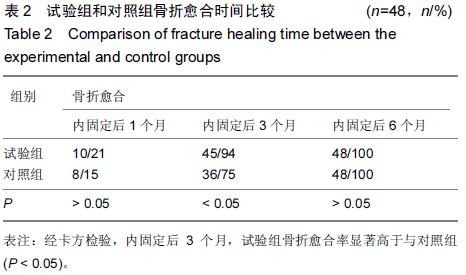
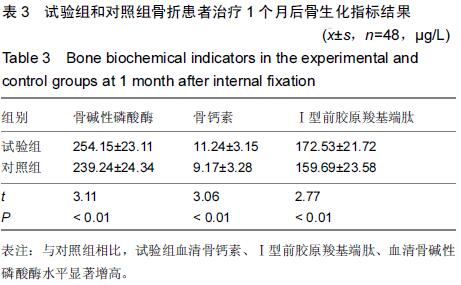
|
[1] Song YE, Tan H, Liu KJ,et al.Effect of fluoride exposure on bone metabolism indicators ALP, BALP, and BGP. Environ Health Prev Med. 2011;16(3):158-163.
[2] Zhou HY, Yan J, Fang L,et al.Change and significance ofIL-8, IL-4, and IL-10 in the pathogenesis of terminal Ileitis in SD rat. CellBiochem Biophys. 2014;69(2):327-331.
[3] Apalset EM, Gjesdal CG, Ueland PM,et al.Interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-mediated inflammation and the kynurenine pathway in relation to risk of hip fractures: the Hordaland Health Study. Osteoporos Int.2014;25(8):2067-2075.
[4] Volpin G, Cohen M, Assaf M,et al.Cytokine levels (IL-4, IL-6, IL-8 and TGFβ) as potential biomarkers of systemic inflammatory response intrauma patients. Int Orthop. 2014;38(6):1303-1309.
[5] Wang L, Park P, La Marca F,et al.BMP-2 inhibits tumor-initiatingability in human renal cancer stem cells and induces bone formation. J Cancer ResClin Oncol. 2015;141(6): 1013-1024.
[6] Muschter D,Göttl C,Vogel M,et al.Reactivity ofrat bone marrow macrophages to neurotransmitter stimulation in the context of collagen II-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17:169.
[7] Echeverri LF, Herrero MA, Lopez JM,et al. Early stages of bone fracture healing: formation of a fibrin-collagen scaffold in the fracture hematoma. Bull Math Biol. 2015;77(1):156-183.
[8] Ozaki A, Tsunoda M, Kinoshita S,et al. Role of fracture hematoma and periosteum during fracture healing in rats: interaction of fracture hematoma and the periosteum in the initial step of the healing process. J Orthop Sci.2000;5(1):64-70.
[9] Song YE,Tan H,Liu Y, et al. Effect of fluoride exposure on bone metabolism indicators ALP, BALP, and BGP. 2011;16(3):158-163.
[10] 邢艳莉,汪春兰,赵宇.复合基因在骨缺损基因治疗中的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2009.5(5):291-294.
[11] Stenfelt S, Hulsart-Billström G, Gedda L,et al. Pre-incubation of chemically crosslinked hyaluronan-based hydrogels,loaded with BMP-2 and hydroxyapatite, and its effect on ectopic bone formation.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(4):1013-1023.
[12] Chouhan S, Sharma S. Down-Regulation of Acid and Alkaline Phosphatases Induced After Prolonged Diclofenac Use in Experimental Mouse Bone. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences. 2014;1:37.
[13] Busti AJ,Hooper JS,Amaya CJ,et al. Effects of perioperative antiinflammatory and immunomodulating therapy on surgical wound healing.Pharmacotherapy. 2005;25(11):1566-1591.
[14] Göbel K, Bittner S, Melzer N,et al. CD4(+) CD25(+) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells suppress cytotoxicity of CD8(+) effector T cells: implications for their capacity to limit inflammatory central nervous system damage at the parenchymal level. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:41.
[15] Cahill EF, Tobin LM, Carty F,et al. Jagged-1 is required for the expansion of CD4(+) CD25(+) FoxP3(+) regulatory T cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells by murine mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6:19.
[16] Chidrawar SM,khan N,Chan YL,et al. Ageing is associated with a decline in peripheral blood CD56bright NK cells. Immun Ageing. 2006;3:10.
[17] Ishikawa M, Nishioka M, Hanaki N ,et al. Postoperative host responses in elderly patients after gastrointestinal surgery. Hepatogastroenterology. 2006;53(71):730-735.
[18] Clowes JA, Riggs BL,Khosla S,et al. The role of the immune system in the pathophysiology of osteoporosis. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:207-227.
[19] Riggs BL, Khosla S ,Melton LJ,et al. Sex steroids and the construction and conservation of the adult skeleton. Endocr Rev. 2002;23(3):279-302.
[20] Opelz G, Döhler B. Association of mismatches for HLA-DR with incidence of posttransplant hip fracture in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation.2011;91(1):65-69.
[21] Plackett TP,Wittle PL,Faunce DE,et al. Aging enhances lymphocyte cytokine defects after injury. FASEB J. 2003;17(6): 688-689.
[22] Gothard D, Smith EL, Kanczler JM,et al. Tissue engineered bone using select growth factors: A comprehensive review of animal studies and clinical translation studies in man. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28:166-207.
[23] Kempen DH,Lu l,Heijink A,et al. Effect of local sequential VEGF and BMP-2 delivery on ectopic and orthotopic bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2009;30(14):2816-2825.
[24] Dimitriou R, Carr IM, West RM,et al. Genetic predisposition to fracture non-union: a case control study of a preliminary single nucleotide polymorphisms analysis of the BMP pathway. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011;12:44.
[25] Zhang Y,Cheng N,Shi B,et al. Delivery of PDGF-B and BMP-7 by mesoporous bioglass/silk fibrin scaffolds for the repair of osteoporotic defects.Biomaterials. 2012;33(28):6698-6708.
[26] Hao X, Silva EA, Brodin LA,et al .effects of sequential release of VEGF-A165 and PDGF-BB with alginate hydrogels after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;75(1):178-185.
[27] Nillesen ST,Wismans R,Daamen R,et al.Increased angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation in acellular collagen-heparin scaffolds containing both FGF2 and VEGF. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):1123-1131.
[28] Kaipel M, Schützenberger S, Schultz A,et al. BMP-2 but not VEGF or PDGF in fibrin matrix supports bone healing in a delayed-union rat model. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(10):1563-1569. |