| [1] Iqbal HJ, Pidikiti P. Treatment of distal tibia metaphyseal fractures; plating versus intramedullary nailing: a systematic review of recent evidence. Foot Ankle Surg. 2013;19(3):143-147.
[2] 王学谦,娄思权,侯筱魁,等.创伤骨科学[M].天津:天津翻译出版社,2007,2087-2088.
[3] Babis GC, Vayanos ED, Papaioannou N, et al. Results of surgical treatment of tibial plafond fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997;(341):99-105.
[4] 李国胜,胡永成.经皮微创锁定加压钢板置入内固定治疗新鲜胫骨远端骨折32例[J].中国组织工程与临床康复,2011,15(31):2454-2457.
[5] 黄鹏,唐佩福,姚琦,等.LCP钢板和带锁髓内钉治疗新鲜胫骨干骨折的对比研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2007,21(11):1167-1170.
[6] 钟建荣,陈建强,丘国际,等.外侧解剖型锁定钢板治疗胫骨远端骨折的疗效观察[J].吉林医学,2011,32(6):1187.
[7] Nowotarski PJ, Turen CH, Brumback RJ, et al. Conversion of external fixation to intramedullary nailing for fractures of the shaft of the femur in multiply injured patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(6):781-788.
[8] 王思辉,范鑫斌,王治,等.前侧入路微创经皮钢板技术治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(2):162-165.
[9] 吴健强,王炳庚,徐兴明,等.胫骨远端内侧型锁定加压钢板微创治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2011,14(2):219-220.
[10] Manninen MJ, Lindahl J, Kankare J, et al. Lateral approach for fixation of the fractures of the distal tibia. Outcome of 20 patients. Technical note. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2007;127(5):349-353.
[11] Grose A, Gardner MJ, Hettrich C, et al. Open reduction and internal fixation of tibial pilon fractures using a lateral approach. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(8):530-537.
[12] 中国知网.中国学术期刊总库[DB/OL].2013-08-16.https://www.cnki.net
[13] 刘畅.正常踝关节不同位置时应力分布的实验研究[D].河北:河北医科大学,2008:1-48.
[14] 魏海强.髓内钉与锁定钢板固定胫骨远端骨折的生物力学研究[D].河北:河北医科大学,2008:1-59.
[15] Ozturk H, Unsaldi T, Oztemur Z, et al. Extreme complications of Fixion nail in treatment of long bone fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2008;128(3):301-306.
[16] Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, et al. Intramedullary nailing of distal metaphyseal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1213-1221.
[17] Marsh JL, Weigel DP, Dirschl DR. Tibial plafond fractures. How do these ankles function over time? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(2):287-295.
[18] Zelle BA, Bhandari M, Espiritu M, et al. Treatment of distal tibia fractures without articular involvement: a systematic review of 1125 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(1):76-79. |
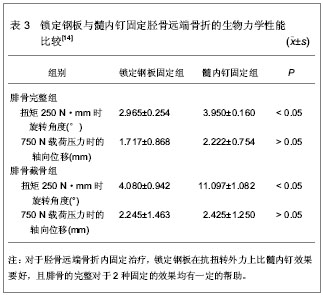
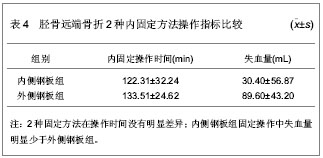
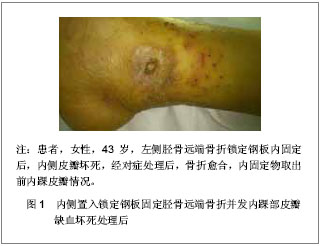
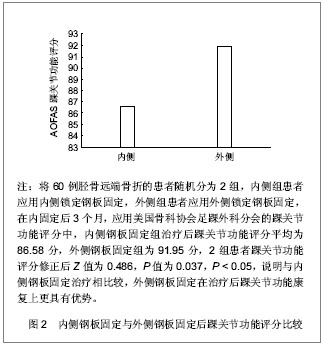
.jpg)