• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
复方中药强骨饮强化髋关节置换后假体周围骨密度:随机对照半年评定
菅志飞1,孙 维1,曹 洪2
- 1湖北医药学院附属东风总医院创伤外科,湖北省十堰市 442000;2十堰市人民医院骨科,湖北省十堰市 442000
Qiangguyin strengthens periprosthetic bone density after hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled half-year evaluation
Jian Zhi-fei1, Sun Wei1, Cao Hong2
- 1Department of Traumatology, Dongfeng General Hospital Affiliated to Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Shiyan People’s Hospital, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
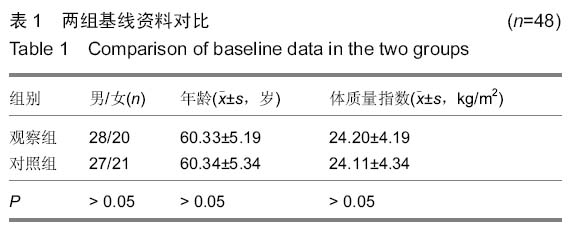
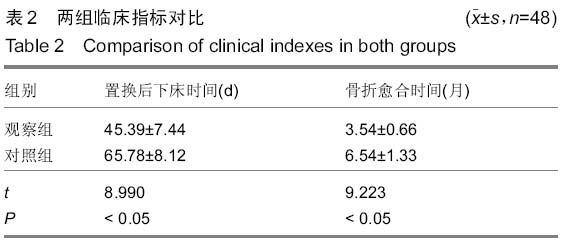
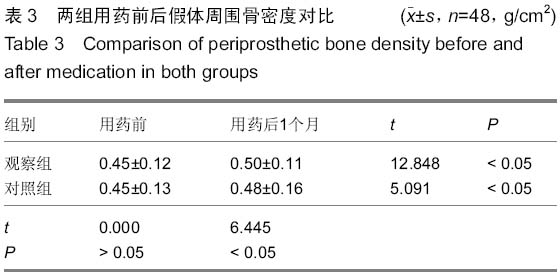
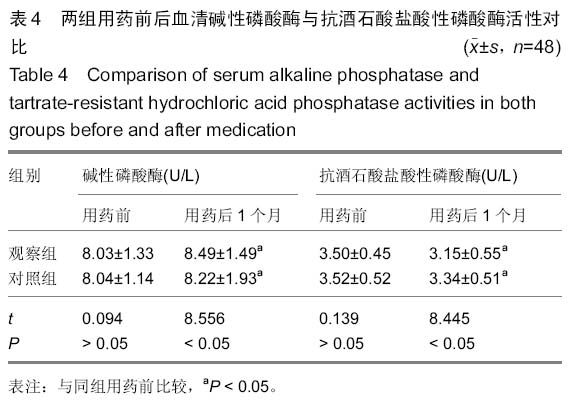
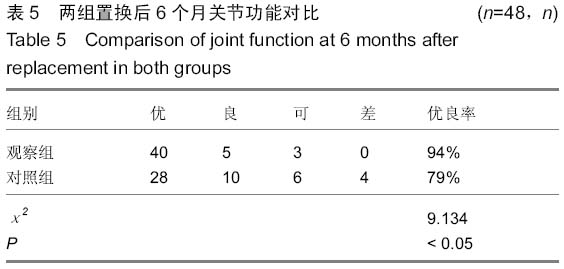
背景:髋关节置换是目前修复股骨颈骨折的有效手段,但是随着手术量的增多,髋关节置换后失败率也随之升高,特别是置换后假体松动与周围骨折比较常见。强骨饮能促进成骨细胞形成,有抗骨质疏松的作用,抑制破骨细胞活性,增加骨密度。其中骨碎补具有补肾、壮骨、强筋、止痛的功能,具有促进骨形成和抑制骨吸收的双向调节作用。 目的:探讨强骨饮对患者股骨颈骨折髋关节置换后假体周围骨密度的影响。 方法:96例股骨颈骨折患者根据随机数字表法分为观察组与对照组,每组48例。两组都给予择期髋关节置换,置入美国史赛克公司的人工股骨头后使用骨水泥固定。置换后对照组口服碳酸钙D3片与阿法骨化醇胶囊,在此基础上观察组加用复方中药强骨饮口服,药物干预时间为1个月。观察两组假体周围骨密度变化情况,检测碱性磷酸酶与抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶活性,并进行修复效果对比。 结果与结论:所有患者均顺利完成手术,均无感染、假体松动的情况发生。观察组的置换后下床时间与骨折愈合时间都明显少于对照组(P < 0.05)。两组用药前的假体周围骨密度差异无显著性意义,用药后都有明显上升的趋势(P < 0.05),用药后观察组的假体周围骨密度明显高于对照组(P < 0.05)。两组用药后的血清碱性磷酸酶活性明显升高,而抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶活性明显降低,与用药前对比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);同时用药后观察组的血清碱性磷酸酶与抗酒石酸盐酸性磷酸酶活性与对照组对比差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。在置换后6个月进行评定,观察组的关节功能优良率显著高于对照组(94%,79%,P < 0.05)。提示强骨饮在髋关节置换后应用能起到抗骨吸收和抑制过高的骨转换的作用,提高假体周围骨密度,从而达到恢复关节功能的目的。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: