| [1]Givissis PK, Symeonidis PD, Ditsios KT, et al. Late results of absorbable pin fixation in the treatment of radial head fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5):1217-1224.
[2]Mason ML. Some observations on fractures of the head of the radius with a review of one hundred cases. Br J Surg. 1954; 42(172):123-132.
[3]赵勇,竺湘江,宋南炎,等.克氏针与微型钢板治疗MasonⅡ型及Ⅲ型桡骨头骨折的病例对照研究[J].中国骨伤,2012,25(4): 310-312.
[4]王维光,刘万军,王振海,等.不同内固定方法治疗Mason Ⅱ型桡骨头骨折临床效果的对比研究 [J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009, 17(22):1700-1703.
[5]陈碌昆,罗鹰.可吸收棒内固定治疗MasonⅡ、Ⅲ型成人桡骨小头骨折[J].广东医学,2010,31(9):1185-1186.
[6]冯宇,朱颖华,程光齐.可吸收钉棒治疗粉碎性桡骨头骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(1):28-30.
[7]Hirvensalo E, Böstman O, Rokkanen P. Absorbable polyglycolide pins in fixation of displaced fractures of the radial head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1990;109(5):258-261.
[8]Jahn R, Diederichs D, Friedrich B. Resorbable implants and their use exemplified by fracture of the head of the radius. Aktuelle Traumatol. 1989;19(6):281-286.
[9]Pelto K, Hirvensalo E, Böstman O, et al. Treatment of radial head fractures with absorbable polyglycolide pins: a study on the security of the fixation in 38 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 1994;8(2):94-98.
[10]Rehm KE, Helling HJ, Claes L. Report of the Biodegradable Implants Study Group. Aktuelle Traumatol. 1994;24(2):70-73.
[11]Helling HJ, Prokop A, Schmid HU, et al. Biodegradable implants versus standard metal fixation for displaced radial head fractures. A prospective, randomized, multicenter study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2006;15(4):479-485.
[12]邢丹谋,勘武生,任东等.可吸收自身增强软骨钉治疗桡骨小头骨折[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(1):50-54.
[13]Broberg MA, Morrey BF. Results of delayed excision of the radial head after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(5): 669-674.
[14]Weiler A, Helling HJ, Kirch U, et al. Foreign-body reaction and the course of osteolysis after polyglycolide implants for fracture fixation: experimental study in sheep. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78(3):369-376.
[15]Dooley JF, Angus PD. The importance of elbow aspiration when treating radial head fractures. Arch Emerg Med. 1991; 8(2):117-121.
[16]Struijs PA, Smit G, Steller EP. Radial head fractures: effectiveness of conservative treatment versus surgical intervention. A systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(2):125-130.
[17]梅国华,张长青,罗从风,等.MasonⅠ、Ⅱ型桡骨小头骨折非手术治疗的比较研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2005,21(3):151-153.
[18]Hotchkiss RN. Fractures of the radial head and related instability and contracture of the forearm. Instr Course Lect. 1998;47:173-177.
[19]Kelberine F, Bassères B, Curvale G, et al. Fractures of the radial head. Analysis of a series of 62 surgically treated cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1991;77(5):322-328.
[20]Khalfayan EE, Culp RW, Alexander AH. Mason type II radial head fractures: operative versus nonoperative treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 1992;6(3):283-289.
[21]蔡晓冰,纪方,曹磊,等.微型钢板治疗Mason Ⅲ型桡骨头骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(2):104-106.
[22]Heim U, Trüb HJ. Experiences with primary osteosynthesis in radial head fractures. Helv Chir Acta. 1978;45(1-2):63-69.
[23]王思成,刘祥飞,杨国庆,等.桡骨小头置换与切开复位内固定:治疗粉碎性桡骨小头骨折谁更有优势?[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(13):2031-2036.
[24]温纪林,杨峻刘,江华等.两种方法治疗桡骨小头骨折的疗效研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(7):591-594.
[25]Böstman OM, Pihlajamäki HK. Adverse tissue reactions to bioabsorbable fixation devices. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (371):216-227.
[26]26Prokop A, Jubel A, Helling HJ, et al. Soft tissue reactions of different biodegradable polylactide implants. Biomaterials. 2004;25(2):259-267.
[27]Ignatius AA, Augat P, Claes LE. Degradation behavior of composite pins made of tricalcium phosphate and poly(L,DL-lactide). J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2001;12(2): 185-194.
[28]Givissis PK, Symeonidis PD, Ditsios KT, et al. Late results of absorbable pin fixation in the treatment of radial head fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(5):1217-1224. |
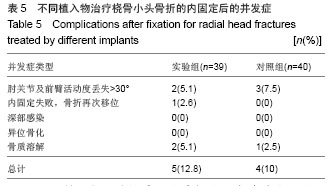
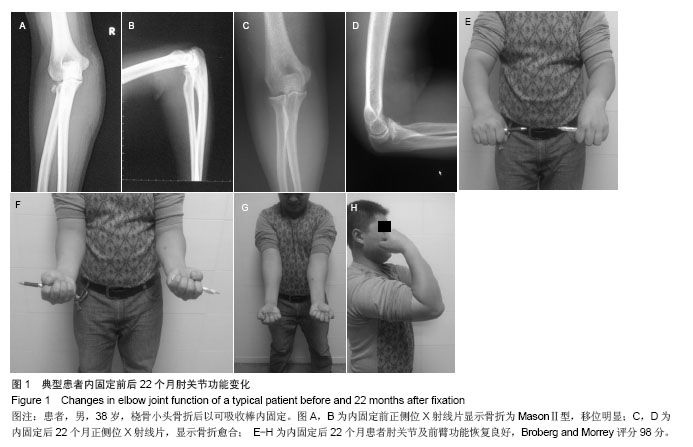
.jpg)