| [1] Siebert E, Prtiss H, Klingebiel R, et al .Lumbar spinal stenosis syndrome diagnostics and treatment.Nat Rev Neurol. 2009; 5(7): 392-403.
[2] Haig AJ, Tong HC, Yamakawa KS, et al. spinal stenosis,back pain,or no symptoms at all A masked study comparing radiologic and electrodiagnostic diagnoses to the clinical impression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2006;8(7):897-903.
[3] 蔡维山,鞠洪斌,郭东明.腰椎管狭窄症诊断新进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(3): 177-186.
[4] Amundsen T, Weber H,Lilleas F, et al.Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical and radiologic features. Spine.1995;20(10):1178-1186.
[5] 赵太茂,邱贵兴,仉建国,等.291例腰椎管狭窄症患者的临床特点分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(1l): 812-814.
[6] Azimi P, Mohammadi HR, Montazeri A.An outcome measure of functionality in patients with lumber spinal stenosis: a validation study of the Iranian version of Neurogenic Claudication Outcome Score. BMC Neurol.2012;9(12): 101.
[7] Airaksinen O, Hemo A, Turunen V, et al. SurgicaI outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine.1997;22(19):2278-2282.
[8] 赵慧毅,梅芳瑞,叶欣,等.腰椎管狭窄症的手术减压与内固定选择(259例临床分析)[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2003,13(1):18-21.
[9] Shabat S, Arinzon Z,Folman Y. Long-term outcome of decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in octogenarians.Eur Spine.2008;17(2):193-198.
[10] Weinstein JN.Surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for lumbar spinal stenosis.NEnglJMed.2008;358:794-810.
[11] Malmivaara A.Surgical or nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis A randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2007; 32:1-8.
[12] Siebert E,Pruss H,Klingebiel R,et al.Lumbar spinal stenosin: syndrome,diagnostics and treatment.Nat Rev Neurol. 2009; 5(7):392-403.
[13] Cakir B, Schmidt R, Reichel H, et al.Lumbar disk hemiation: what are reliable criterions indicative for suigery. Orthpedics. 2009;32 :589.
[14] Jansson AK, Nemeth G, Granath F, et al.Spinal stenosis reoperation rate in Sweden is 11% at 10 years a-national analysis of 9664 operations. Eur Spinal J.2005;14 (1): 659-633.
[15] Kaptan H, Kasin O, Cakiroglu K, et al. Lumber spinal stenosis in elderly patients.Amm N Y Acad Sci.2007;4(2):173.
[16] 刘付明.退行性多节段腰椎管狭窄症定位诊断[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(9): 651-653.
[17] Szpalski M,Gunzburg R.Lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly:an overview. Eur Spine J.2003;12 Suppl 2:S170-175.
[18] Tetsuhiro I, Akira K, Junichi N, et al. Minimum 10years outcome of decompressive laminectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis.Spine.2000;25(14):754-756.
[19] Guigui P,Ulivieri JM,Lassale B,et al.Reoperations after surgical treatment of lumbar stenosis.Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot.1995;81:663-671.
[20] Gelalis ID,Stafilas KS,Korompilias AV,et al.Decompressive surgery for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis:long-term results.Int Orthop(SICOT).2006,30(1):59-63.
[21] 赵延胜,王文军.腰椎管狭窄症手术治疗进展[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2009,13(1):70-73.
[22] Yucesoy K,Crawford NR.Increase in spinal canal area after inverse laminoplasty:an anatomical study.Spine.2000; 25(21): 2771-2776.
[23] Johnsson KE,Willner S,Johnsson K.Postopertive instability after decompression for lumbar spina stenosis. Spine. 1986; 11:107.
[24] 卢宁,汤荣光,陈国强,等.改良全椎板切除术治疗腰椎管狭窄的疗效评价[J].中国伤残医学,2006,14(3):1-3.
[25] Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MH, et al. Unilateral laminotomyfor bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. PartII:Clinical experiences.ActaNeuroc hir(Wien). 1997;139(5):397-403.
[26] 吴叶,李家顺,贾连顺.单椎板切除双侧减压和保守治疗腰椎管狭窄疗效的比较[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2003, 24(4): 210-213.
[27] Gelalis ID,Stafilas KS,Korompilias AV,et al.Decompressire surgery for degenerative Lumbar spinal stenosisLong-term results.Int Orthop.2006;30(3):59-63.
[28] Fu YS,Zeng BF,Xu JG.Long-term outcomes of two different decompressive techniques for lumbar spinal stenosis.Spine. 2008;33(5):524-518.
[29] Nair GM,Nery PB,Diwakaramenon S,et al.A systematic review of randomized trials comparing radiofrequency ablation with antiarrhythmic medications in patients with atrial fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.2009;20(2):138-144.
[30] Chou R,Baisden J,Carragee EJ,et al.Surgery for low back paln:a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline.Spine.2009;34(10):1094-1109.
[31] 张贵林,荣国威,丁古云,等.脊柱胸腰段骨折术后椎弓根螺钉断裂及弯曲松动的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(8):470-472.
[32] 贾连顺,扬立利.退变性腰椎管狭窄症的现代外科学概念[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,2(8):509 -512.
[33] Breen A, Muggleton J, Mellor F, et al. Lumbar intervertebralmotion in asymptomatic and postfusion subjects. J Bone JointSurg Br. 2005,87-B(SUPP_I): 35.
[34] Airaksinen O,Herno A.Turunen V,et al.Surgical outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stcnosis. Spine. 1997;22(19):2278-2282.
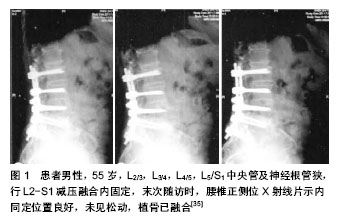
[35] 朱迪,李危石,陈仲强,等. 腰椎管狭窄症减压定融合术后远期疗效及其影响因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(10): 865-871.
[36] 杨晋才,海摇涌,藏摇磊,等.加压植骨联合单枚cage的椎体间融合与后外侧融合治疗双节段腰椎椎管狭窄症临床效果的回顾性研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(4):216-219.
[37] Yu CH,Lee JE,Yang JJ,et al.Adjacent segment Degeneration after Single-Level PLIF:Comparison between Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis,Degenerative Spondylolisthesisand spinal stenosis.Asian spine J.2011;5(2):82-90.
[38] Mulholland RC, Sengupta DK. Rationale, principles and experimental evaluation of the conceptofsoftstabilization. Eur Spine J.2002;11 Suppl2: S198-S205.
[39] 王洪立,姜建元.腰椎棘突间分离装置研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008;18(8):631-634.
[40] 祝明浩,夏茂凤.Dynesys系统内固定联合椎板开窗减压术治疗腰椎退变性疾病[J].中医正骨,2011,23(12):53-55.
[41] Fayyazi AH, Ordway NR, Park SA, et al. Radiostereometric analysis of postoperative motion after application of dynesys dynamic posterior stabilization system for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. J spinal Disord Tech.2010; 23(4):236-241.
[42] Alimi M, Njoku I Jr, Cong GT, et al.Minimally Invasive Foraminotomy Through Tubular Retractors Via a Contralateral Approach in Patients With Unilateral Radiculopathy.Neurosurgery. 2014 Mar 27. [Epub ahead of print].
[43] Aleem IS, Rampersaud YR.Elderly Patients Have Similar Outcomes Compared to Younger Patients After Minimally Invasive Surgery for Spinal Stenosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Dec 4. [Epub ahead of print].
[44] Nandyala SV, Fineberg SJ, Pelton M, et al.Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: one surgeon's learning curve.Spine J. 2013 Oct 3. pii: S1529-9430(13) 01493-9.
[45] Anand N, Baron EM, Khandehroo B.Does Minimally Invasive Transsacral Fixation Provide Anterior Column Support in Adult Scoliosis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Nov 6. [Epub ahead of print].
[46] Zou S, Wang J, Pan W, et al.Comparison of traumatic related index in serum between minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for tissue injury.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013; 27(8):960-964.
[47] Perez-Cruet MJ, Hussain NS, White GZ,et al.Quality-of-life outcomes with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion based on long-term analysis of 304 consecutive patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(3): E191-198.
[48] Hironaka Y, Morimoto T, Motoyama Y,et al.Surgical management of minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion with stand-alone interbody cage for L4-5 degenerative disorders: clinical and radiographic findings.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).2013;53(12):861-869.
[49] Ang CL, Phak-Boon Tow B, Fook S,et al.Minimally invasive compared with open lumbar laminotomy: no functional benefits at 6 or 24 months after surgery.Spine J. 2013 Oct 4. pii: S1529-9430(13)01382-X.
[50] Chen KS, Than KD, Lamarca F, et al.Minimally invasive unilateral approach for bilateral decompression of spinal stenosis and modified transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis.Neurosurg Focus.2013; 35(2 Suppl):Video 4.
[51] Ding Y, He S, Zhang H.Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis stenosis.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013;27(4):404-408.
[52] Toyoda H,Nakamura H,Konishi S,et al.Clinical outcomeof microsurgical bilateral decompression via unilateral approach for lumbar canal stenosis:minimum five-year follow-up. Spine. 2011;36(5):410-415. |