| [1] Boerma M. Experimental radiation-induced heart disease: past, present, and future. Radiat Res. 2012;178(1):1-6.
[2] Boerma M, Hauer-Jensen M. Potential targets for intervention in radiation-induced heart disease. Curr Drug Targets. 2010; 11(11):1405-1412.
[3] Filopei J, Frishman W. Radiation-induced heart disease. Cardiol Rev. 2012;20(4):184-188.
[4] Lee PJ, Mallik R. Cardiovascular effects of radiation therapy: practical approach to radiation therapy-induced heart disease. Cardiol Rev. 2005;13(2):80-86.
[5] Stewart JR, Fajardo LF. Radiation-induced heart disease: an update. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1984;27(3):173-194.
[6] Andratschke N, Maurer J, Molls M, et al. Late radiation- heart disease after radiotherapy. Clinical importance, radiobiological mechanisms and strategies of prevention. Radiother Oncol. 2011;100(2):160-166.
[7] Finch W, Shamsa K, Lee MS. Cardiovascular complications of radiation exposure. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2014;15(3): 232-244.
[8] Lee MS, Finch W, Mahmud E. Cardiovascular complications of radiotherapy. Am J Cardiol. 2013;112(10):1688-1696.
[9] Basavaraju SR, Easterly CE. Pathophysiological effects of radiation on atherosclerosis development and progression, and the incidence of cardiovascular complications. Med Phys. 2002;29(10):2391-2403.
[10] Baker JE, Moulder JE, Hopewell JW. Radiation as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011; 15(7):1945-1956.
[11] Balonov M. Third annual Warren K. Sinclair keynote address: retrospective analysis of impacts of the Chernobyl accident. Health Phys. 2007;93(5):383-409.
[12] Ermak G, Figge JJ, Kartel NA, et al. Genetic aberrations in Chernobyl-related thyroid cancers: implications for possible future nuclear accidents or nuclear attacks. IUBMB Life. 2003; 55(12):637-641.
[13] Adams MJ, Lipshultz SE, Schwartz C, et al. Radiation- associated cardiovascular disease: manifestations and management. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2003;13(3):346-356.
[14] Liu HR, Tao L, Gao E, et al. Anti-apoptotic effects of rosiglitazone in hypercholesterolemic rabbits subjected to myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 2004; 62(1):135-144.
[15] Hart CM, Roman J, Reddy R, et al. PPARgamma: a novel molecular target in lung disease. J Investig Med. 2008;56(2): 515-517.
[16] Das SK, Chakrabarti R. Role of PPAR in cardiovascular diseases. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2006;1(2): 193-209.
[17] Gao D, Ning N, Hao G, et al. Pioglitazone attenuates vascular fibrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. PPAR Res. 2012; 2012:856426.
[18] Ehanire T, Ren L, Bond J, et al. Angiotensin II stimulates canonical TGF-β signaling pathway through angiotensin type 1 receptor to induce granulation tissue contraction. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. in press.
[19] Chen K, Chen J, Li D, et al. Angiotensin II regulation of collagen type I expression in cardiac fibroblasts: modulation by PPAR-gamma ligand pioglitazone. Hypertension. 2004; 44(5):655-661.
[20] Gao S, Wu R, Zeng Y. Up-regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in radiation-induced heart injury in rats. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2012;51(1):53-59.
[21] Wu R, Zeng Y. Does angiotensin II-aldosterone have a role in radiation-induced heart disease? Med Hypotheses. 2009; 72(3):263-266.
[22] 吴荣,马天馨,曾越灿,等.血管紧张素Ⅱ1型受体拮抗剂在大鼠放射性心脏损伤中保护作用的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2014. in press.
[23] Wang J, MacKenzie JD, Ramachandran R, et al. Identifying neutrophils in H&E staining histology tissue images. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2014;17(Pt 1):73-80.
[24] Pei Y, Fan JJ, Zhang XQ, et al. Repairing the osteochondral defect in goat with the tissue-engineered osteochondral graft preconstructed in a double-chamber stirring bioreactor. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:219203.
[25] Xia QY, Rao Q, Shen Q, et al. Immunohistochemical study of perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2013;42(6):381-385.
[26] Michalik L, Auwerx J, Berger JP, et al. International Union of Pharmacology. LXI. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2006;58(4):726-741.
[27] Macpherson AM, Archer DF, Leslie S, et al. The effect of etonogestrel on VEGF, oestrogen and progesterone receptor immunoreactivity and endothelial cell number in human endometrium. Hum Reprod. 1999;14(12):3080-3087.
[28] Horiuchi M, Iwanami J, Mogi M. Regulation of angiotensin II receptors beyond the classical pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). 2012;123(4):193-203.
[29] Issemann I, Green S. Activation of a member of the steroid hormone receptor superfamily by peroxisome proliferators. Nature. 1990;347(6294):645-650.
[30] Sime PJ. The antifibrogenic potential of PPARgamma ligands in pulmonary fibrosis. J Investig Med. 2008;56(2):534-538.
[31] Genovese T, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R, et al. Effect of rosiglitazone and 15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 on bleomycin-induced lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2005;25(2): 225-234.
[32] Iglarz M, Touyz RM, Viel EC, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and receptor-gamma activators prevent cardiac fibrosis in mineralocorticoid- dependent hypertension. Hypertension. 2003;42(4):737-743.
[33] Tsukamoto H, She H, Hazra S, et al. Anti-adipogenic regulation underlies hepatic stellate cell transdifferentiation. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21 Suppl 3:S102-105.
[34] Fliegner D, Westermann D, Riad A, et al. Up-regulation of PPARgamma in myocardial infarction. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008; 10(1):30-38.
[35] Chintalgattu V, Harris GS, Akula SM, et al. PPAR-gamma agonists induce the expression of VEGF and its receptors in cultured cardiac myofibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res. 2007;74(1): 140-150.
[36] Zou Y, Komuro I, Yamazaki T, et al. Cell type-specific angiotensin II-evoked signal transduction pathways: critical roles of Gbetagamma subunit, Src family, and Ras in cardiac fibroblasts. Circ Res. 1998;82(3):337-345.
[37] Ramires FJ, Sun Y, Weber KT. Myocardial fibrosis associated with aldosterone or angiotensin II administration: attenuation by calcium channel blockade. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1998;30(3): 475-483.
[38] Jawien J, Toton-Zuranska J, Gajda M, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) receptor Mas agonist ameliorates progress of atherosclerosis in apoE-knockout mice. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;63(1): 77-85.
[39] Ceravolo GS, Montezano AC, Jordão MT, et al. An Interaction of renin-angiotensin and kallikrein-kinin systems contributes to vascular hypertrophy in angiotensin II-induced hypertension: in vivo and in vitro studies. PLoS One. 2014; 9(11): e111117.
[40] Lan TH, Huang XQ, Tan HM. Vascular fibrosis in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):401-407.
[41] Zhao SM, Li HW, Guo CY, et al. Cardiac fibrosis in diabetic rats: regulation and mechanism of activation of the PPARgamma signal pathway. Chin J Physiol. 2010;53(4): 262-267.
[42] Takeda K, Ichiki T, Tokunou T, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activators downregulate angiotensin II type 1 receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation. 2000;102(15):1834-1839.
[43] Zhuo J, Moeller I, Jenkins T, et al. Mapping tissue angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin AT1, AT2 and AT4 receptors. J Hypertens. 1998;16(12 Pt 2):2027-2037.
[44] Su EJ, Lombardi DM, Siegal J, et al. Angiotensin II induces vascular smooth muscle cell replication independent of blood pressure. Hypertension. 1998;31(6):1331-1337.
[45] Laplante MA, Wu R, El Midaoui A, et al. NAD(P)H oxidase activation by angiotensin II is dependent on p42/44 ERK-MAPK pathway activation in rat's vascular smooth muscle cells. J Hypertens. 2003;21(5):927-936.
[46] Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL. Signal transduction mechanisms mediating the physiological and pathophysiological actions of angiotensin II in vascular smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52(4):639-672. |
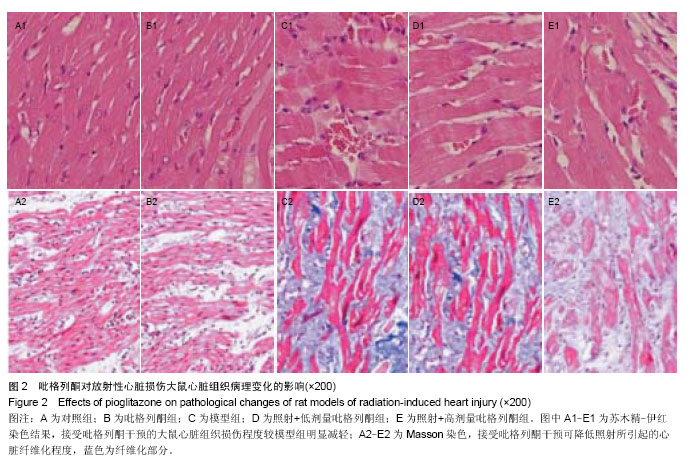
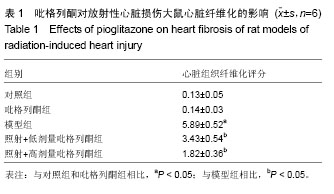

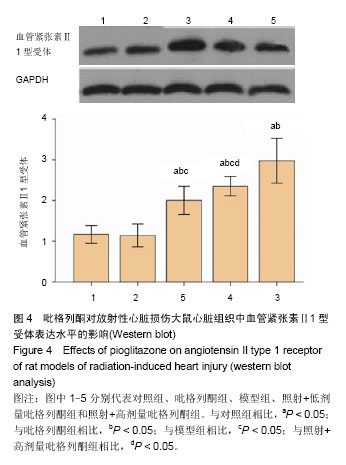
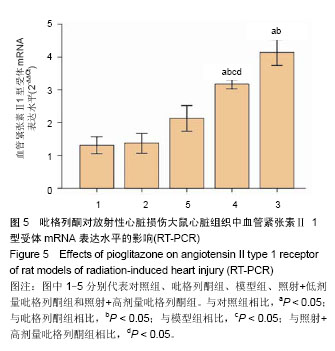
.jpg)