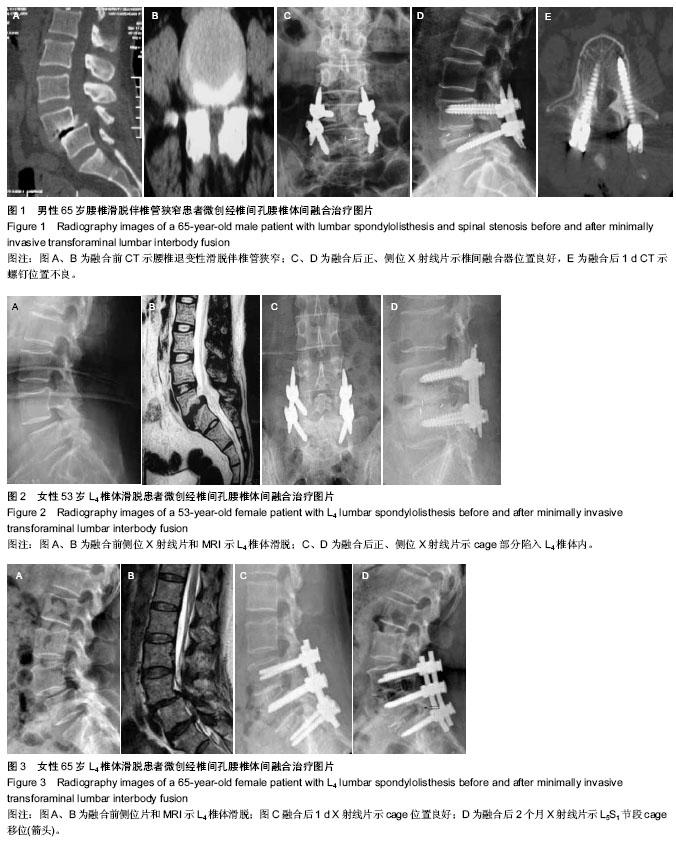
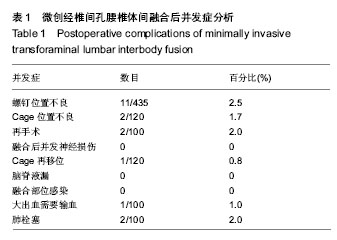
| [1] 汤优,张为,申勇,等. 经Quadrant通道下微创TLIF与开放TLIF治疗腰椎退变性疾病疗效的对比研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(21):1935-1938.
[2] Habib A, Smith ZA, Lawton CD, et al. Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Perspective on Current Evidence and Clinical Knowledge.Minim Invasive Surg. 2012;2012:657342.
[3] 康辉,蔡贤华,徐峰,等.Quadrant通道下经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术治疗复发性腰椎间盘突出症的疗效[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2013,23(3):198-203.
[4] Lee JC, Jang HD, Shin BJ. Learning curve and clinical outcomes of minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: our experience in 86 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(18):1548-1557.
[5] 吴文坚,粱裕,张兴凯,等.微创腰椎经椎间孔椎体间融合术的并发症分析:131例病例回顾和文献复习[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2012,5(2):100-104.
[6] 陈云生,陈荣春,郭朝阳,等.微创经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合术治疗老年腰椎退变性疾病[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(12): 1079-1085.
[7] Aoki Y, Yamagata M, Nakajima F, et al.Posterior migration of fusion cages in degenerative lumbar disease treated with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a report of three patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(1):E54-58.
[8] 赵凤东,杨伟,刘军辉,等.经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术后融合器移位及其危险因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(10):922-927.
[9] 肖波,毛克亚,王岩,等. 微创经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术与传统后路腰椎椎体间融合术并发症的比较分析[J].脊柱外科杂志, 2013,11(1):23-27.
[10] Chrastil J, Patel A. Complications associated with posterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(5):283-291.
[11] Chen L, Yang H, Tang T.Cage migration in spondylolisthesis treated with posterior lumbar interbody fusion using BAK cages.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(19):2171-2175.
[12] Nandyala SV, Fineberg SJ, Pelton M,et al.Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: one surgeon's learning curve. Spine J. 2013;(13)1493-1499.
[13] 肖波,毛克亚,王岩,等.直视下微创经椎间孔腰椎体间融合术的并发症分析[J].解放军医学院学报,2013,34(5):446-448.
[14] 张亚峰,杨惠林,唐天驷,等.后路椎体间融合术后融合器脱出的原因及其翻修术[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(12):909-912.
[15] Abbushi A,Cabraja M,Thomale UW. The influence of cage positioning and cage type on cage migration and fusion rates in patients with monosegmental posterior lumbar interbody fusion and posterior fixation. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(11): 1621-1628.
[16] Grant JP, Oxland TR, Dvorak MF. Mapping the structural properties of the lumbosacral vertebral endplates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(8):889-896.
[17] Chang TS, Chang JH, Wang CS, et al. Evaluation of unilateral cage-instrumented fixation for lumbar spine. J Orthop Surg Res. 2010;5:86.
[18] Vadapalli S, Robon M, Biyani A, et al. Effect of lumbar interbody cage geometry on construct stability: a cadaveric study. Spine (PhilaPa 1976). 2006;31(19):2189-2194.
[19] 苗惊雷,张朝跃,詹瑞森,等.置入椎间融合器行腰椎融合后Cage移位的原因[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39): 7307-7310.
[20] Niemeyer TK,Koriller M,Claes L. In vitro study of biomechanical behavior of anterior and transforaminal lumbar interbody instrumentation techniques. Neurosurgery. 2006; 59(6):1271-1276.
[21] Sudo H,Oda I,Abumi K. Biomechanical study on the effect of five different lumbar reconstruction techniques on adjacent-level intradiscal pressure and lamina strain. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006;5(2):150-155.
[22] Ntoukas V, Muller A. Minimally invasive approach versus traditional open approach for one level posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Minim Invas Neurosurg.2010;53(1):21-24.
[23] Wang J, Zhou Y, Zhang ZF, et al. Comparison of one-level minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis grades 1 and 2. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(10):1780-1784. |