| [1] 胥少汀,葛宝丰,徐印钦.实用骨科学[M].3 版.北京:人民军医出版社,2005:194-218.
[2] 牛宏伟.解剖型钢板治疗的胫骨远端骨折的效果分析[J].中外健康文摘,2013,10(14):170.
[3] 陈义明,汪剩勇,邹鹏飞.解剖钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].当代医学,2013,20(12):104-105.
[4] 孙志祥.解剖型钢板治疗胫骨远端骨折的效果分析[J].中外健康文摘,2013,10(11):175-176.
[5] 明立功,明立德,明新文,等.解剖型钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2010,25(8):740-741.
[6] 薛双桃,黄玉生,戎祖华,等.胫骨远端匙形解剖型钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].皖南医学院学报,2010,29(5):354-356.
[7] Tropet Y,Garbuio P,Coral HP.One-stage emergency treatment of open tibial shaft fractures with bone loss. Specifics and indications.Ann Chir Plast Esthet.2000; 45(3):323-335.
[8] Tielinen L,Lindahl JE,Tukiainen EJ. Acute unreamed intramedullary nailing and soft tissue reconstruction with muscle flaps for the treatment of severe open tibial shaft fractures.Injury.2007;38(8):906-912.
[9] Zeman P,Zeman J,Matejka J,et al.Long-term results of calcaneal fracture treatment by open reduction and internal fixation using a calcaneal locking compression plate from an extended lateral approach.Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2008;75(6):457-464.
[10] Dedmond BT,Kortesis B,Punger K,et al.Subatmospheric pressure dressings in the temporary treatment of soft tissue injuries associated with type III open tibial shaft fractures in children.J Pediatr Orthop.2006;26(6):728-732.
[11] Ueno M,Yokoyama K,Nakamura K,et al.Early unreamed intramedullary nailing without a safety interval and simultaneous flap coverage following external fixation in type IIB open tibial fractures: a report of four successful cases. Injury. 2006;37(3):289-294.
[12] Zlowodzki M1,Williamson S,Cole PA,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system, angled blade plate, and retrograde intramedullary nail for the internal fixation of distal femur fractures.J Orthop Trauma.2004;18 (8): 494-502.
[13] Zlowodzki M,Williamson S,Zardiackas LD,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system and the 95-degree angled blade plate for the internal fixation of distal femur Fractures in human cadaveric bones with high bone mineral density.J Trauma.2006;60(4):836-840.
[14] Khalafi A,Curtiss S,Hazelwood S,et al.The effect of plate rotation on the stiffness of femoral LISS: a mechanical study.J Orthop Trauma.2006;20(8):542-546.
[15] Frigg R,Appenzeller A,Christensen R,et al.The development of the distal femur Less Invasive Stabilization System (LISS). Injury.2001;32 Suppl 3:SC24-31.
[16] 顾龙殿,姜新华,王永安,等.锁定钢板微创内固定治疗胫骨Pilon骨折[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2008,4(4):330.
[17] Krettek C,Schandelmaier P,Miclau T,et al.Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures.Injury. 1997;28 Suppl 1: A20-30.
[18] 李国胜,胡永成.经皮微创锁定加压钢板置入内固定治疗新鲜胫骨远端骨折32例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13): 2454-2457.
[19] Collinge C,Protzman R.Outcomes of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for metaphyseal distal tibia fractures.J Orthop Trauma.2010;24(1):24-29.
[20] 许俊胜,吕建军,江淮,等.经皮微创锁定加压钢板治疗胫骨骨折[J].安徽卫生职业技术学院学报,2013,12(5):33-34.
[21] 刘欣伟,许硕贵,张春才,等.微侵入经皮钢板植入技术结合锁定加压钢板与普通钢板治疗胫骨远端粉碎性骨折的临床评价[J].临床骨科杂志,2009,12(5):524-526.
[22] 肖志林,周明昌,冯经旺,等.微创经皮钢板接骨术结合锁定加压钢板与切开复位解剖型钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(1):91-92.
[23] 纪方,王秋根,沈洪兴,等.经皮微创钢板固定技术(MIPO)在胫骨近、远端粉碎性骨折中的应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2004, 6(10):1105-1108.
[24] Johner R,Wruhs O.Classification of tibial shaft fractures andcorrelation with results after rigid internal fixation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;(178):7-25.
[25] 郭世绂.临床骨科解剖学[M].天津:天津科学技术出版社,1986: 872.
[26] 袁天祥,马宝通,王宝成,等.股骨远端、胫骨近端骨折LISS手术相关因素分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(4):246.
[27] Chung KC,Watt AJ,Kot sis SV.Treatment of Unstable Distal Radial Fractures with the Volar Locking Plating System.J BoneJoint Surg(Am).2006;88:2687-2694. |
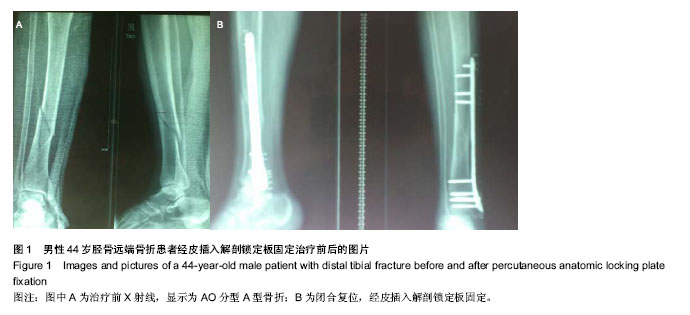
.jpg)