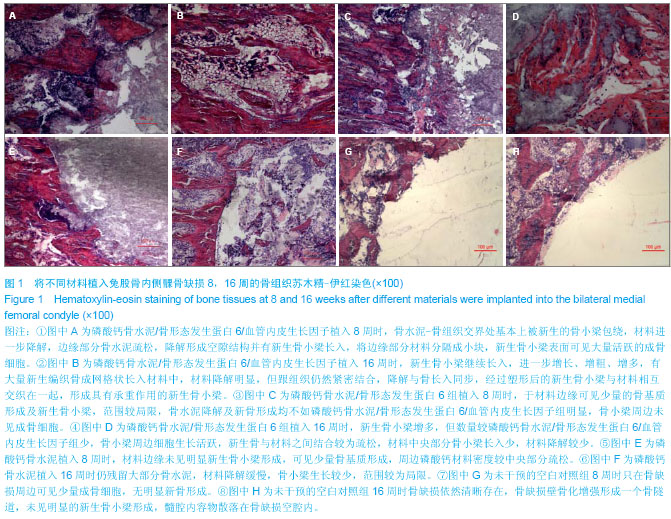
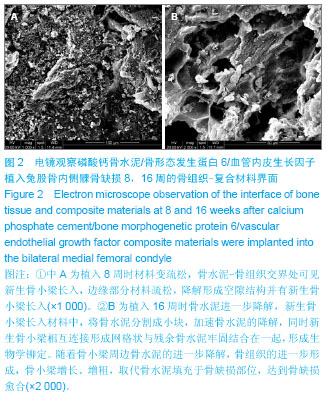
| [1] Scharpfenecker M,van Dinther M,Liu Z,et al.BMP-9 signals via ALK1 and inhibits bFGF-induced endothelial cell prolifer-ation and VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis.J Cell Sci. 2007;120:964-972.
[2] 孙明林,胡蕴玉.磷酸钙骨水泥作为骨形成蛋白载体修复节段性骨缺损及相关研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(2):114-120.
[3] Ducheyne P, Qiu Q.Bioactive ceramics: the effect of surface reactivity on bone formation and bone cell function. Biomaterials.1999;20:2287-2303.
[4] Xu HH,Burguera EF,Carey LE.Strong, macroporous, and in situ-setting calcium phosphate cement-layered structures. Biomaterials.2007;28(26):3786-3796.
[5] Kruyt MC, Persson C, Johansson G, et al.Towards injectable cell-based tissue-engineered bone: the effect of different calcium phosphate microparticles and pre-culturing. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(2):309-317.
[6] Hollinger JO, Kleinechmidt JC. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg.1990;1(1):60-68.
[7] Schmitz JP,Hollinger JO.The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;205(4):299-307.
[8] 李朵,魏启幼,范松青,等.不脱钙骨组织包埋技术的改进[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2005,21(6):731-733.
[9] Flautre B, Descamps M, Delecourt C, et al.Porous HA ceramic forbone replacement:role of the pores and interconnections-experimental study in the rabbit. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2001;12:679-682.
[10] Manjubala I,Sivakumar M, Sureshkumar RV, et al. Bioactive and osseointegration study of calcium phosphate ceramic of different chemical composition.J Biomed Mater Res, 2002; 63(2):200-208.
[11] Kang Q,Sun MH,Cheng H,et al.Characterization of the distinct orthotopic bone-forming activity of 14 BMPs using recombinant adenovirus-mediated gene delivery. Gene Ther. 2004;11:1312-1320.
[12] Govender S,Csimma C,Genant HK,et al.Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for treatment of open tibial fractures: A prospective, controlled, randomized study of four hundred and fifty patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2002; 84-A: 2123-2134.
[13] Dohin B,Dahan-Oliel N,Fassier F, et al.Enhancement of difficult nonunion in children with osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1): early experience.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2009;467: 3230-3238.
[14] Scharpfenecker M,van Dinther M,Liu Z,et al.BMP-9 signals via ALK1 and inhibits bFGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation and VEGF-stimulated angiogenesis.J Cell Sci. 2007;120:964-972.
[15] Zelzer E, Mamluk R,Ferrara N,et al.VEGFA is necessary for chondrocyte survival during bone development. Development. 2004; 131(9): 2161-2171.
[16] Dai J,Rabie AB.VEGF: an essential mediator of both angiogenesis and endochondralossification. J Dent Res. 2007; 86:937-950.
[17] Hou H,Zhang X,Tang T,et al.Enhancement of boneformation by genetically-engineered bone marrow stromal cells expressing BMP-2, VEGF and angiopoietin-1.Biotechnol Lett. 2009;31(8):1183-1189.
[18] Kempen DH,Lu L,Heijink A,et al.Effect of local sequential VEGF and BMP-2 delivery on ectopic and orthotopic bone regeneration. Biomaterials.2009;30:2816-2825.
[19] Li G,Corsi-Payne K,Zheng B,et al.The dose of growth factors influences the synergistic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on bone morphogenetic protein 4-induced ectopic bone formation. Tissue Eng Part A.2009;15:2123-2133.
[20] Li JZ,Li H,Sasaki T,et al.Osteogenic potential of five different recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein adenoviral vectors in the rat. Gene Ther. 2003;10:1735-1743. |