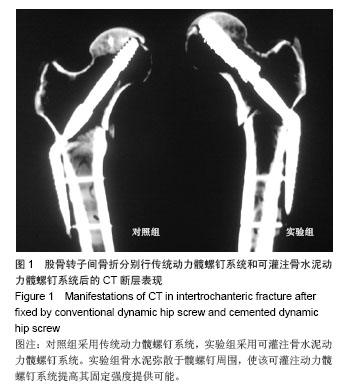
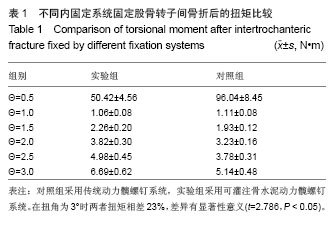
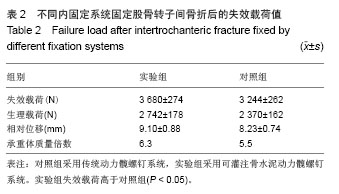
| [1]Liporace FA,Egol KA,Tejwani N,et al.What's new in hip fractures? Current concepts. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2005;34(2):66-74.
[2]Jahng JS,Yoo JH,Sohn JS.The Relationship between the Fracutures of the Hip and the Bone Mineral Density over Fifty years.J Korean Orthop Surg.1997;32:46-52.
[3]Mak JC,Cameron ID,March LM,et al.Evidence-based guidelines for the management of hip fractures in older persons: an update.Med J Aust.2010;192(1):37-41.
[4]Boyd HB,Griffin LL.Classification and treatment of trochanteric fractures. Arch Surg.1949;58(6):853-863.
[5]Ongkiehong BF,Leemans R.Proximal femoral nail failure in a subtrochanteric fracture:the 147 importance of fracture to distal locking screw distance.Inj Extra. 2007;38:445-450.
[6]Pajarinen J,Lindahl J,Michelsson O,et al.Pertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with a dynamic hip screw or a proximal femoral nail. A randomised study comparing post-operative rehabilitation. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2005;87:76-81.
[7]Saudan M,Lubbeke A,Sadowski C,et al.Pertrochanteric fractures: is there an advantage to an intramedullary nail?a randomized, prospective study of 206 patients comparing the dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nail.J Orthop Trauma.2002;16(6):386-393.
[8]Parker MJ,Handoll HH.Gamma and other cephalocondylic intramedullary nails versus extramedullary implants for extracapsular hip fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2008;(3):CD000093.
[9]Seibert FJ,Schippinger G,Szyszkowitz R.Invited commentary to:‘Gamma nail versus dynamic hip screw in 120 elderly patients-a randomised trial’. Eur Surg. 1997; 29: 294-295.
[10]Menezes DF,Gamulin A,Noesberger B.Is the proximal femoral nail a suitable implant for treatment of all trochanteric fractures? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2005;439: 221-227.
[11]Laohapoonrungsee A,Arpornchayanon O,Phornputkul C.Two-hole side-plate DHS in the treatment of intertrochanteric fracture: results and complications. Injury. 2005;36(11):1355-1360.
[12]Davis TRC,Sher JL,Horsman A,et al.Intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Mechanical failure after internal fixation.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1990;72(1):26-31.
[13]Evans EM .The treatment of trochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1949;31:190-203.
[14]Flores LA,Harrington IJ,Heller M.The stability of intertrochanteric fractures treated with a sliding screw-plate.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1990;72(1):37-40.
[15]Laros GS,Moore JF.Complications of fixation in intertrochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop.1974;101:110-119.
[16]Madsen JE,Naess L,Aune AK,et al.Dynamic hip screw with trochanteric stabilising plate in the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. A comparative study with Gamma nail and compression hip screw.J Orthop Trauma.1998; 12(4): 241-248.
[17]Evans EM.Trochanteric fractures; a review of 110 cases treated by nail-plate fixation.J Bone Joint Surg Br.1951; 33B(2):192-204.
[18]Liu M,Yang Z,Pei F,et al.A meta-analysis of the Gamma nail and dynamic hip screw in treating peritrochanteric fractures. Int Orthop.2010;34(3):323-328.
[19]Oger P,Katz V,Lecorre N,et al.Fracture of the greater trochanter treated by dynamic hip screw plate: measure of impaction according to fracture type. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot.1998;84(6):539-545.
[20]Rao JP,Banzon MT,Weiss AB,et al.Treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures with anatomic reduction and compression hip screw fixation. Clin Orthop.1983;175:65-71.
[21]Thomas AP.Dynamic hip screws that fail.Injury.1991;22(1): 45-46.
[22]Kyle RF,Gustilo RB,Premer RF.Analysis of six hundred and twenty-two intertrochanteric hip fractures. A retrospective and prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1976;61:216-221.
[23]Parker MJ.Cutting-out of the dynamic hip screw related to its position. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1992;74:625.
[24]Nordin S,Zulkifli O,Faisham WI.Mechanical failure of dynamic Hip Screw (DHS) fixation in intertrochanteric fracture of the femur.Med J Malaysia.2001;56:12-17.
[25]Simpson AH,Varty K,Dodd CAF.Sliding hip screw:modes of failure.Injury.1989; 20:227-231.
[26]郭继民,占晨光,董万超,等.髋部螺钉加骨水泥治疗老年人骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2006,8(4):325-327.
[27]Swiontkowski MF,Harrington RM,Keller TS,et al.Torsion and bending analysis of internal fixation techniques for femoral neck fractures: the role of implant design and bone density.J Orthop Res.1987;5:433-444.
[28]Joseph TN,Chen AL,Kummer FJ, et al.The effect of posterior sag on the fixation stability of intertrochanteric hip fractures.J Trauma.2002;52(3):544-547.
[29]Zhao C,Liu DY,Guo JJ et al.Comparison of proximal femoral nail and dynamic hip screw for treating intertrochanteric fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009;22(7):535-537.
[30]Bonamo JJ, Accettola AB. Treatment of intertrochanteric fractures with a sliding nail-plate. J Trauma. 1982; 22: 205-215.
[31]Kaufer H,Mattews LS,Sonstegard D.Stable fixation of intertrochanteric fracture. A biomechanical evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1974;56:899-907.
[32]Kyle RF.Fractures of the proximal part of the femur.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1994;76:924-950.
[33]Klinger HM,Baums MH,Eckert M,et al.Acomparative study of unstable per- and intertrochanteric femoral fractures treated with dynamic hip screw (DHS) and trochanteric butt-press plate versus proximal femoral nail (PFN). Zentralbl Chir. 2005; 130(4):301-306.
[34]Kafer M,Palm M,Zwank L,et al.What influence does the implant have on the perioperative morbidity following internal fixation of proximal femur fracture? Analysis of dynamic hip screw and proximal femoral nailing. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2005;143(1):64-71.
[35]Jones HW,Johnston P,Parker M.Are short femoral nails superior to the sliding hip screw? A meta-analysis of 24 studies involving 3279 fractures. Int Orthop.2006;30:69-78.
[36]Mainds CC,Newman RJ.Implant failures in patients with proximal fractures of the femur treated with a sliding screw device. Injury.1986;20:98-100.
[37]Pervez H,Parker MJ,Vowler S.Prediction of fixation failure after sliding hip screw fixation. Injury.2004;35:994-998.
[38]Gundle R,Gargan MF,Simpson AH.How to minimize failure of fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures.Injury. 1995;26: 611-614.
[39]Wu CC,Shih CH,Lee MY,et al.Biomechanical analysis of location of lag screw of a dynamic hip screw in treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fracture.J Trauma. 1996;41(4): 699-702.
[40]Baumgaertner MR, Solberg BD. Awareness of tip-apex distance reduces failure of fixation of trochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1997;79:969-971.
[41]Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, et al. The value of the tip-apex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1995;77(7):1058-1064.
[42]Hsueh KK, Fang CK, Chen CM, et al. Risk factors in cutout of sliding hip screw in intertrochanteric fractures: an evaluation of 937 patients.Int Orthop.2010;34:1273-1276.
[43]Lee PC, Hsieh PH, Chou YC, et al. Dynamic hip screws for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients- encouraging results with a cement augmentation technique.J Trauma.2010;68(4):954-964. |