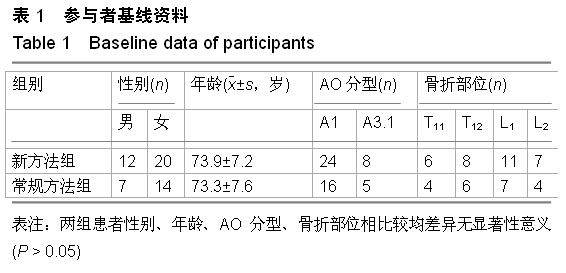
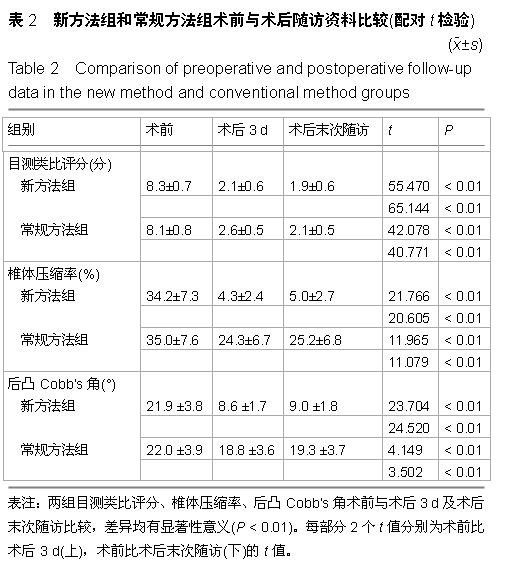
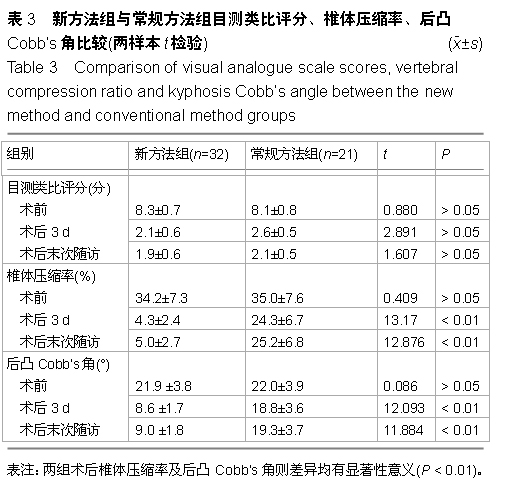
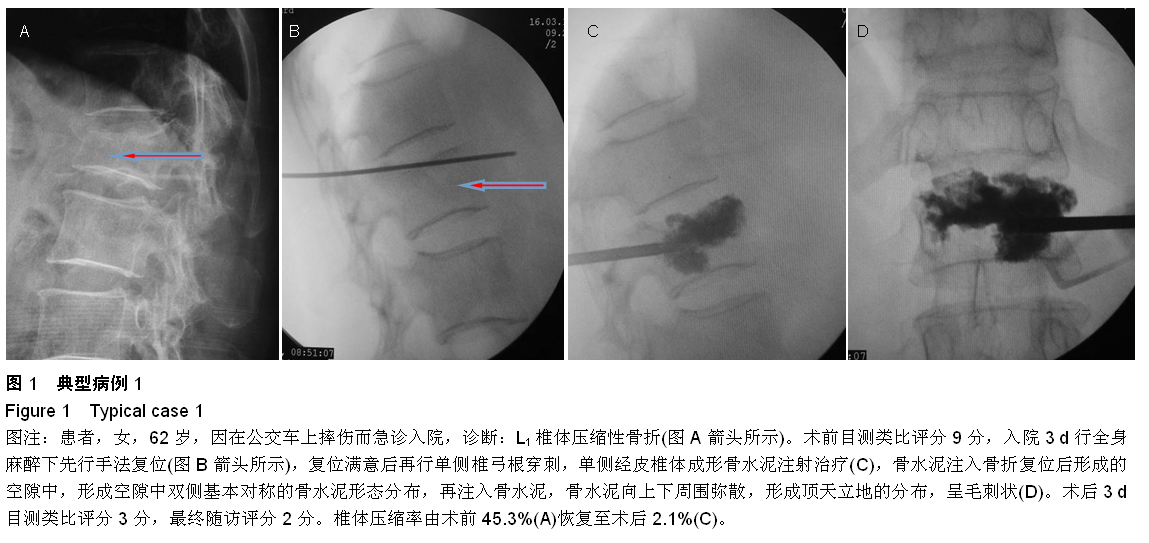
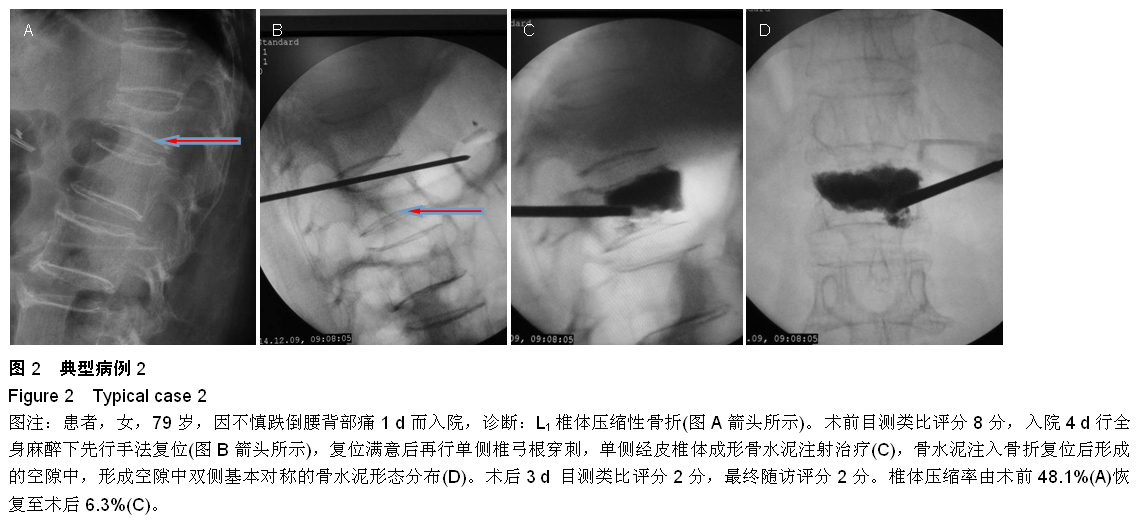
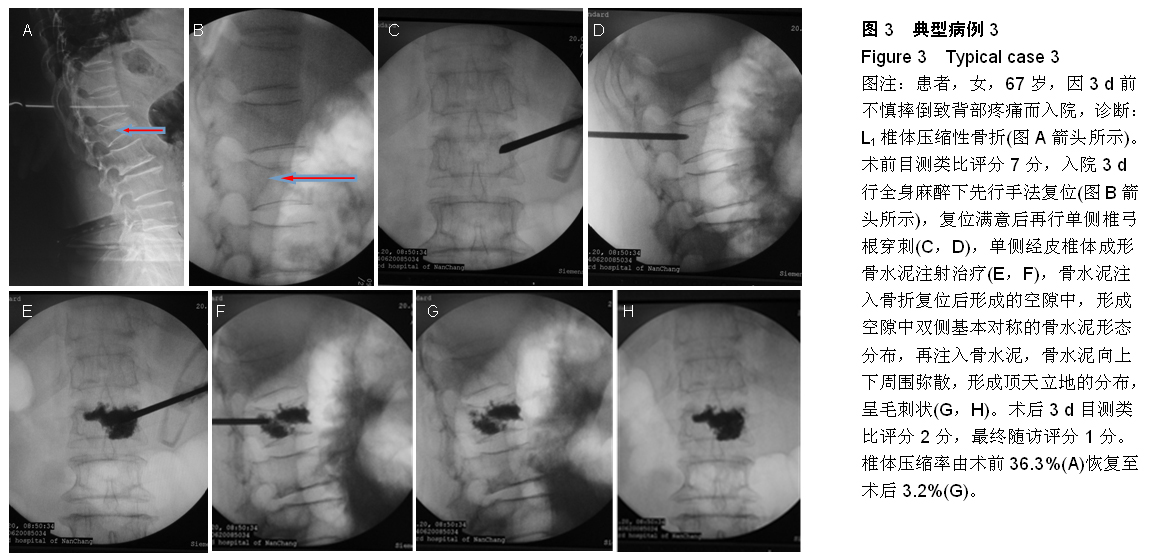
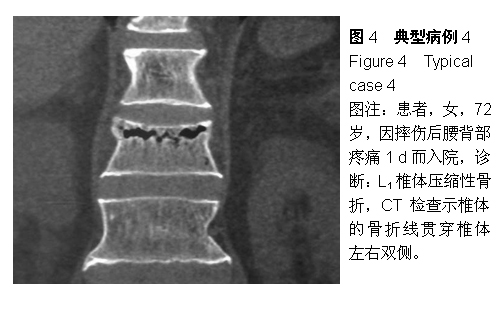
| [1] Kovacs FM, Abraira V, Zamora J, et al. Correlation between pain, disability, and quality of life in patients with common low back pain. Spine. 2004;(29):206-210.
[2] 秦子琈,徐有俊.老年骨质疏松症的危险因素研究[J].中国医学创新,2011,8(34):31-33.
[3] 高万旭,宓士军,高景春,等.经皮椎体成形治疗高龄骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2010,16(4):288-289.
[4] 刘文贵,吕锦瑜,孙建华,等.PVP与保守方法治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎椎体压缩骨折的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(10): 914-918.
[5] Weisskopf M, Ohnsorge JA, Niethard FU. Intravertebral pressure during vertebroplasty and balloon kyphoplasty:an in vitro study. Spine. 2008;33:178-182.
[6] Chen D, An ZQ, Song S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures. J Clin Neurosci. 2014; 21(3):473-477.
[7] Tan HY, Wang LM, Zhao L, et al. A prospective study of percutaneous vertebroplasty for chronic painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Pain Res Manag. 2015;20(1): 8-11.
[8] 朱洲,王生介,厉晓龙,等.聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形与保守治疗胸腰椎体新鲜骨质疏松性压缩骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(39):6271-6275.
[9] Stevenson M, Gomersall T, Lloyd Jones M, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(17):1-290.
[10] 李卉,顾一峰,李永东,等.比较经皮椎体成形与保守治疗对慢性疼痛性骨质疏松性椎体骨折患者疗效的非随机前瞻性试验[J].介入放射学杂志,2012,21(11):921-926.
[11] Ryu KS, Park CK. The prognostic factors influencing on the therapeutic effect of percutaneous verteboplasty in treating osteoportic vertebral compression fractures. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009;45(1):16-23.
[12] Joseph RN, Swift AJ, Maliakal PJ. Single centre prospective study of the efficacy of percutaneous cement augmentation in the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. Br J Neurosurg. 2013,27(4):459-464.
[13] 杜曼•吐鲁木汗,祖帕尔•苏来曼,塔扎别克.后凸成形与椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(13):2089-2095.
[14] 彭小忠,陈明,武振国,等.经皮椎体成形102例中22例骨水泥渗漏原因[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1515-1518.
[15] 周英杰,赵刚,李森,等.经皮聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥椎体成形结合手法牵引复位治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(21):3823-3827.
[16] 李涛,朱裕成,郑红兵,等.经皮椎体后凸成形中单双侧经椎弓根穿刺路径的选择[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(24):1863-1865.
[17] 王珏,刘杨青,原涟靖,等.经皮椎体成形单侧人路穿刺路径方法的选择及疗效[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(7):1144-1146.
[18] 郝定均,刘摇鹏,贺宝荣,等.陈旧性与新鲜性压缩骨折行椎体成形的临床对比研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(2):83-86.
[19] Lieberman IH, Dudeney S, Reinhardt MK, et al. Initial outcome and efficacy of “kyphoplasty” in the treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. Spine. 2001;26:1631-1638.
[20] Kuklo TR, Polly DW, Owens BD, et al. Measurement of thoracic and lumbar variability. Spine. 2001;26:61-65.
[21] 黄洪斌,范顺武,鲍丰,等.椎体成形结合体位复位治疗创伤性胸腰椎骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2008,28(1):20-24.
[22] Xiao H, Yang J, Feng X, et al. Comparing complications of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of the randomized and non-randomized controlled studies. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014.
[23] Liliang PC, Su TM, Liang CL, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty improves pain and physical functioning in elderly osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture patients. Gerontology. 2005;51:34-39.
[24] 陈卫,倪才方,王煊,等.经皮椎体成形及后凸成形治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的临床对比研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2011,45(9): 858-862.
[25] 吴海辉,吴晓,吴晓天,等.经皮椎体后凸成形与经皮椎体成形治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段骨折的疗效对比研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2014,13(9):737-740.
[26] Galin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine:kyphoplasty and vertebruplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine. 2001;26: 1511-1515.
[27] Foumey DR. Schomer DF, Nader R. et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for painful vertebral body fractures in cancer patients. J Neurosurg. 2003;98(1 Suppl): 21-30.
[28] Movrin I, Vengust R, Komadina R. Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130:1157-1166.
[29] Huang Z, Wan S, Ning L, et al. Is unilateral kyphoplasty as effective and safe as bilateral kyphoplasties for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(9):2833-2842.
[30] 廖旭昱,周雷杰,马维虎,等.经皮椎体后凸成形中单侧经椎弓根穿刺角度与骨水泥分布情况的关系[J].临床骨科杂志,2012,15(3): 241-244.
[31] Kim YY,Rhyu KW.Recompression of vertebral body after balloon kyphoplasty for osteoporotlc vertebral compression fracture. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(11):1907-1912.
[32] Nieuwenhuijse MJ, Muijs SP, van EAR, et al. A clinical comparative study on low versus medium viscosity polymethylmetacrylate bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty: viscosity associated with cement leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(20):E1037-E1044.
[33] Gravius S, Kraska N, Maus U, et al. Intravertebral pressure during vertebroplasty - an in-vitro study. Z Orthop Unfall. 2009;147(1):43-47.
[34] Jin YJ, Yoon SH, Park KW, et al. The volumetric analysis of cement in vertebroplasty: relationship with clinical outcome and complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(12):E761- E772.
[35] Molly S, Mathis JM, Belkoff SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill in mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebro plasty. Spine. 2003;28:1549-1554.
[36] Komemushi A, Tanigawa N, Kariya S, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for compression fracture: analysis of vertebral body volume by CT volumetry. Acta Radiol. 2005;46(3):276- 279.
|