2.1 文献筛检结果 共检索到文献768篇,经过阅读题录后排除重复文献及无关文献567篇,严格按照排除标准及纳入标准阅读全文后,最终纳入9篇文献,其中试验组398例,对照组382例;发表时间为2011至2014年之间。其中有2篇对术后POP-Q分期进行比较,根据POP-Q客观评价手术效果,屏气加腹压,分期小于Ⅱ期为客观治愈,Ⅱ期及Ⅱ期以上为复发[5]。
2.2 纳入研究的质量评价 所有纳入文献均为随机对照研究,但未提及分配隐藏和盲法,纳入文献均对术后做了随访工作,但具体随访时间长短不一,并且对失访情况进行了描述。因此,所有文献均存在选择性偏倚和测量性偏倚的可能性,详见表1。
2.3 Meta分析结果
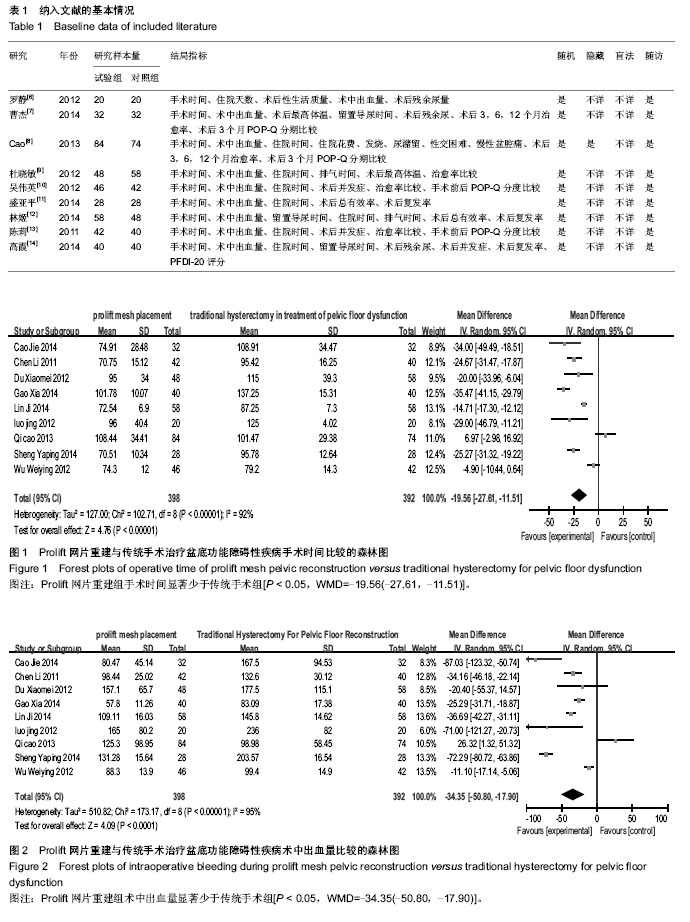
2.3.1 手术时间 对纳入的9篇文献报道的手术时间进行异质性检测,不符合同质性(χ2=102.71,P < 0.000 01),经异质性检验各项研究中手术时间异质性明显(I2=92%),采用随机效应模型分析,合并效应量分析,试验组手术时间显著少于对照组[P < 0.05,WMD=-19.56(-27.61,-11.51)](图1)。
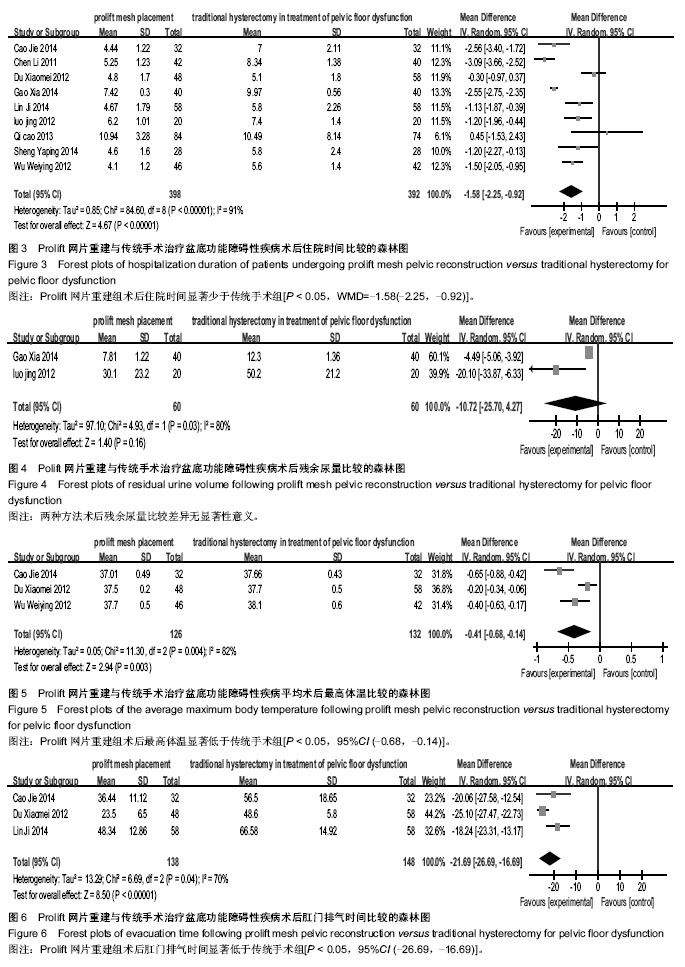
2.3.2 术中出血量 对纳入的9篇文献报道的术中出血量进行异质性检测,不符合同质性(χ2=173.17,P < 0.000 01),经异质性检验各项研究中术后出血量异质性明显(I2=95%),采用随机效应模型分析,合并效应量分析,试验组术中出血量显著少于对照组[P < 0.05,WMD=-34.35(-50.80,-17.90)] (图2)。
2.3.3 住院时间 对纳入的9篇文献报道的住院时间进行异质性检测,不符合同质性(χ2=84.60,P <0.000 01),经异质性检验各项研究中术后住院时间异质性明显(I2=91%),采用随机效应模型分析,合并效应量分析,试验组术后住院时间显著少于对照组[P < 0.05,WMD=-1.58(-2.25,-0.92)](图3)。
2.3.4 术后残余尿量 纳入研究9篇中,有2篇对术后残余尿量进行了报道[6,14],经异质性检验各项研究中术后残余尿量异质性明显(I2=80%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组60例,对照组60例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组在术后残余尿量比较差异无显著性意义[P > 0.05,95%CI (-25.70,4.27)](图4)。
2.3.5 术后最高体温 纳入研究9篇报道中,有3篇对术后最高体温进行了报道[7,9-10],经异质性检验各项研究中术后最高体温异质性明显(I2=82%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组126例,对照组132例,合并效应量分析,结果显示prolift网片重建组在术后最高体温方面显著低于传统手术组[P < 0.05,95%CI (-0.68,-0.14)](图5)。
2.3.6 肛门排气时间 纳入研究9篇均报道中,有3篇对术后肛门排气时间进行了报道[7,9,12],经异质性检验各项研究中术后肛门排气时间异质性明显(I2=70%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组138例,对照组148例,合并效应量分析,结果显示试验组术后肛门通气时间显著低于对照组[P < 0.05,95%CI (-26.69,-16.69)](图6)。
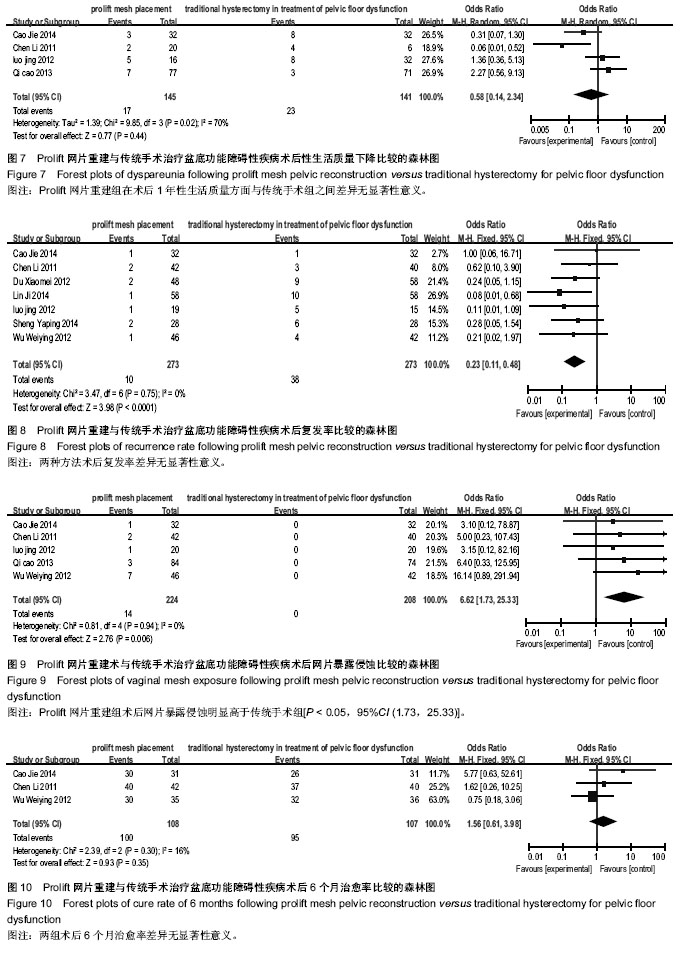
2.3.7 术后1年性生活质量 纳入研究9篇报道中,有4篇对术后性生活质量进行了报道[6-8,13],经异质性检验各项研究中术后性生活质量异质性明显(I2=70%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组145例,对照组141例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组术后1年性生活质量差异无显著性意义[P > 0.05,95%CI (0.14,2.34)](图7)。
2.3.8 术后复发率 纳入研究9篇报道中,有7篇对术后复发率进行了报道[6-7,9-13],经异质性检验各项研究中术后复发率无异质性(I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型分析,试验组273例,对照组273例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组术后复发率差异无显著性意义[P > 0.05,95%CI (0.11,0.48)](图8)。
2.3.9 术后阴道网片暴露侵蚀 纳入研究9篇报道中,有5篇对术后网片暴露侵蚀进行了报道[6-8,10,13],经异质性检验各项研究中术后网片暴露侵蚀无异质性(I2=0%),故采用固定效应模型分析,试验组224例,对照组208例,合并效应量分析,结果显示试验组在术后网片暴露侵蚀方面明显高于对照组[P < 0.05,95%CI (1.73,25.33)](图9)。这种比较或许没有可比性,但作为网片盆地重建术不可忽略的一个术后并发症,本文在此做了此研究。
2.3.10 术后6个月治愈率 纳入研究9篇报道中,有3篇对术后6个月治愈率进行了报道[7,10,13],经异质性检验各项研究中术后6个月治愈率比较同质性明显(I2=16%),故采用固定效应模型分析,试验组108例,对照组107例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组术后6个月治愈率差异无显著性意义[P > 0.05,95%CI (0.61,3.98)](图10)。
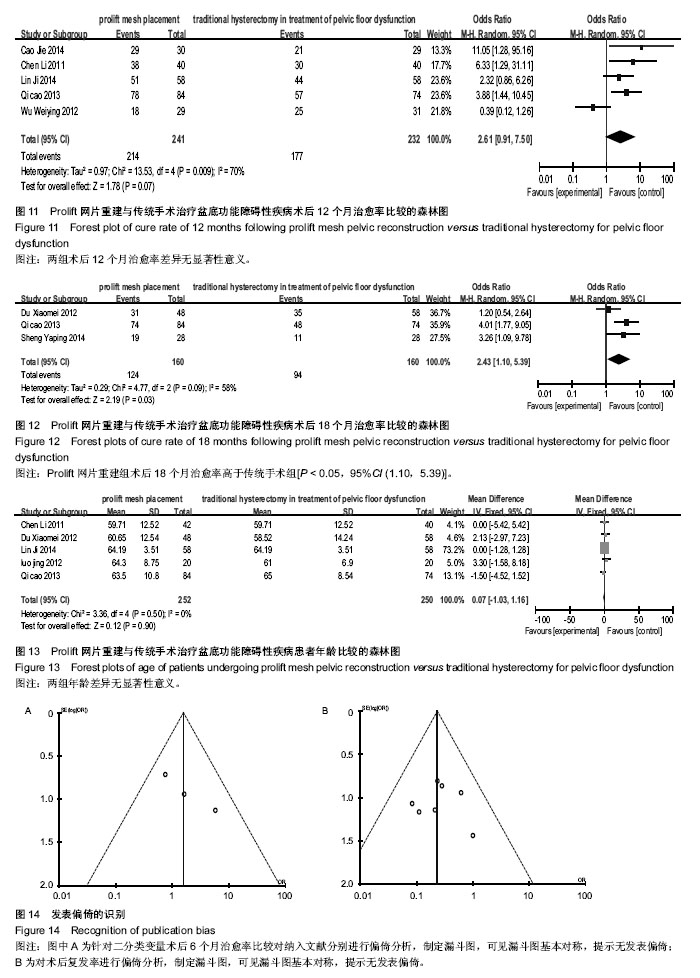
2.3.11 术后12个月治愈率 纳入研究9篇报道中,有5篇对术后12个月治愈率进行了报道[7-8,10-13],经异质性检验各项研究中术后12个月治愈率比较异质性明显(I2=70%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组241例,对照组232例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组术后12个月治愈率差异无显著性意义 [P > 0.05,95%CI (0.91,7.50)](图11)。
2.3.12 术后18个月治愈率 纳入研究9篇报道中,有3篇对术后18个月治愈率进行了报道[8-9,11],经异质性检验各项研究中术后18个月治愈率比较异质性明显(I2=58%),故采用随机效应模型分析,试验组160例,对照组160例,合并效应量分析,结果显示试验组术后18个月治愈率高于对照组[P < 0.05,95%CI (1.10,5.39)](图12)。
2.3.13 患者年龄 纳入研究9篇报道中,有5篇对两组的年龄进行了确切的数据报道[6,8-9,1-13],其余文献只是得出两手术方式患者年龄之间差异无显著性意义,经异质性检验各项研究中年龄比较无异质性(I2=0),故采用固定效应模型分析,试验组252例,对照组250例,合并效应量分析,结果显示两组年龄差异无显著性意义[P > 0.05,95%CI (-1.03,1.16)] (图13)。
2.4 发表偏倚的识别 针对二分类变量术后6个月治愈率比较对纳入文献分别进行偏倚分析,制定漏斗图(图14A),可见漏斗图基本对称,提示无发表偏倚。对术后复发率进行偏倚分析,制定漏斗图(图14B),可见漏斗图基本对称,提示无发表偏倚。