中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (35): 5588-5592.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.35.003
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
不同通气方式对髋关节置换高血压患者应激反应的影响
佘树松1,周 波1,徐顺才2
- 1江苏省沭阳仁慈医院麻醉科,江苏省沭阳县 223600;2徐州医学院附属淮安市第二人民医院,江苏省淮安市 223002
Effects of different ventilation modes on stress reaction of hypertensive patients treated with hip arthroplasty
She Shu-song1, Zhou Bo1, Xu Shun-cai2
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Shuyang Renci Hospital, Shuyang 223600, Jiangsu Province, China; 2the Huai’an Second People’s Hospital Affiliated to Xuzhou Medical College, Huai’an 223002, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
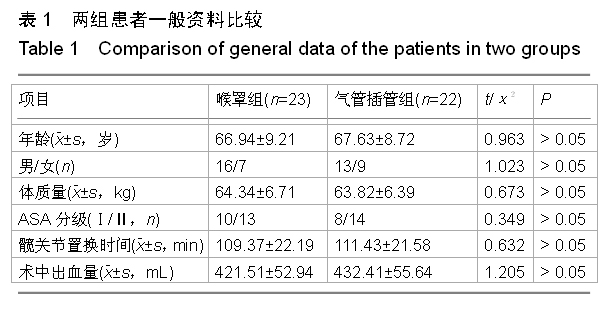
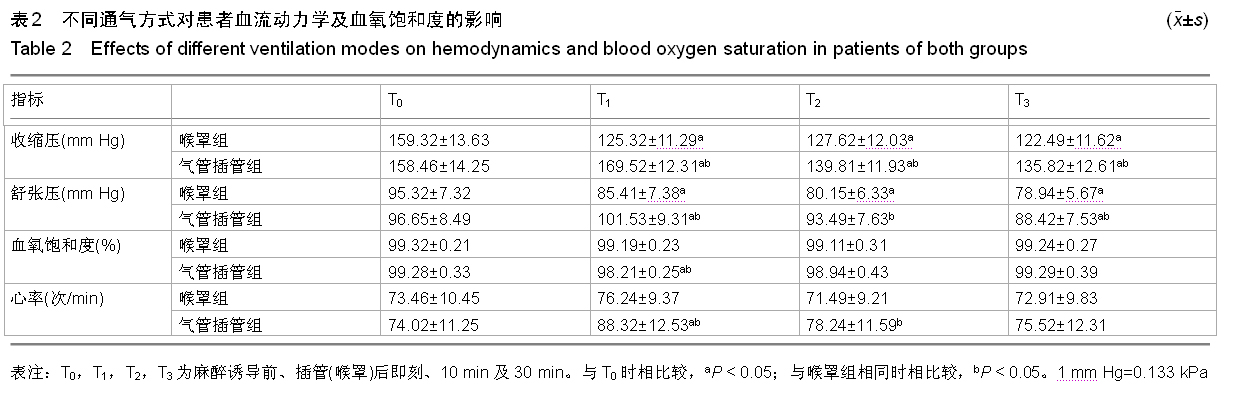
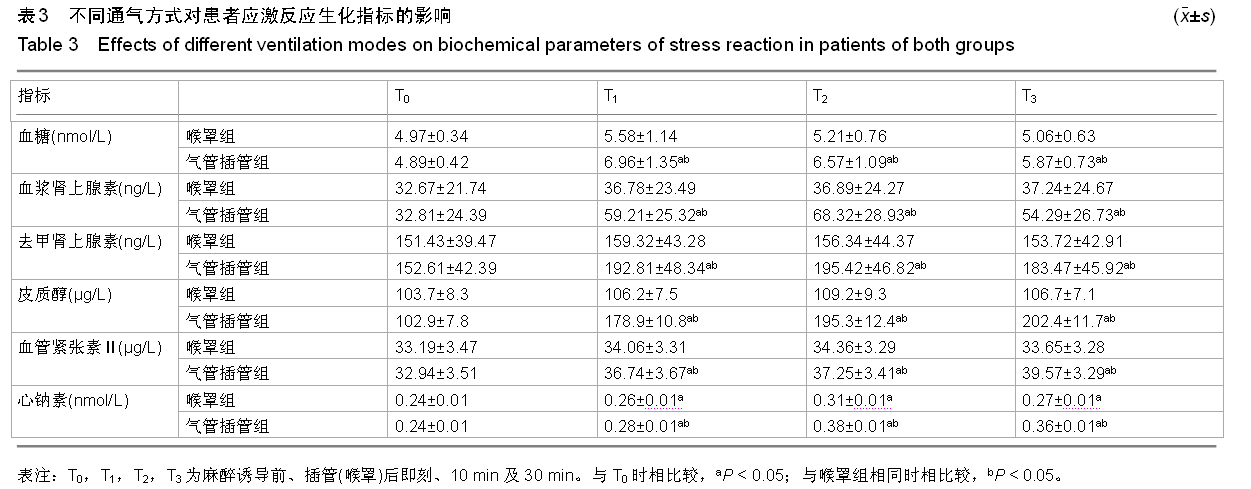
背景:髋关节置换患者全麻时,气管插管可造成咽喉和气管感受器的物理刺激,会引起患者的应激反应增强,尤其是高血压患者。Supreme喉罩能够减轻围术期患者心血管应激反应,降低气道并发症。 目的:观察Supreme喉罩和气管插管对高血压患者髋关节置换应激反应的影响。 方法:取2010年1月至2014年9月于江苏省沭阳仁慈医院行人工髋关节置换的患者45例,采用随机数字表法将患者均分为两组,喉罩组23例,气管插管组22例。两组患者均采用相同的麻醉诱导和维持方法,置换过程中连续监测患者的收缩压、舒张压、心率及血氧饱和度,分别记录两组麻醉诱导前(T0)、插管(喉罩)后即刻(T1)、5 min(T2)、15 min(T3)时收缩压、舒张压、血氧饱和度、心率及血糖、血浆肾上腺素、去甲肾上腺素、血清皮质醇、血管紧张素Ⅱ及心钠素水平。 结果与结论:喉罩组患者收缩压与舒张压在T1-T3时间点较T0时明显降低(P < 0.05);心率、血氧饱和度在T0-T3各时间点比较平稳,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。气管插管组患者收缩压、舒张压在T1时较T0时显著升高,收缩压在T2、T3时较T0明显降低,舒张压在T3时较T0显著降低(P < 0.05),心率、血氧饱和度在T1时间点显著升高(P < 0.05)。与T组比较,喉罩组患者收缩压与舒张压在T1-T3时间点显著降低(P < 0.05),心率在T1、T2较T组明显减慢(P < 0.05),血氧饱和度在T1显著高于T组(P < 0.05)。与T0时比较,T1-T3时气管插管组血糖、血浆肾上腺素、去甲肾上腺素浓度和皮质醇含量明显升高,且显著高于喉罩组(P < 0.05)。T1-T3时气管插管组血管紧张素Ⅱ水平较T0时显著增高,且均高于喉罩组。T1-T3时两组心钠素含量明显升高,气管插管组显著高于喉罩组(P < 0.05)。可见喉罩对于这些与应激相关的生化指标的影响较小,这也是其对患者血流动力学影响较小的生理基础。提示与气管插管比较,喉罩可明显减轻高血压患者全麻状态下髋关节置换时的应激反应。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: