中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (35): 5652-5657.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.35.015
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
髓内钉与动力髋螺钉置入修复老年股骨转子间骨折:循环血容量的比较
缪世昌1,2,周荣魁1,牛晓娟3
- 江阴市中医院,1骨科,3麻醉科,江苏省江阴市 214400;2南京中医药大学江阴附属医院骨科,江苏省江阴市 214400
Intramedullary nail versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly: circulatory blood volume
Miao Shi-chang1, 2, Zhou Rong-kui1, Niu Xiao-juan3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Jiangyin Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jiangyin 214400, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Jiangyin Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jiangyin 214400, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Anesthesiology, Jiangyin Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jiangyin 214400, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
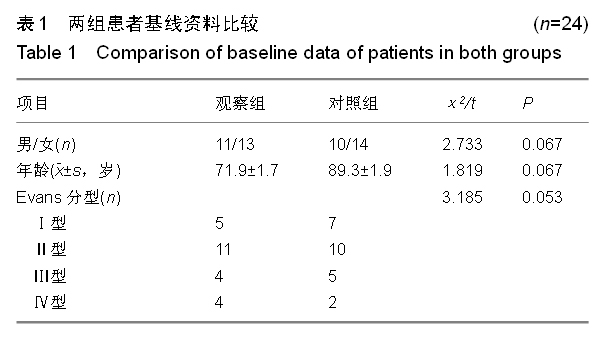
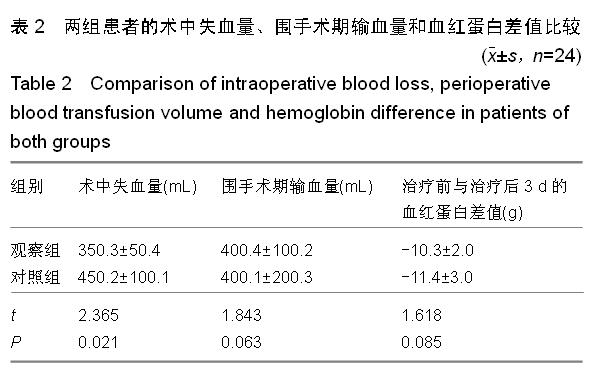
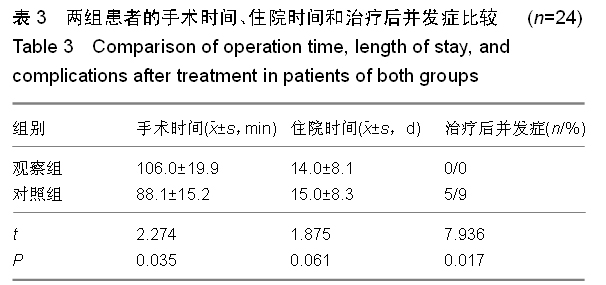
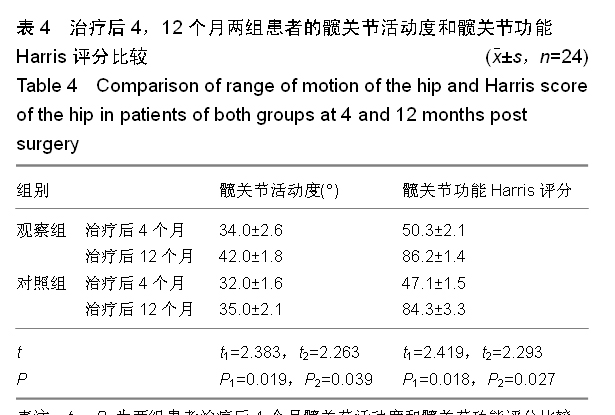
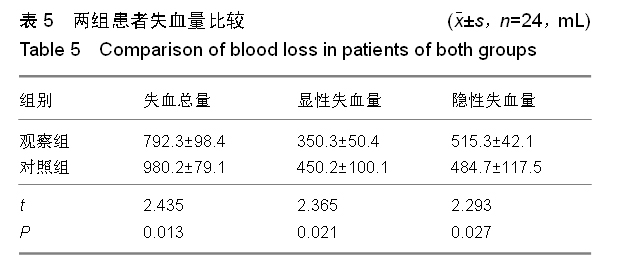
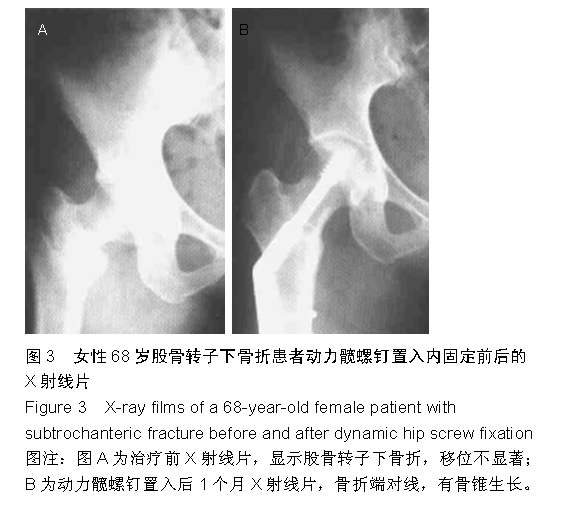
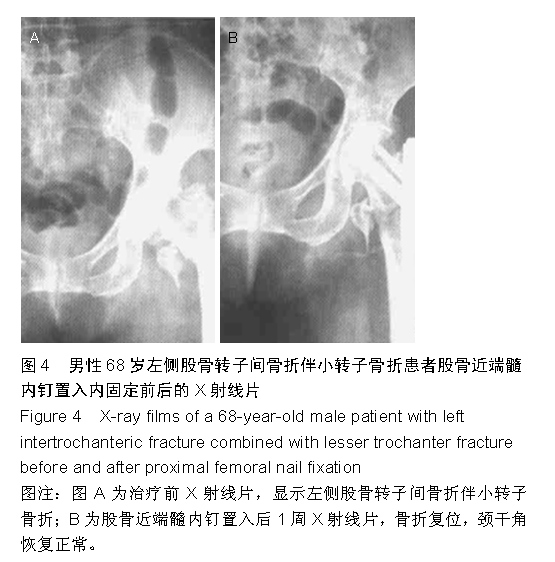
背景:股骨转子间骨折老年患者治疗的关键在于选取适当的内固定方案,但是关于不同内固定方案对股骨转子间骨折老年患者血循环系统血容量影响的研究不多。 目的:观察股骨近端髓内钉与动力髋螺钉对股骨转子间骨折老年患者循环系统血容量的影响,并进行对比。 方法:选取2012年1月至2014年9月南京中医药大学江阴附属医院收治的股骨转子间骨折老年患者48例,采用随机数表法分为两组,每组24例。观察组患者行股骨近端髓内钉置入内固定治疗,对照组患者行动力髋螺钉置入内固定治疗。比较两组患者的术后失血量、围手术期输血量、治疗前与治疗后3 d的血红蛋白差值、治疗后并发症发生率、显性失血及隐性失血情况,并对两组患者治疗后4,12个月的髋关节活动度和髋关节功能Harris评分进行比较。 结果与结论:观察组患者的术中失血量少于对照组患者(P < 0.05)。两组患者的围手术期输血量、治疗前与治疗后3 d的血红蛋白差值比较,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。观察组患者的手术时间显著长于对照组(P < 0.05)。观察组患者的治疗后并发症发生率显著低于对照组(P < 0.05)。两组患者的住院时间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。同时间段内观察组患者的髋关节活动度和髋关节功能Harris评分均优于对照组患者,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。观察组患者的失血总量、显性失血量均少于对照组,隐性失血量多于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。提示与动力髋螺钉相比,股骨近端髓内钉置入内固定修复股骨转子间骨折术中失血量较少,治疗后并发症发生率较低,治疗后髋关节活动度和髋关节功能评分较佳;但是股骨近端髓内钉置入的手术时间较长,两种内固定方案的血红蛋白差值和围手术期输血量无明显差异。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
.jpg)