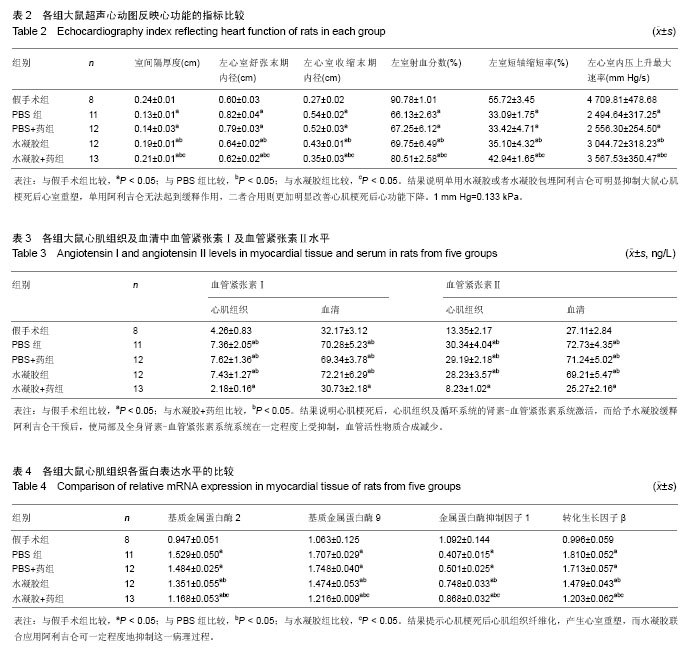
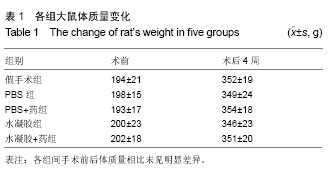
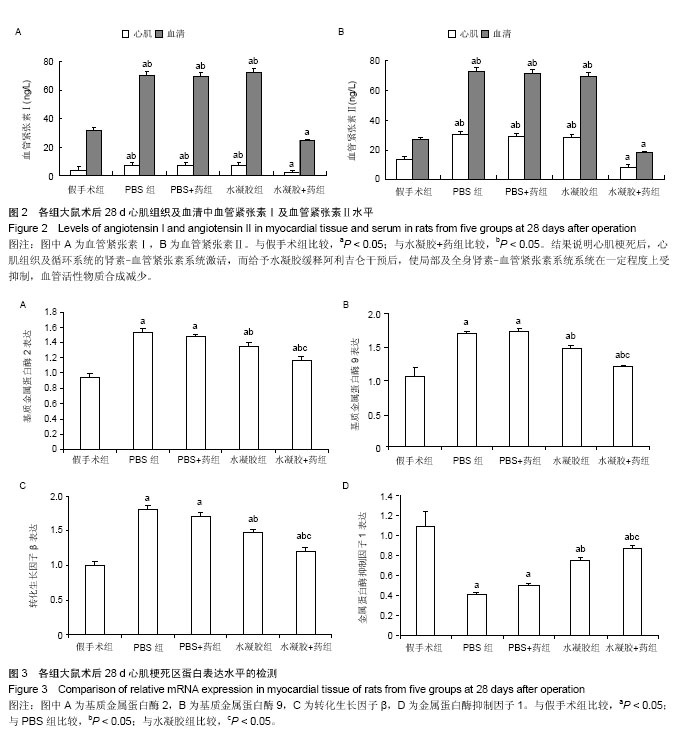
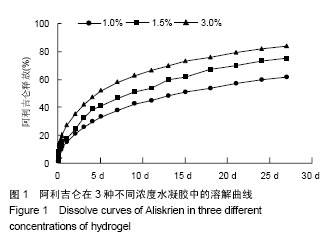
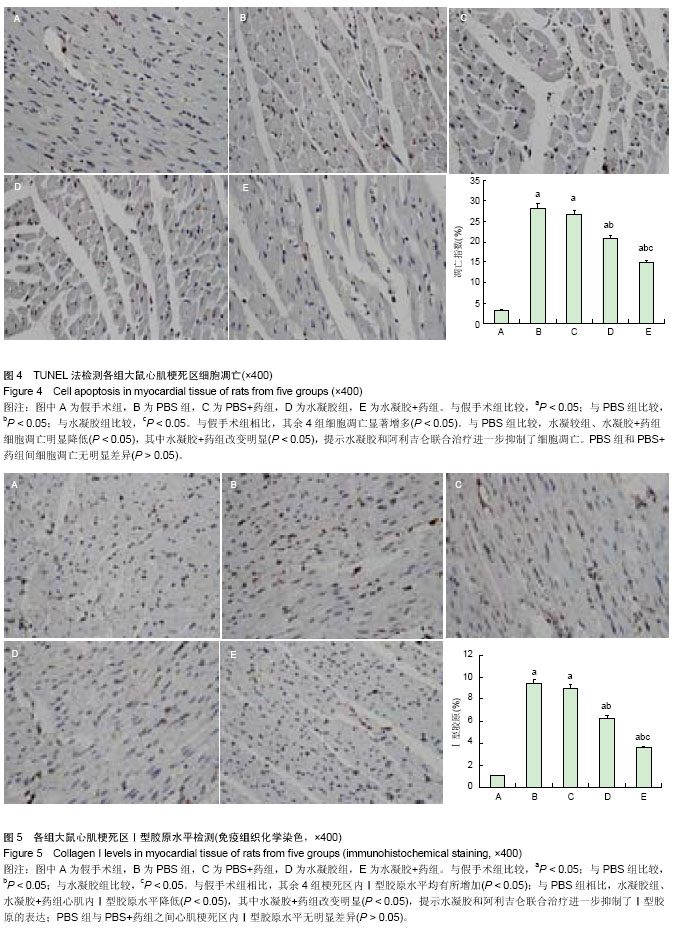
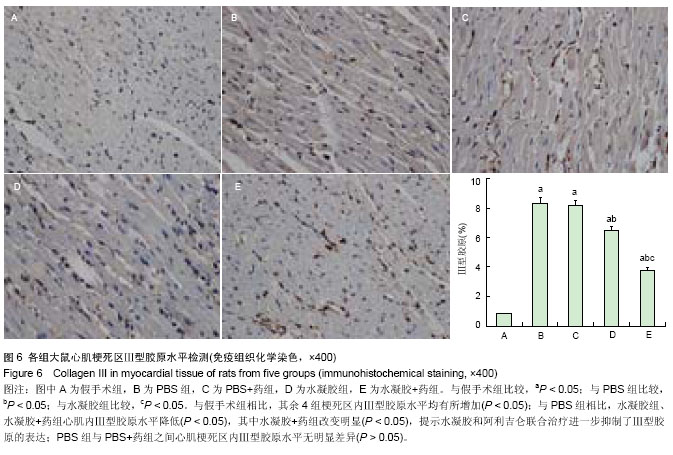
| [1] van der Linde D,Konings EE,Slager MA,et al.Birth prevalence of congenital heart disease worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(21):2241-2247.
[2] Abbate A,Biondi-Zoccai GG,Baldi A.Pathophysiologic role of myocardial apoptosis in post-infarction left ventricular remodeling. J Cell Physiol. 2002;193(2):145-153.
[3] Cohn JN,Ferrari R,Sharpe N.Cardiac remodeling--concepts and clinical implications: a consensus paper from an international forum on cardiac remodeling. Behalf of an International Forum on Cardiac Remodeling.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35(3):569-582.
[4] Kloner RA,Rezkalla SH.Cardiac protection during acute myocardial infarction: where do we stand in 2004?J Am Coll Cardiol.2004;44(2):276-286.
[5] Savoia C,Volpe M.Angiotensin receptor modulation and cardiovascular remodeling. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.2011;12(3):381-284.
[6] Ferrario CM.Role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and proinflammatory mediators in cardiovascular disease.Am J Cardiol.2006;98(1):121-128.
[7] Mentz RJ,Bakris GL,Waeber B,et al.The past,present and future of renin-angiotensin aldosterone system inhibition.Int J Cardiol. 2013;167(5):1677-1687.
[8] Vijayaraghavan K,Deedwania P. Renin-angiotensin- aldosterone blockade for cardiovascular disease prevention. Cardiol Clin.2011;29(1):137-156.
[9] Cohn JN.Reducing cardiovascular risk by blockade of the renin-angiotensin- aldosterone system.Adv Ther. 2007;24(6): 1290-304.
[10] Horký K.Does the rennin inhibitor aliskiren offer promising novel opportunities in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases?Vnitr Lek.2007;53(4):364-370.
[11] Van Tassell BW,Munger MA.Aliskiren for renin inhibition: a new class of antihypertensives.Ann Pharmacother. 2007; 41(3):456-464.
[12] Volpe M,Battistoni A,Chin D,et al.Renin as a biomarker of cardiovascular disease in clinical practice.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.2012;22(4):312-317.
[13] 罗芳.生物医用水凝胶材料的研究进展[J].广东化工,2011,38(8): 104-105.
[14] Wu DQ,Wang T,Lu B,et al.Fabrication of Supramolecular Hydrogels for Drug Delivery and Stem Cell Encapsulation. Langmuir.2008;24(18):10306-10312.
[15] McMurray JJ,Adamopoulos S,Anker SD,et al.ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2012: The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. 2012;33(14):1787-1847.
[16] Gallagher GL,Jackson CJ,Hunyor SN.Myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling in ischemic heart failure.Front Biosci.2007;12:1410-1419.
[17] Jiang XJ,Wang T,Li XY,et al.Injection of a novel synthetic hydrogel preserves left ventricle function after myocardial infarction.J Biomed Mater Res A.2009;90(2):472-477.
[18] Riccioni G.Aliskiren in the treatment of hypertension and organ damage.Cardiovasc Ther.2011;29(1):77-87.
[19] Abramov D,Carson PE.The role of angiotensin receptor blockers in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13(3):317-327.
[20] McMurray JJ,Pitt B,Latini R,et al.Aliskiren Observation of Heart Failure Treatment(ALOFT)Investigators. Effects of the oral direct renin inhibitor aliskiren in patients with symptomatic heart failure.Circ Heart Fail.2008;1(1):17-24.
[21] Pilz B,Shagdarsuren E,Wellner M,et al.Aliskiren, a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in double-transgenic rats.Hypertension. 2005;46(3):569-576.
[22] Puig JG,Schunkert H,Taylor AA,et al.Evaluation of the dose--response relationship of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor, in an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled study in adult patients with stage 1 or 2 essential hypertension.Clin Ther. 2009;31(12): 2839-2850. |