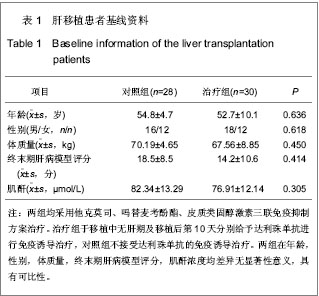
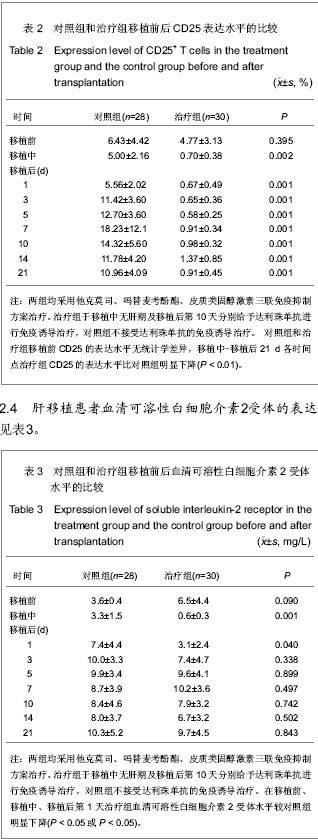
| [1] Schluns KS. Window of opportunity for daclizumab. Nat Med. 2011;17(5):545-547.[2] Uemura T, Schaefer E, Hollenbeak CS, et al. Outcome of induction immunosuppression for liver transplantation comparing anti-thymocyte globulin, daclizumab, and corticosteroid. Transpl Int. 2011;24(7):640-650.[3] Post M, Raszeja-Wyszomirska J, Jarosz K, et al. Immunosuppression with low-dose daclizumab in liver transplant recipients with impaired kidney function: a single-center experience. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(8): 3107-3109.[4] Zhang Y, Wen T, Yan L,et al. Following-up of a four-dose daclizumab induction therapy without calcineurin inhibitors in a liver transplantation recipient with severe renal dysfunction: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2008;40(10):3819-3820.[5] Przepiorka D, Keman NA, Ippoliti C, et al. Daclizumab, a humanized Anti-interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain antibody, for treatment of acute Graft-versus-host disease. Am Soci Hematol. 2000;95(1):83-89.[6] Foroncewicz B, Mucha K, Ryszkowska E, et al. Safety and efficacy of steroid-free immunosuppression with tacrolimus and daclizumab in liver transplant recipients: 6-year follow-up in a single center. Transplant Proc. 2009;41(8):3103-3106.[7] Bingyi S, Ming C, Yeyong Q, et al. The effect of anti-CD25 monoclonal antibody (Simulect) to the lymphocytes in the peripheral blood of the recipients of kidney transplantation. Transplantation Proc. 2003;35(1):243-245.[8] Sohrevardi SM, Azmandian J, Shafii Z, et al. Combination of a low dose of daclizumab and standard regimen for prevention of rejection in men and women receiving a kidney transplant. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2013;7(2):142-146.[9] Hao WJ, Zong HT, Cui YS, et al. The efficacy and safety of alemtuzumab and daclizumab versus antithymocyte globulin during organ transplantation: a meta-analysis. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(10):2955-2960.[10] State Council of the People's Republic of China. Administrative Regulations on Medical Institution. 1994-09-01.[11] Church AC. Clinical advances in therapies targeting the interleukin-2 receptor. QJM. 2003;96(2):91-102.[12] Wuest SC, Edwan JH, Martin JF, et al. A role for interleukin-2 trans-presentation in dendritic cell-mediated T cell activation in humans, as revealed by daclizumab therapy. Nat Med. 2011; 17(5):604-609.[13] Calmus Y, Kamar N, Gugenheim J, et al. Assessing renal function with daclizumab induction and delayed tacrolimus introduction in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2010;89(12):1504-1510.[14] Eckhoff DE, McGuire B, Sellers M, et al. The safety and efficacy of a two-dose daclizumab (zenapax) induction therapy in liver transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2000; 69(9):1867-1872. [15] Sellers MT, McGuire BM, Haustein SV, et al. Two-dose daclizumab induction therapy in 209 liver transplants: a single-center Analysis. Transplantation. 2004,78(8): 1212-1217.[16] Lee SJ, Zahrieh D, Agura E, et al. Effect of up-front daclizumab when combined with steroids for the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease: results of a randomized trial. Blood. 2004;104(5):1559-1564.[17] Hurst FP, Altieri M, Nee R, et al. Poor outcomes in elderly kidney transplant recipients receiving alemtuzumab induction. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34(6):534-541.[18] Ocampo C, Aristizabal A, Nieto J, et al. Induction therapies in kidney transplantation: the experience of Hospital Pablo Tobon Uribe, Medellín, Colombia 2005-2010. Transplant Proc. 2011;43(9):3359-3363.[19] Saghafi H, Rahbar K, Nobakht Haghighi A, et al. Efficacy of anti-interleukin-2 receptor antibody (daclizumab) in reducing the incidence of acute rejection after renal transplantation. Nephrourol Mon. 2012;4(2):475-477.[20] Koch M, Niemeyer G, Patel I, et al. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and immunodynamics of daclizumab in a two-dose regimen in liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2002;73(10):1640-1646. |
.jpg)