| [1]Moe OW.Kidney stones: pathophysiology and medical management.Journa.2006;367(9507):333-344.
[2]Evan AP,Lingeman JE,Coe FL,et al.Randall's plaque of patients with nephrolithiasis begins in basement membranes of thin loops of Henle.Journa.2003;111(5):607-616.
[3]Evan AP, Lingeman JE, Coe FL,et al. Role of interstitial apatite plaque in the pathogenesis of the common calcium oxalate stone. Journa.2008;28(2):111-119.
[4]Khan SR.Crystal-induced inflammation of the kidneys: results from human studies, animal models, and tissue-culture studies. Journa.2004;8(2):75-88.
[5]de Water R,Noordermeer C,Houtsmuller AB,et al.Role of macrophages in nephrolithiasis in rats: an analysis of the renal interstitium. Journa.2000;36(3):615-625.
[6]Okada A, Yasui T, Hamamoto S, et al. Genome-wide analysis of genes related to kidney stone formation and elimination in the calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis model mouse: detection of stone-preventive factors and involvement of macrophage activity. Journa.2009;24(5):908-24.
[7]Okada A,Yasui T,Fujii Y,et al.Renal macrophage migration and crystal phagocytosis via inflammatory-related gene expression during kidney stone formation and elimination in mice: Detection by association analysis of stone-related gene expression and microstructural observation. Journa.2010; 25(12):2701-2711.
[8]de Water R, Leenen PJ, Noordermeer C, et al. Cytokine production induced by binding and processing of calcium oxalate crystals in cultured macrophages. Journa. 2001;38(2): 331-338.
[9]Blackwell TS, Christman JW. Sepsis and cytokines: current status. Journa.1996;77(1):110-117.
[10]Commins SP, Borish L, Steinke JW. Immunologic messenger molecules: cytokines, interferons, and chemokines. Journa. 2010;125(2 Suppl 2):S53-72.
[11]Ogura N, Satoh K, Akutsu M, et al. MCP-1 production in temporomandibular joint inflammation. Journa.2010;89(10): 1117-1122.
[12]Lukens JR,Gross JM,Kanneganti TD.IL-1 family cytokines trigger sterile inflammatory disease. Journa.2012;3:315.
[13]Kutlu B,Darville MI,Cardozo AK,et al.Molecular regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in pancreatic beta-cells. Journa.2003;52(2):348-355.
[14]Hoebe K, Janssen E, Beutler B.The interface between innate and adaptive immunity. Journa.2004;5(10):971-974.
[15]Conze D, Weiss L, Regen PS, et al. Autocrine production of interleukin 6 causes multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells. Journa.2001;61(24): 8851-8858.
[16]Lotze MT, Tracey KJ. High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Journa. 2005; 5(4): 331-342.
[17]Bustin M. Regulation of DNA-dependent activities by the functional motifs of the high-mobility-group chromosomal proteins. Journa.1999; 19(8): 5237-5246.
[18]Goodwin GH, Sanders C, Johns EW. A new group of chromatin-associated proteins with a high content of acidic and basic amino acids. Journa.1973; 38(1): 14-19.
[19]Landsman D, Bustin M. A signature for the HMG-1 box DNA-binding proteins. Journa. 1993; 15(8): 539-546.
[20]Boonyaratanakornkit V, Melvin V, Prendergast P, et al. High-mobility group chromatin proteins 1 and 2 functionally interact with steroid hormone receptors to enhance their DNA binding in vitro and transcriptional activity in mammalian cells. Journa.1998; 18(8): 4471-4487.
[21]Melvin VS, Edwards DP. Coregulatory proteins in steroid hormone receptor action: the role of chromatin high mobility group proteins HMG-1 and -2. Journa.1999; 64(9): 576-586.
[22]Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Journa.1999; 285(5425): 248-251.
[23]Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ. Extracellular role of HMGB1 in inflammation and sepsis. Journa.2004; 255(3): 320-331.
[24]Lin X, Yang H, Sakuragi T, et al. Alpha-chemokine receptor blockade reduces high mobility group box 1 protein-induced lung inflammation and injury and improves survival in sepsis. Journa.2005; 289(4): L583-590.
[25]Sunden-Cullberg J, Norrby-Teglund A, Treutiger CJ. The role of high mobility group box-1 protein in severe sepsis. Journa. 2006; 19(3): 231-236.
[26]Scaffidi P, Misteli T, Bianchi ME.Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Journa.2002; 418(6894): 191-195.
[27]Penzo M, Molteni R, Suda T,et al.Inhibitor of NF-kappa B kinases alpha and beta are both essential for high mobility group box 1-mediated chemotaxis [corrected]. Journa.2010; 184(8): 4497-4509.
[28]秦阳华. HMGB1与LPS协同刺激巨噬细胞产生致炎细胞因子的机制研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2009.
[29]Randall A. The Origin and Growth of Renal Calculi. Journa .1937; 105(6): 1009-1027.
[30]Asplin JR, Mandel NS, Coe FL.Evidence of calcium phosphate supersaturation in the loop of Henle. Journa.1996; 270(4 Pt 2): F604-13.
[31]Resnick MI, Boyce WH. Spherical calcium bodies in stone-forming urine. Journa 1978; 15(6): 449-451.
[32]Kok DJ, Schell-Feith EA. Risk factors for crystallization in the nephron: the role of renal development. Journa.1999; 10 Suppl 14: S364-370.
[33]Gambaro G, D'Angelo A, Fabris A,et al. Crystals, Randall's plaques and renal stones: do bone and atherosclerosis teach us something? Journa.2004; 17(6): 774-777.
[34]Shimada O, Ishikawa H, Tosaka-Shimada H,et al. Rearrangements of actin cytoskeleton during infection with Escherichia coli O157 in macrophages. Journa. 1999; 24(5): 237-246.
[35]Barsness KA, Bensard DD, Partrick DA, et al. Endotoxin induces an exaggerated interleukin-10 response in peritoneal macrophages of children compared with adults. Journa.2004; 39(6): 912-5; discussion -5.
[36]Fulton SA, Reba SM, Pai RK, et al.Inhibition of major histocompatibility complex II expression and antigen processing in murine alveolar macrophages by Mycobacterium bovis BCG and the 19-kilodalton mycobacterial lipoprotein.Journa. 2004; 72(4): 2101-2110.
[37]Andersson U, Wang H, Palmblad K, et al. High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. Journa.2000; 192(4): 565-570.
[38]Park JS, Arcaroli J, Yum HK, et al.Activation of gene expression in human neutrophils by high mobility group box 1 protein. Journa.2003; 284(4): C870-879.
[39]Rendon-Mitchell B, Ochani M, Li J, et al. IFN-gamma induces high mobility group box 1 protein release partly through a TNF-dependent mechanism. Journa .2003; 170(7): 3890-3897. |
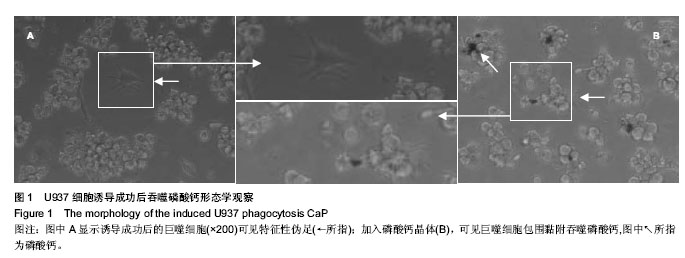
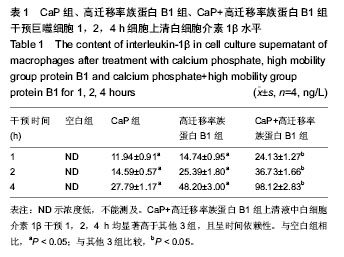
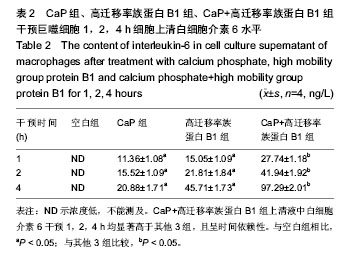
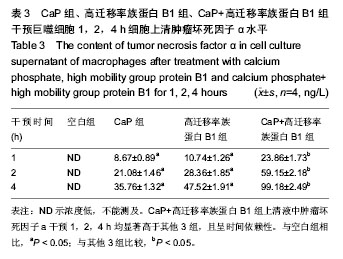
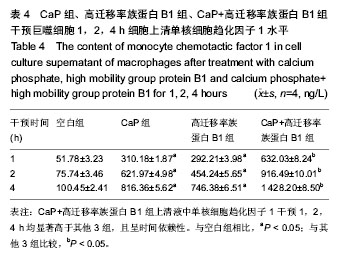
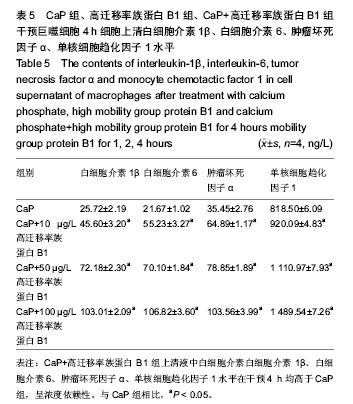
.jpg)
.jpg)