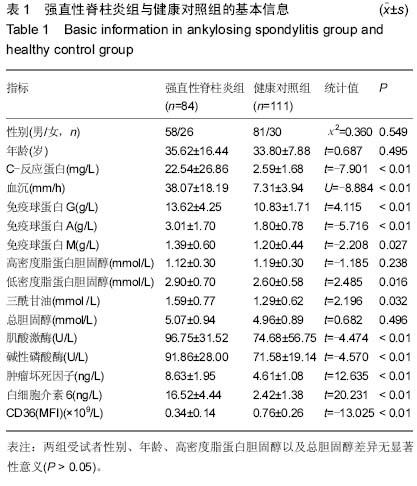
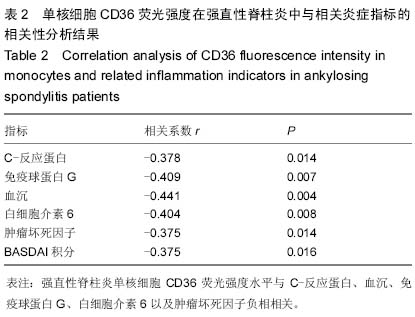
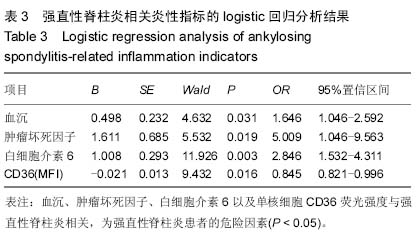
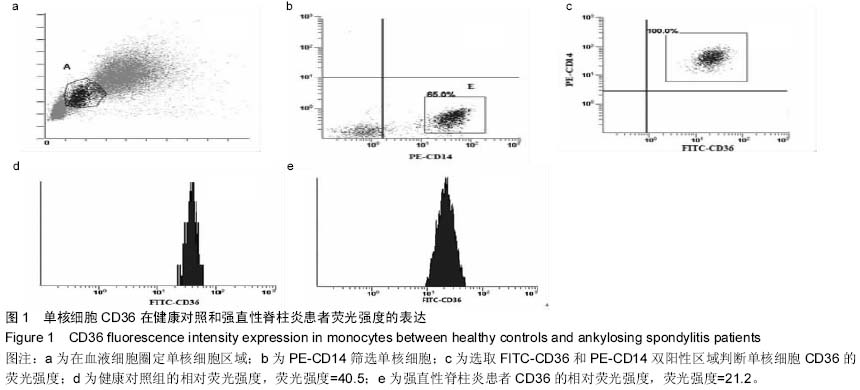
| [1] El Maghraoui A.Extra-articular manifestations of ankylosing spondylitis: prevalence, characteristics and therapeutic implications.Eur J Intern Med. 2011;22(6):554-560 560.
[2] Braun J, van den Berg R, Baraliakos X, et al.2010 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management ofankylosing spondylitis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 2011;70(6):896-904
[3] Gonzalez-Juanatey C, Vazquez-Rodriguez TR, Miranda-Filloy JA, et al.The high prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis without clinically evident cardiovascular disease.Medicine.2009;88(6)358-365.
[4] Ge Y, Elghetany MT.CD36: a multiligand molecule. Lab Hematol.2005;11(1):31- 37.
[5] Collot-Teixeira S, Martin J, McDermott-Roe C,et al. CD36 and macrophages in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Res.2007;75: 468-477.
[6] Boyer JF, Balard P, Authier H, et al.Tumor necrosis factor alpha and adalimumab differentially regulate CD36 expression in human monocytes. Arthritis Res Ther.2007; 9(2):R22.
[7] Wang C, Liao Q, Hu Y,et al.T lymphocyte subset imbalances in patients contribute to ankylosing spondylitis. Exp Ther Med. 2015;9(1):250-256.
[8] 冯家烜,徐茂锦.CD36与糖尿病动脉粥样硬化关系的研究进展[J], 实用糖尿病杂志,2013,5(1):3-6.
[9] Ramos-Arellano LE, Muñoz-Valle JF, De la Cruz-Mosso U, et al.Circulating CD36 and oxLDL levels are associated with cardiovascular risk factors in young subjects. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2014;14:54.
[10] Kim EH, Tolhurst AT, Szeto HH, Cho SH.Targeting CD36-mediated inflammation reduces acute brain injury in transient, but not permanent, ischemic stroke.CNS Neurosci Ther.2015;21(4):385-391.
[11] 杨敏,李林瑞,孟燕妮,等.凝血酶敏感蛋白-1及其受体CD36在支气管肺发育不良患儿中的表达及临床意义[J].中外医学研究, 2015,11(13):1-5.
[12] 罗俊一,马依彤,谢翔,等.CD36基因多态性与急性冠脉综合征关联性的研究. 中华流行病学杂志2014, 2(35):200-204.
[13] Peng YF, Cao L, Zeng YH, et al. Platelet to lymphocyte ratio and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Open Med. 2015; 10: 249-253.
[14] Peng YF, Zhang Q, Cao L, et al. Red blood cell distribution width: a potential marker estimating disease activity of ankylosing spondylitis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7(12):5289-5295.
[15] Kawakami M,Murase T,Ogawa H,et al.Human recombinant TNF suppresses lipoprotein lipase activity and stimulates lipolysis in 3T3-l1 cells. J Biochem. 1987;101:331-338.
[16] 申成凯,吕成昱,王英振,等.白细胞介素10启动子基因多态性与强直性脊柱炎的易感性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,20(17): 3793-3799.
[17] 彭隽,贾汝汉,党建中,等.CD36在高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球系膜细胞凋亡中的作用及机制[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2014,30(5):370-376.
[18] Huang JT, Welch JS, Ricote M, et al.Interleukin-4-dependent production of PPAR-gamma ligands in macrophages by 12/15-lipoxygenase.Nature.1999; 400:378-382.
[19] Draude G, Lorenz RL.TGF-beta1 downregulates CD36 and scavenger receptor A but upregulates LOX-1 in human macrophages.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000;278: 1042-1048.
[20] Rubic T, Lorenz RL.Downregulated CD36 and oxLDL uptake and stimulated ABCA1/G1 and cholesterol efflux as antiatherosclerotic mechanisms of interleukin-10. Cardiovasc Res.2006;69:527-535.
[21] Suzawa M, Takada I, Yanagisawa J,et al.Cytokines suppress adipogenesis and PPAR-gamma function through the TAK1/TAB1/NIK cascade.Nat Cell Biol 2003;5:224-230.
[22] Sung CK, She H, Xiong S,et al.Tumor necrosis factoralpha inhibits peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity at a posttranslational level in hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:722-729.
[23] Boyer JF, Balard P, Authier H,et al.“Tumor necrosis factor alpha and adalimumab diffrentially regulate CD36 expression in human monocytes,” ArthritisResearchandThrapy.2007; 99(2):22-25.
[24] Peng YF, Zhang ZX, Cao W, et al.The association between red blood cell distribution width and acute pancreatitis associated lung injury in patients with acute pancreatitis. Open Med.2015; 10: 176-179.
[25] Driscoll WS, Vaisar T, Tang J, et al.Raines.Macrophage ADAM17 defiiency augments CD36-dependent apoptotic cell uptake and the linked anti-inflmmatory phenotype,” Circulation Research.2013;113(1):52-61.
[26] Asada K,Sasaki S,Suda T,et al.Antiinflammatory roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2004; 169:195-200.
[27] Chung EY, Liu J, Homma Y, et al.Interleukin-10 expression in macrophages during phagocytosis of apoptotic cells is mediated by homeodomain proteins Pbx1 and Prep-1. Immunity.2007;27:952–964.
[28] Bottcher A,Gaipl US,Furnrohr BG,et al.Involvement of phosphatidylserine,alphavbeta3, CD14, CD36, and complement C1q in the phagocytosis of primarynecrotic lymphocytes by macrophages.Arthritis Rheum.2006;54: 927-938.
[29] Hu YF, Yeh HI, Tsao HM, et al..Impact of circulating monocyte CD36 level on atrial fibrillation and subsequent catheter ablation.Heart Rhythm.2011; 8(5):650-656.
[30] Serghides L,Kain KC.Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-retinoid X receptor agonists increase CD36-dependent phagocytosis of Plasmodium falciparum-parasitized erythrocytes and decrease malaria-induced TNF-alpha secretion by monocytes/ macrophages. Immunol.2001;166:6742-6748.
[31] Boyer JF, Balard P, Authier H, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and adalimumab differentially regulate CD36 expression in human monocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9: 22.
[32] Tontonoz P, Nagy L, Alvarez JG, et al. PPARgamma promotes monocyte/macrophage differentiation and uptake of oxidized LDL.Cell.1998;93:241-252. |