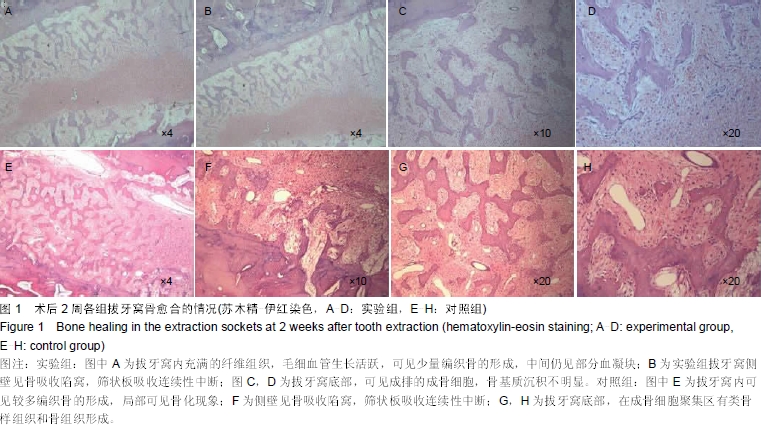
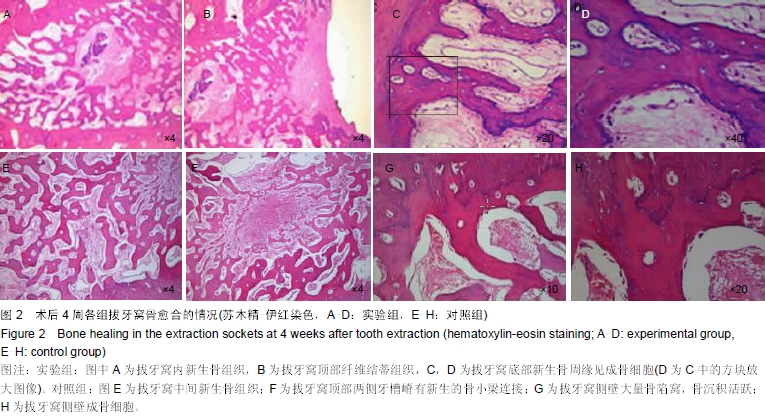
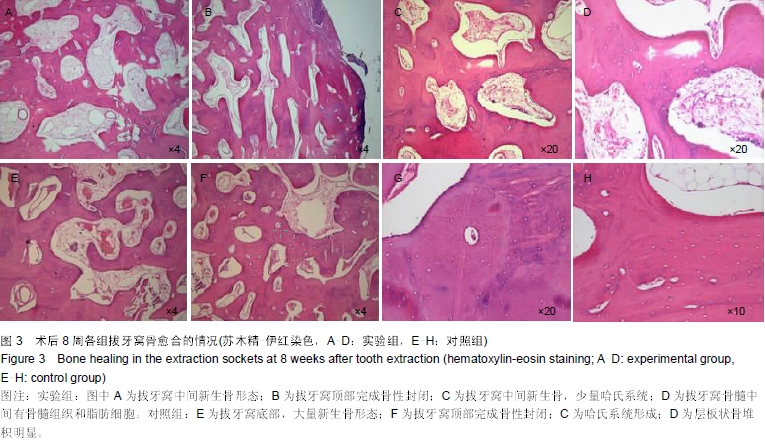
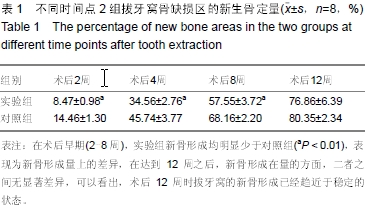
| [1] Wiesen M, Kitzis R. Preservation of the alveolar ridge at implant sites. Periodontal Clin Investiq. 1998;20(2):17-20.
[2] Jones KB, Mollano AV, Morcuende JA, et al. Bone and brain: a review of neural, hormonal, and musculoskeletal connections. Iowa Orthop J. 2004;24:123-132.
[3] Togari A, Arai M, Kondo A. The role of the sympathetic nervous system in controlling bone metabolism. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2005;9:931-940.
[4] Togari A, Arai M. Pharmacological topics of bone metabolism: the physiological function of the sympathetic nervous system in modulating bone resorption. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;106: 542-546.
[5] 王承勇,陈伟辉,等.神经支配与种植体骨结合和骨感知的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(4):684-688.
[6] 陈伟辉,乔鞠,田卫东.应力作用下生长因子对成骨细胞增殖和分化的调节[J].国外医学:口腔医学分册,1999,26(6):347-350.
[7] Ransjo M, lie A, Mukohyama H, et al. Miroisolated mouse osteoclasts express VIP-1 and PACAP receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;274:400.
[8] Boggio V, Ladizesky MG, Cutrera RA, et al. Autonomic neural signals in bone: physiological implications for mandible and dental growth. Life Sci. 2004;75:383-395.
[9] Sherman BE, Chole RA. Effects of catecholamines on calvarial bone resportion in vitro. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001;110:682-689.
[10] 林海,王承勇.神经支配与拔牙窝的骨愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(7):1141-1144.
[11] The Ministry of Science and Technology of the People,s Republic of China. Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use of LaboratoryAnimals. 2006-09-30.
[12] 陈伟辉,林海.失交感神经支配对拔牙窝骨愈合期间血管再生的影响[J].福建医科大学学报,2013,47(6):335-339.
[13] 王承勇,林海.失交感神经支配与新骨形成及改建[J]福建医科大学学报,2014,48(1):29-33.
[14] Yoshimoto M, Konig B, Allegrini S, et al. Bone healing after the inferior alveolar nerve lateralization: a histologic study in rabbits. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62(9):131-135.
[15] 徐琳,谭颖辉,葛永玲,等.离断下齿槽神经对兔下颌骨骨折愈合影响的实验研究[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2006;16(1):19-22.
[16] 马高旗,李焰.下牙槽神经缺失对下颌骨骨缺损骨痂血肿期炎症因子表达影响的实验研究[J]华西口腔医学杂志,2011,29(6): 640-642.
[17] Madsen JE, Hukkanen M, Aune AK, et al. Fracture healing and callus innervation after peripheral nerve resection in rats. Clin Orthop. 1998;351:230-240.
[18] Claflin RS. Healing of disturbed and undisturbed extraction wounds. J Am Dent A. 1936;23:945-959.
[19] Cardaropoli G, Araujo M, Lindhe J. Dynamics of bone tissue formation in tooth extraction sites. An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol. 2003;30:809-818.
[20] Ishizuka K, Hirukawa K, Nakamura H, et al. Inhibitory effect of CGRP on osteoclast formation by mouse bone marrow cells treated with isoproterenol. Neurosci Lett. 2005;379:47-51.
[21] Villa I, Dal Fiume C, Maestroni A, et al. Human osteoblast-like cell proliferation induced by calcitonin-related peptides involves PKC activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2003; 284:627-633.
[22] 张静,李纾,吕琳琳.失神经支配对牙周组织中P物质及破骨细胞的影响.[J]华西口腔医学杂志,2014,32(2):162-165.
[23] Sundaramoorthi R, Shakespeare WC, Keenan TP, et al. Bone-targeted Src kinase inhibitors: novel pyrrolo- and pyrazolopyrimidine analogues. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003; 13(18):3063-3066.
[24] Nied?wiedzki T, Filipowska J. Bone remodeling in the context of cellular and systemic regulation: the role of osteocytes and the nervous system. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;55(2):R23-R36. |