| [1] 刘彬,张春媛,张媛,等.肾移植患者围手术期的心理分析及护理对策[J].中国疗养医学,2012,21(5):477-478.[2] 李玉华.肾移植患者的心理干预护理效果分析[J].护理研究,2010, 17(19):159-160.[3] 雷俊,朱姝娟,晏晓颖,等.肾移植患者的应对方式和社会支持与抑郁情绪关系的结构方程模型[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(14): 1511-1513.[4] Guo HB, Fu FQ. Comparison of medical coping styles in renal transplant patients and hemodialysis patients. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(40): 7982-7985.[5] Zhang SJ, Huang LH, Wen YL, et al. Impact of personality and coping mechanisms on health related quality of life in liver transplantation recipients. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005;4(3):356-359.[6] Terán-Escandón D, Ruiz-Ornelas J, Estrada-Castillo JG. Anxiety and depression among renal transplantation candidates: Impact of donor availability. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. 2001;29(2):91-94.[7] 王静新,叶桂荣.肾移植受者手术前、后心理状态调查分析及对策[J].实用护理杂志,2001,8(3):39-41.[8] 周英,黄婉琳,廖苑,等.肾移植受者生存质量的研究[J].护理研究, 2005,19(12):2567-2568.[9] 李玲,刘慧玲,谢翠媚,等.高龄肾移植围手术期患者心理障碍特点[J].广东医学,2005,26(1):134-135.[10] 徐金哲,张继云.肾移植患者围手术期的心理护理[J].北京军区医药,2000,12(3):216-217.[11] 黄秀英.正性暗示疗法在肾移植术后早期的应用[J].护理学杂志, 2002,17(4):291-293.[12] 轧春妹,尤炜,王佩,等.慢性乙型肝炎患者应对方式,社会支持与生活质量的相关性调查[J].解放军护理杂志,2007,24(6): 232-235.[13] 王娜,张伟,赫英娟.脑卒中患者应对方式的相关研究[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2009,30(18):2242-2243.[14] Youmossi IM,Braum WE, Protive DA, et al. Chronic viral hepatitis in renal transplant recipients with allografts functioning.for more than 20 years. Transplantation. 1999; 67(2):272-275.[15] McKercher CM, Venn AJ, Blizzard L, et al. Psychosocial factors in adults with chronic kidney disease: characteristics of pilot participants in the Tasmanian Chronic Kidney Disease study. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14(1):83.[16] Tayyebi A, Raiesifar A, Najafi Mehri S, et al. Measuring health related quality of life (hrqol) in renal transplant patients: psychometric properties and cross-cultural adaptation of kidney transplant questionnaire (ktq-25) in persian. Nephrourol Mon. 2012;4(4):617-621.[17] Evenepoel P. Recovery versus persistence of disordered mineral metabolism in kidney transplant recipients. Semin Nephrol. 2013;33(2):191-203.[18] Bonuel N, Cesario SK. Experiences of the transplant nurses caring for renal transplant patients in an acuity-adaptable patient room. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2013;36(2):195-212.[19] Silva DS, Andrade Edos S, Elias RM, et al. The perception of sleep quality in kidney transplant patients during the first year of transplantation. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67(12): 1365-1371.[20] Janiszewska J, Lichodziejewska-Niemierko M, Go??biewska J, et al. Determinants of anxiety in patients with advanced somatic disease: differences and similarities between patients undergoing renal replacement therapies and patients suffering from cancer. Int Urol Nephrol. In press.[21] Koca TG, Koca N, Ersoy A. The comparison of the relationship between sociocultural-economic features and sexual dysfunction frequency in sexually active premenopausal female patients on renal replacement therapy. J Sex Med. 2012;9(12):3171-3179.[22] Li PK, Chu KH, Chow KM, et al. Cross sectional survey on the concerns and anxiety of patients waiting for organ transplants. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012;17(5):514-518.[23] Látos M, Barabás K, Lázár G, et al. Psychological factors of successful kidney transplantations. The effects of anxiety and intrapsychic integration of the organ on recovery. Orv Hetil. 2012;153(15):592-597.[24] Ye HJ, Hu LJ, Yao YY, et al. The effects of two health education models on psychological and nutritional profile of patients waiting for kidney transplantation. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2011;50(10):845-847.[25] Pérez Domínguez TS, Rodríguez Pérez A, Buset Ríos N, et al. Psychonephrology: psychological aspects in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nefrologia. 2011;31(6): 716-722.[26] Corruble E, Barry C, Varescon I, et al. Report of depressive symptoms on waiting list and mortality after liver and kidney transplantation: a prospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry. 2011;11:182.[27] Calia R, Lai C, Aceto P, et al. Preoperative psychological factors predicting graft rejection in patients undergoing kidney transplant: a pilot study. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(4): 1006-1009.[28] Pascazio L, Nardone IB, Clarici A, et al. Anxiety, depression and emotional profile in renal transplant recipients and healthy subjects: a comparative study. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42(9):3586-3590.[29] Nilsson M, Forsberg A, Bäckman L, et al. The perceived threat of the risk for graft rejection and health-related quality of life among organ transplant recipients. J Clin Nurs. 2011; 20(1-2):274-282. |
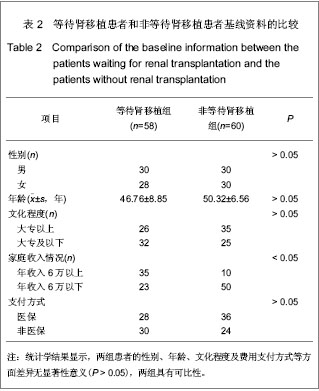
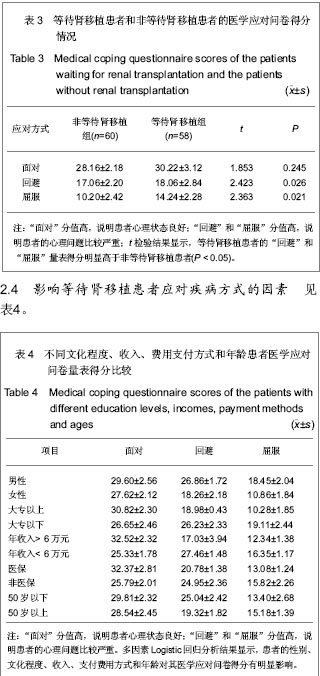
.jpg)