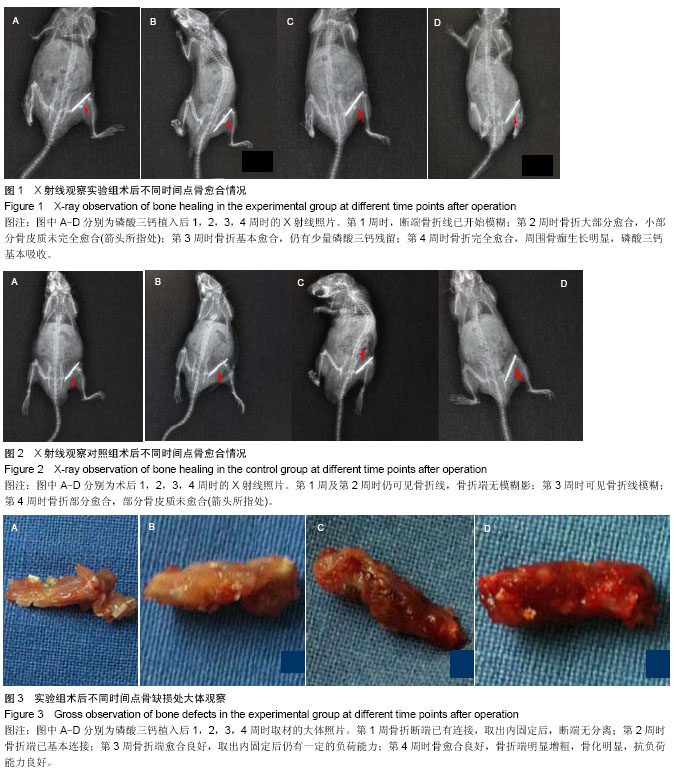
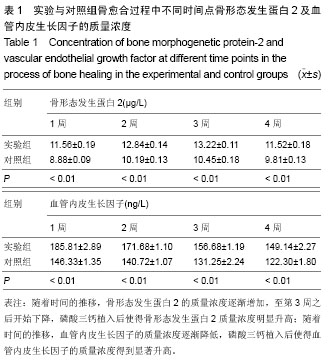
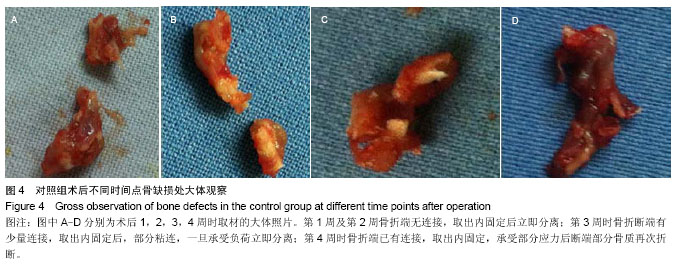
| [1] Liu Y,Lim J,Teoh SH.Review: Development of clinically relevant scaffolds for vascularised bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2013;31(5):688-705.
[2] Yin X,Li J, Xu J,Huang Z,et al.Clinical assessment of calcium phosphate cement to treat tibial plateau fractures.J Biomater Appl.2013;28(2):199-206.
[3] Seebach C,Henrich D,Kähling C,et al. Endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto beta-TCP granules enhance early vascularization and bone healing in a critical-sized bone defect in rats.Tissue Eng Part A.2010; 16(6):1961-1970.
[4] 钱成雄,叶毓粦,吴坤南,等.生物陶瓷(β-TCP人工骨)治疗四肢骨折22例临床研究[J]. 中国当代医药,2010,17(10):37-38.
[5] Raghunath M,Singh N,Singh T,et al.Defect nonunion of a metatarsal bone fracture in a cow: successful management with bone plating and autogenouscancellous bone graft. Vet Comp OrthopTraumatol.2013;26:233-237.
[6] 何晨光,赵莉,林柳兰,等.基于快速成形的磷酸钙多孔陶瓷成骨性能初步研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2010,24(7): 792-796.
[7] 钱剑,刘国文,王哲.微量元素铜对软骨细胞胰岛素样生长因子mRNA基因表达的影响[J].中国兽医科技,2005,35(7):565-569.
[8] Liu Y,Chan JK,Teoh SH.Review of vascularised bone tissue-engineering strategies with a focus on co-culture systems.J Tissue EngRegen Med.2012.doi: 10.1002/term.1617. [Epub ahead of print]
[9] Thitiset T,Damrongsakkul S,Bunaprasert T,et al.Development of collagen/demineralized bone powder scaffolds and periosteum-derived cells for bone tissue engineering application.Int J Mol Sci.2013;14:2056-2071.
[10] 张路,赵文志.不同生物支架材料修复骨缺损的性能与评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(51):9679-9682.
[11] 殷潇凡,罗从风,张晓阳,等.应用多孔磷酸三钙植骨治疗胫骨平台骨折的组织学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(21):4165-4168.
[12] 李剑勇,殷潇凡,徐俊.磷酸三钙植骨治疗胫骨远端骨缺损后的骨组织变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(38): 7037-7041.
[13] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007: 196-199.
[14] Fujioka-Kobayashi M,Ota MS,Shimoda A,et al.Cholesteryl group- and acryloyl group-bearing pullulannanogel to deliver BMP2 and FGF18 for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2012;33:7613-7620.
[15] Gao W,Qiao X,Ma S,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells accelerate neovascularization in ischaemic diabetic skin flap via expression of hypoxiainducible factor-1alpha. J Cell Mol Med.2011;15:2575-2585.
[16] 徐建强,周密,张树明,等.复合骨形态发生蛋白-2的人工骨结合带血供组织修复羊桡骨大段骨缺损的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(8):697-702.
[17] 陆梦漪,任毅,胡万青,等.血管内皮生长因子混合Ⅰ型胶原修饰 β-磷酸三钙多孔支架的血管化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(12):1839-1845.
[18] Peng LH,Wei W,Qi XT,et al.Epidermal Stem Cells Manipulated by pDNA-VEGF165/CYD-PEI Nanoparticles Loaded Gelatin/beta-TCP Matrix as a Therapeutic Agent and Gene Delivery Vehicle for Wound Healing.Mol Pharm. 2013; 10(8):3090-3102.
[19] Yang P,Huang X,Wang C,et al.Repair of bone defects using a new biomimetic construction fabricated by adipose-derived stem cells, collagen I, and porous beta-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds.Exp Biol Med.2013;238(12):1331-1343.
[20] 董黎强,尹航,王昌兴,等.不同手术时间对骨折愈合过程中骨形态发生蛋白-2表达的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(3):682.
[21] 曾中华,余黎,龚玲玲,等.骨折愈合过程中BMP-2和VEGF的表达[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2005,26(4):467-469.
[22] 叶永成.EGF和VEGF在创伤性骨折愈合中的变化与意义[J].中国医药指南,2012,9(10):412-414.
[23] 李阳,钱栋,马鹏,等.大鼠股骨骨不连模型不同位点骨形态发生蛋白2基因的表达[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2010,20(2):141-144.
[24] 初同伟,王正国,朱佩芳,等.血管内皮生长因子在骨折愈合中的作用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2002,16(2):75-78.
[25] 高全文,柳春明,宋慧锋,等.血管内皮生长因子165基因转染的骨髓基质细胞异位成骨的初步观察[J].中国美容医学, 2009,18(1): 69-71.
[26] 王簕,覃俊君,陈思园,等.血管束植入组织工程骨修复兔股骨缺损对血管内皮生长因子表达的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2009, 11(6):540-545.
[27] Lindhorst D,Tavassol F,Von See C,et al.Effects of VEGF loading on scaffold-confined vascularization.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;95(3):783-792.
[28] 王昌兴,刘琦,董黎强,等.浓缩自体骨髓移植结合金葡液局部注射对骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程中BMP-2 和VEGF 表达的调控[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2014,38(2):188-195.
[29] 王庆,陈光兴,郭林,等.骨形态发生蛋白-2和7联合基因修饰构建组织工程骨的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013,15(11): 984-989.
[30] Bai Y,Leng Y,Yin G,et al. Effects of combinations of BMP-2 with FGF-2 and/or VEGF on HUVECs angiogenesis in vitro and CAM angiogenesis in vivo.Cell Tissue Res. 2014.[Epub ahead of print]
[31] Nillesen ST ,Geutjes PJ ,Wismans R ,et al.Increased angiogenesis and blood vessel maturation in acellular collagen-heparin scaffolds containing both FGF2 and VEGF. Biomaterials.2007;28(6):1123-1131. |