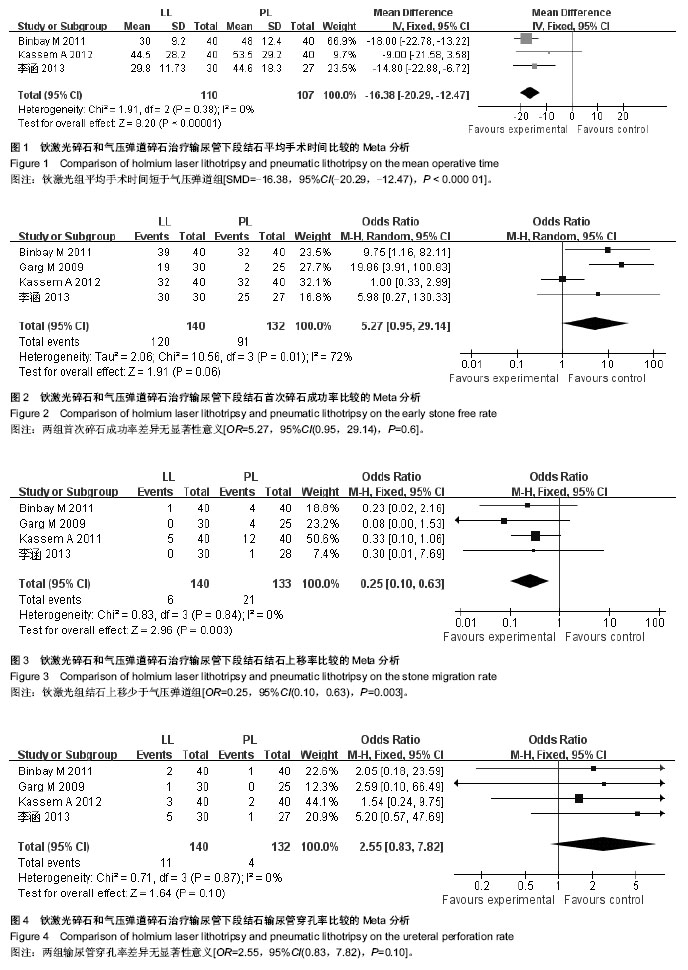
| [1] 刘志华,周祥福.输尿管下段结石的治疗进展[J].中华腔镜泌尿外科杂志:电子版,2010,4(1):62-64.
[2] Jüni P,Altman DG,Egger M.Systematic reviews in health care: Assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001; 323(7303):42-46.
[3] Binbay M,Tepeler A,Singh A, et al. Evaluation of pneumatic versus holmium:YAG laser lithotripsy for impacted ureteral stones.Int Urol Nephrol.2011;43:989-995.
[4] Garg SK,Mandal AK,Singh SK,et al. Ureteroscopic Laser Lithotripsy versus Ballistic Lithotripsy for Treatment of Ureteric Stones: A Prospective Comparative Study.Urol Int. 2009;82: 341-345.
[5] Kassem A,ElFayoumy H,ElSaied W,et al.Laser and Pneumatic Lithotripsy in the Endoscopic Management of Large Ureteric Stones: A Comparative Study.Urol Int. 2012;88:311-315.
[6] 李涵.输尿管镜气压弹道碎石与钬激光碎石治疗输尿管下段结石的比较[J].现代临床医学杂志,2013,2(39):26-28.
[7] 覃钦友,许海燕,覃超平.输尿管镜弹道碎石术与体外震波碎石术治疗输尿管中下段结石的临床疗效分析[J].中国中医药咨询, 2011,3(22):195-196.
[8] 尹继云,吴志贤,何文强,等.标准通道下肾镜结合输尿管镜治疗上尿路结石1120例报告[J].临床泌尿外科杂志, 2012,21(3): 171-173.
[9] 冯振华,黄强,邱光进,等.耻骨上膀胱穿刺微造瘘输尿管镜碎石术在儿童下尿路结石中的应用[J].中国医药导报, 2012,15(3): 167-168.
[10] 孙清,俞弘颀,印荣.冲击波碎石术与输尿管镜取石术治疗输尿管中下段结石的临床研究[J].中国医药指南,2012,3(5):410-411.
[11] 马波,汪中扬,吴荣佩,等.经皮肾微造瘘输尿管镜气压弹道碎石术治疗上尿路结石[J].中国内镜杂志,2006,18(9):919-921.
[12] 杨琦,王养民,景德善,等.输尿管镜下钬激光治疗结石梗阻性急性肾功能衰竭[J].西北国防医学杂志,2010,10(4):258-260.
[13] 彭波,施建昌,郑金良,等.输尿管镜下钬激光治疗尿路结石230例[J].中国内镜杂志,2005,8(6):203-605.
[14] 马勇,初雪云,张波.输尿管镜下气压弹道碎石术222例临床体会[J]山东医药,2011,51(23):88-89.
[15] 徐留玉,李青,魏学斌,等.钬激光碎石术与气压弹道碎石术治疗输尿管结石的疗效比较[J].中国激光医学杂志,2007,15(4): 228-230.
[16] Bapat SS,Kitan MD,Pumapatre SS,et al.Comparision of holmium laser and pneumatic lithotripsy in managing upper-ureteral stones.J Endourol.2007;21(12):1425-1427.
[17] Teichman JM,Vassar GJ,Bishoff JT,et al.Holmium: YAG lithotripsy yields smaller fragments than lithoclast,pulsed dye laser or electrohydraulic lithotripsy.J Urol.1998;160:320-324.
[18] Jou YC,Shen JH,Cheng MC.Perculaneous nephrolithotomy with holmium: Yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser and fiber guider-report of 394 cases.Urology.2005;65(3):454-458.
[19] Sofer M,Watterson JD,Wollin TA,et al.Holmium: YAG laser lithotripsy for upper urinary tract calculi in 598 patients. J Urol. 2002;167:31.
[20] Kostakopoulos A,stavropoulos NJ,Picramenos D,et al.The swiss lithoclast: an ideal intracorporeal lithotriptor. Urol Int. 1995;55:19-20.
[21] Yip KH, Lee F, Tam PC. Holmium laser lithotripsy for ureteral calculi :an outpatient procedure. J Endourol1998;12:241-246.
[22] Jiang H,Wu Z, Ding Q,et alUreteroscopic treatment of ureteral calculi with holmium: YAG laser lithotripsy.J Endourol. 2007; 21(2):151-154.
[23] FarkasA, Peteri L, Lorincz L, et al .Holmium: YAG laser treatment of ureteral calculi: A5-year experience.Lasers Med Sci.2006;21(3):170-174.
[24] Hecht SL,Wolf JJ.Techniques for holmium laser lithotripsy of intrarenal calculi.Urology.2013;81(2):442-445.
[25] Sun YH,Wang LH,Qian SX,et al.Treatment of urinary calculi with the ureteroscopy and Swiss-Lithoclast pneumatic lithotriptor(report of 150 cases).J Endourol.2000;14:281-283.
[26] 广辉,杨为民,庄乾元,等.双J管在上尿路梗阻性疾病中的应用及其并发症[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2001,22(2):24-26.
[27] 纪冰.D-J管在泌尿外科诊疗中的应用[J].中国实用医药, 2009, 4(29):87-88.
[28] 刘勇,王佳,魏强,等.经皮肾镜取石术后D-J管与传统肾造瘘管引流效果的系统评价[J].中国循证医学杂志,2009,9(2):230-238.
[29] 汪官富,章灵芝,朱汝健,等.术前置D-J管后腹腔镜手术治疗输尿管结石[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,2007,22(7):500-502.
[30] 范地福,刘泰荣.D-J管在肾绞痛治疗中的应用[J].中国内镜杂志, 2007,13(4):431-432.
[31] 王德生,马小芹.D-J管与T管引流在输尿管结石术后应用的比较[J].中国现代医学杂志,2003,13(8):86-87. |