| [1] Sabokbar A, Kudo O, Athanasou NA.Two distinct cellular mechanisms of osteoclast formation and bone resorption in periprosthetic osteolysis.J Orthop Res. 2003;21(1):73-80.
[2] 杜斌,Noble PC.骨水泥外套开裂对股骨假体柄微动和松动的影响:附18例骨水泥型假体尸体标本观察[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(48):9583-9586.
[3] 杜斌,Noble PC.骨水泥型人工髋关节置换后假体柄的无菌性松动:36例翻修标本分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(26):5176-5180.
[4] Jacobs JJ, Roebuck KA, Archibeck M,et al.Osteolysis: basic science.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):71-77.
[5] Kadoya Y, Kobayashi A, Ohashi H.Wear and osteolysis in total joint replacements.Acta Orthop Scand Suppl. 1998; 278:1-16.
[6] Rader CP, Sterner T, Jakob F,et al.Cytokine response of human macrophage-like cells after contact with polyethylene and pure titanium particles.J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(7): 840-848.
[7] Katayama K, Maezawa H, Uesato N,et al.Physicochemical and biomechanical examination of surfaces of retrieved polyethylene heads from total hip prostheses with rotating polyethylene head system.J Orthop Sci. 2001;6(6):503- 509.
[8] McKellop H, Shen FW, Lu B,et al.Effect of sterilization method and other modifications on the wear resistance of acetabular cups made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. A hip-simulator study.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82-A(12): 1708-1725.
[9] Marx R, Qunaibi M, Wirtz DC,et al.Surface pretreatment for prolonged survival of cemented tibial prosthesis components: full- vs. surface-cementation technique.Biomed Eng Online. 2005;4:61.
[10] 杨斌.淫羊藿苷药理研究概况[J].中国药房,2009,20(24):1915- 1917.
[11] 贾晓斌,兰雪莲,陈彦,等.淫羊藿黄酮类成分抗骨质疏松作用及其机制研究进展[J].中国药房,2010,21(3):269-270.
[12] 李慧英,孟东方.淫羊藿提取液对激素性股骨头坏死的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(50):9395-9398.
[13] 刘仕杰,莫新民,李劲平,等.淫羊霍苷对去卵巢骨质疏松症雌鼠的疗效及机理初步研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012,18(3): 271-272,275.
[14] 钱力,翁文杰,李成荫,等.淫羊藿黄酮类化合物对骨及软骨细胞作用研究进展[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012,18(3):347-349.
[15] 杨乾栩,刘艳秋,王莉,等.基于模型群体分析的淫羊藿抗骨质疏松活性成分筛选研究[J].药学学报,2012,47(9):1205-1209.
[16] 康学,刘仁慧,王秀娟. 淫羊藿、女贞子抗骨质疏松症的应用与机制研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(21):331-334.
[17] Rader CP, Sterner T, Jakob F,et al.Cytokine response of human macrophage-like cells after contact with polyethylene and pure titanium particles.J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(7): 840-848.
[18] Ingham E, Fisher J.Biological reactions to wear debris in total joint replacement.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2000;214(1):21-37.
[19] 张大威,程岩,张金超,等.淫羊藿苷对破骨细胞的分化及骨吸收功能的影响[J] .中国药理学通报,2007,23(4): 463-467.
[20] 郑洪军,吕振华,胡有谷,等.淫羊藿对体外培养破骨细胞的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2000,17(5)460-461.
[21] 鲍加荣,杨继文,李树峰,等.淫羊藿苷对去卵巢大鼠骨质疏松症的影响[J] .卫生研究,2005,34(2): 191-193.
[22] 吕明波,刘兴炎,葛宝丰.淫羊藿苷对小鼠骨髓源性破骨细胞诱导生成及骨吸收功能的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(5): 315-319.
[23] Zhang DW, Cheng Y, Wang NL,et al.Effects of total flavonoids and flavonol glycosides from Epimedium koreanum Nakai on the proliferation and differentiation of primary osteoblasts. Phytomedicine. 2008;15(1-2):55-61.
[24] 叶纯,苏进,王凡.淫羊藿影响去势大鼠椎骨微环境中TNF-α、TGF-β1表达的研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2006,24(6): 687-690.
[25] 蒋允昌,郭开今,龚维成,等. 淫羊藿总黄酮对聚乙烯微粒刺激单核细胞分泌IL-6的影响[J].徐州医学院学报,2007,27(7): 429-431.
[26] 叶纯,苏进,王凡.淫羊藿水提液对去势大鼠松质骨的影响[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2008,26(1):87-90.
[27] 张秀珍,韩峻峰,杨黎娟,等.淫羊藿总黄酮对体外培养破骨细胞功能的影响[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2004,23(9):602-606.
[28] 殷晓雪,陈仲强,党耕町,等.淫羊藿苷对人成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J] .中国中药杂志, 2005, 30(4): 289-291.
[29] 于波,杨久山,刘岩,等.淫羊藿苷对人成骨细胞的作用[J] .中医正骨,2006,18(6):17-18.
[30] 刘素彩,孔德娟,赵京山,等.淫羊藿甙对大鼠成骨细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2001,7(8):28-30
[31] Goater JJ, O'Keefe RJ, Rosier RN,et al.Efficacy of ex vivo OPG gene therapy in preventing wear debris induced osteolysis.J Orthop Res. 2002;20(2):169-173.
[32] Wooley PH,Fitzgerald RH,Song Z.Proteins bound to polyethylene components in patients who have aseptic loosening after total joint arthroplasty. A preliminary report.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81(5):616-623.
[33] Blaine TA, Pollice PF, Rosier RN,et al.Modulation of the production of cytokines in titanium-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes by pharmacological agents. The role of cAMP-mediated signaling mechanisms.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997;79(10):1519-1528.
[34] Kim YH, Kim JS, Cho SH.Primary total hip arthroplasty with a cementless porous-coated anatomic total hip prosthesis: 10- to 12-year results of prospective and consecutive series.J Arthroplasty. 1999;14(5):538-548.
[35] Carmody EE, Schwarz EM, Puzas JE,et al.Viral interleukin-10 gene inhibition of inflammation, osteoclastogenesis, and bone resorption in response to titanium particles.Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(5):1298-1308.
[36] von Knoch F, Wedemeyer C, Heckelei A,et al.Promotion of bone formation by simvastatin in polyethylene particle-induced osteolysis.Biomaterials. 2005;26(29): 5783-5789.
[37] Ren W, Li XH, Chen BD,et al.Erythromycin inhibits wear debris-induced osteoclastogenesis by modulation of murine macrophage NF-kappaB activity.J Orthop Res. 2004;22(1): 21-29.
[38] Ren W, Wu B, Peng X,et al.Erythromycin inhibits wear debris-induced inflammatory osteolysis in a murine model.J Orthop Res. 2006;24(2):280-290. |
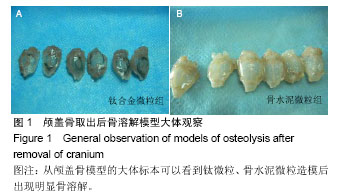
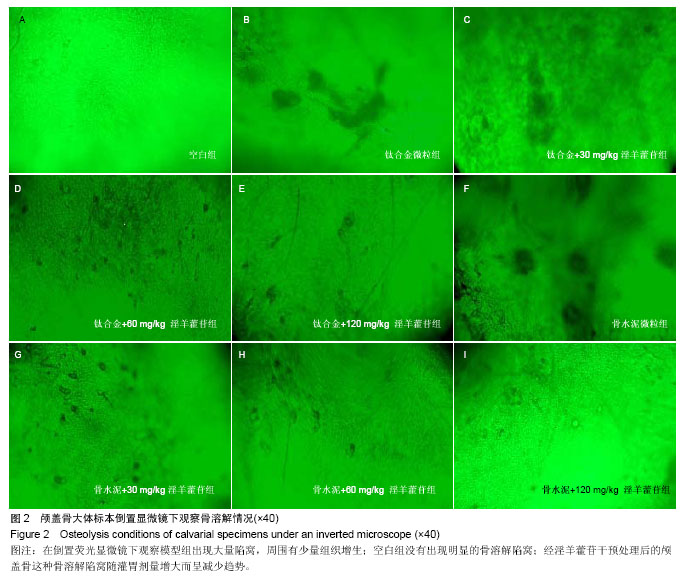
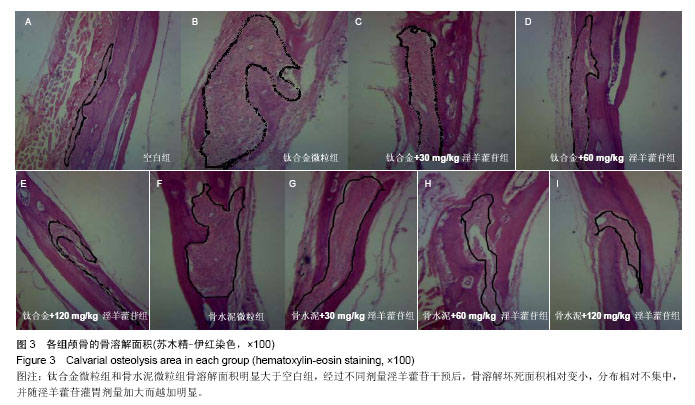
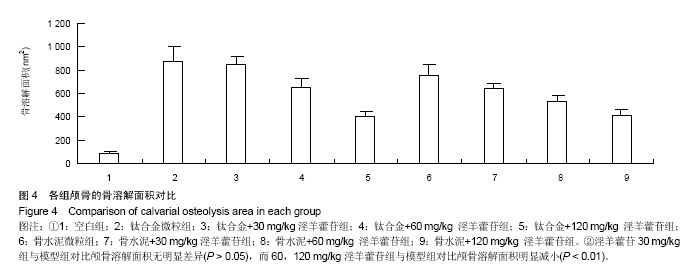
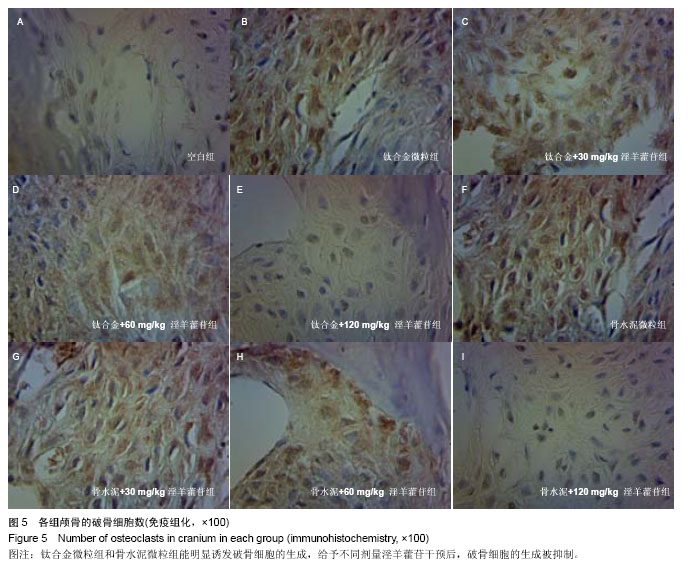
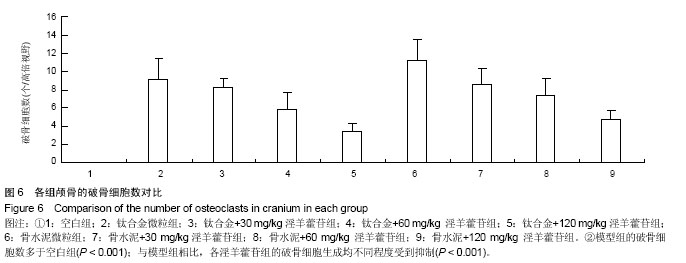
.jpg)
.jpg)