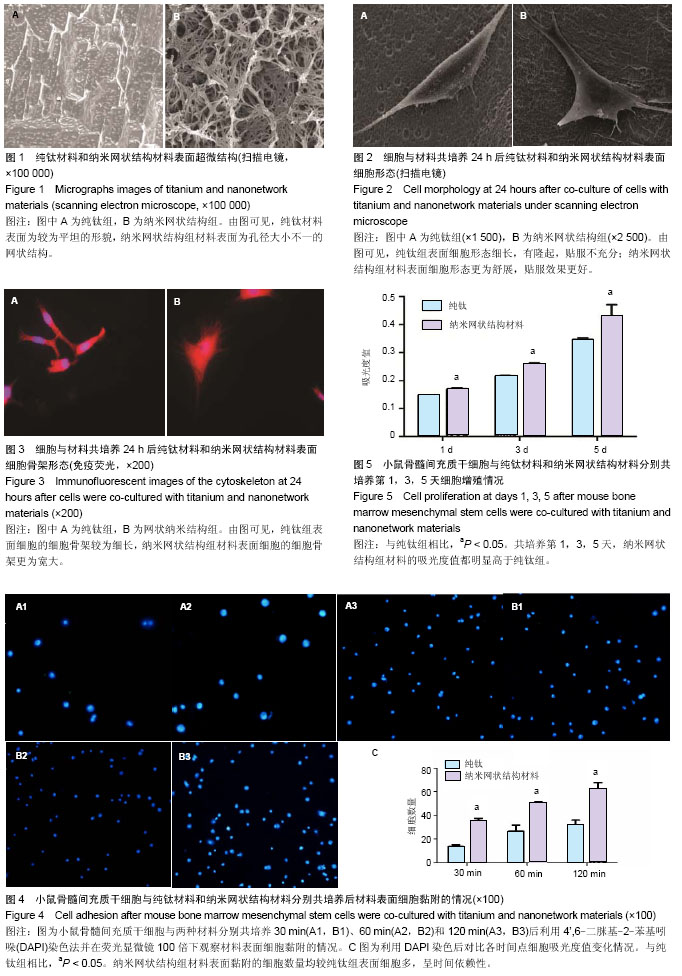
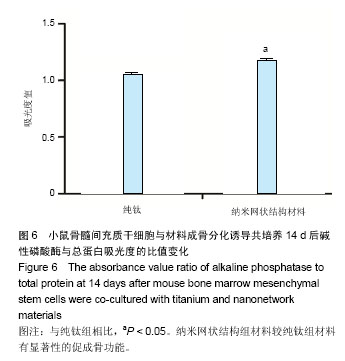
| [1] Chaudhari A, Braem A, Vleugels J, et al. Bone tissue response to porous and functionalized titanium and silica based coatings. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24186.
[2] Tran N, Webster TJ. Nanotechnology for bone materials. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2009; 1(3): 336-351.
[3] Lentino JR. Prosthetic joint infections: bane of orthopedists, challenge for infectious disease specialists. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36(9):1157-1161.
[4] de Oliveira PT, Nanci A. Nanotexturing of titanium-based surfaces upregulates expression of bone sialoprotein and osteopontin by cultured osteogenic cells. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(3):403-413.
[5] Mendonça G, Mendonca D, Aragao FJ, et al. Advancing dental implant surface technology–from micron-to nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3822-3835.
[6] Sato M, Aslani A, Sambito M A, et al. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite/titania coatings on titanium improves osteoblast adhesion. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;84(1): 265-272.
[7] Fujihara K, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S. Guided bone regeneration membrane made of polycaprolactone/calcium carbonate composite nano-fibers. Biomaterials. 2005;26(19): 4139-4147.
[8] Kay S, Thapa A, Haberstroh KM, et al. Nanostructured polymer/nanophase ceramic composites enhance osteoblast and chondrocyte adhesion. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(5):753-761.
[9] Boyan BD, Bonewald LF, Paschalis EP, et al. Osteoblast-mediated mineral deposition in culture is dependent on surface microtopography. Calcif Tissue Int. 2002;71(6):519-529.
[10] Schneider GB, Zaharias R, Seabold D, et al. Differentiation of preosteoblasts is affected by implant surface microtopographies. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;69(3): 462-468.
[11] Zinger O, Zhao G, Schwartz Z, et al. Differential regulation of osteoblasts by substrate microstructural features. Biomaterials. 2005;26(14):1837-1847.
[12] Damsky CH. Extracellular matrix-integrin interactions in osteoblast function and tissue remodeling. Bone. 1999; 25(1):95-96.
[13] Ercan B, Webster TJ. The effect of biphasic electrical stimulation on osteoblast function at anodized nanotubular titanium surfaces. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3684-3693.
[14] Variola F, Vetrone F, Richert L, et al. Improving biocompatibility of implantable metals by nanoscale modification of surfaces: an overview of strategies, fabrication methods, and challenges. Small. 2009;5(9):996-1006.
[15] 于卫强,张益琳,张富强,等.阳极氧化TiO2纳米管碱热处理对成骨细胞行为的影响[J].口腔医学研究,2009,25(6):696-698.
[16] Cavalcanti-Adam EA, Volberg T, Micoulet A, et al. Cell spreading and focal adhesion dynamics are regulated by spacing of integrin ligands. Biophys J. 2007;92(8):2964-2974.
[17] Curtis ASG. Small is beautiful but smaller is the aim: review of a life of research. Eur Cell Mater. 2004;8:27-36.
[18] Dalby MJ, Kayser MV, Bonfield W, et al. Initial attachment of osteoblasts to an optimised HAPEXTM topography. Biomaterials. 2002;23(3):681-690.
[19] Xu L, Pan F, Yu G, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the surface bioactivity of a calcium phosphate coated magnesium alloy. Biomaterials. 2009;30(8):1512-1523.
[20] Heidi A, Ronald M, Leo I, et al. Calcification as an indicator of osteoinductive capacity of biomaterials in osteoblastic cell cultures. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4964-4974.
[21] Webster TJ, Erqun C, Doremus RH, et al, Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanophase ceramics. Biomaterials. 2000;21: 1803-1810.
[22] Allen MJ, Biochemical markers of bone metabolism in animals: uses and limitations. Vet Clin Pathol. 2003;32:101-113.
[23] Salvatore F, Sacchetti L, Castaldo G. Multivariate discriminant analysis of biochemical parameters for the differentiation of clinically confounding liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 1997; 257(1):41-58.
[24] D’Amico E, Paroli M, Fratelli V, et al. Primary biliary cirrhosis induced by interferon-α therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Dig Dis Sci. 1995;40(10):2113-2116.
[25] Mcnamara LE, Mcmurray RJ, Biggs MJ, et al. Nanotopographical control of stem cell differentiation. J Tissue Eng. 2010;2010:120623.
[26] Dalby MJ, Biggs MJP, Gadegaard N, et al. Nanotopographical stimulation of mechanotransduction and changes in interphase centromere positioning. J Cell Biochem. 2007; 100(2):326-338.
[27] Ingber DE, Tensegrity I. Cell structure and hierarchical systems biology. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(7):1157-1173.
[28] Anselme K, Davidson P, Popa AM, et al. The interaction of cells and bacteria with surfaces structured at the nanometre scale. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:3824-3826.
[29] Dalby MJ, Andar A, Nag A, et al. Genomic expression of mesenchymal stem cells to altered nanoscale topographies. J R Soc Interface. 2008;5(26):1055-1065.
[30] Hamilton DW, Brunette DM. The effect of substratum topography on osteoblast adhesion mediated signal transduction and phosphorylation. Biomaterials. 2007;28(10): 1806-1819. |